Abstract
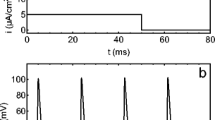
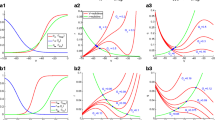
Low calcium increases the excitability of neurones and can induce autorhythmicity in excitable cells. Numerical solutions of the Hodgkin-Huxley membrane equations, and numerical evaluations of the small-signal impedance and admittance are used to illustrate the increase in resonance produced by low [Ca2+]0. The resonant frequency may be located either by the peak of the amplitude of the impedance, or by the frequency at which the phase angle is zero for 1:1 entrained action potentials. Autorhythmicity is produced by any mechanism which increases the resonant peak of the amplitude of the membrane impedance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agin, D.: Hodgkin-Huxley equations: logarithmic relation between membrane current and frequency of repetitive activity. Nature (London) 201, 625–626 (1964)
Arvanitaki, A.: Recherches sur la réponse oscillatoire locale de l'axone géant isole de Sepia. Arch. Int. Physiol. 49, 209–256 (1939)
Brown, R.H.: Membrane surface charge: discrete and uniform modelling. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 28, 341–370 (1974)
Chandler, W.K., Fitzhugh, R., Cole, K.S.: Theoretical stability properties of a space-clamped axon. Biophys. J. 2, 102–128 (1962)
Chen, Y.-D.: On the admittance of membranes associated with channel conduction. Application to channels at nonequilibrium steady-state. J. Theor. Biol. 81, 633–644 (1979)
Chiu, S.Y., Ritchie, J.M., Rogart, R.B., Stagg, D.: A quantitative description of membrane currents in rabbit myelinated nerve. J. Physiol. (London) 292, 149–166 (1979)
Cole, K.S.: Dynamic electrical characteristics of the squid axon membrane. Arch. Sci. Physiol. 3, 253–258 (1949)
De Haan, R.L., De Felice, L.J.: Oscillatory properties and excitability of the heart cell membrane. In: Theoretical chemistry-4-Periodicity in chemistry and biology. Eyring, H., Henderson, D. (eds.), pp. 181–233. New York: Academic Press 1978
Fishman, H.M., Poussart, D.J.M., Moore, L.E., Siebenga, E.: K+ conductance description from the low frequency impedance and admittance of squid axon. J. Membr. Biol. 32, 255–290 (1977)
Frankenheuser, B., Hodgkin, A.L.: The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J. Physiol. (London) 137, 218–244 (1957)
Guttman, R., Feldman, L.: White noise measurement of squid axon membrane impedance. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 67, 427–432 (1975)
Guttman, R., Feldman, L.: Frequency entrainment of squid axon membrane (preprint) (1979)
Guttman, R., Hachmeister, L.: Effect of calcium, temperature, and polarizing currents upon alternating current excitation of spaceclamped squid axons. J. Gen. Physiol. 58, 304–321 (1971)
Grisell, R.D.: Toward a multi-membrane model for potassium conduction in squid giant axon. J. Theor. Biol. 76, 233–266 (1979)
Grissel, R.D., Fishman, H.N.: K+ conduction phenomena applicable to the low frequency impedance of squid axons. J. Membr. Biol. 46, 1–25 (1979)
Hill, A.V.: Excitation and accommodation in nerve. Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. B 119, 305–355 (1936)
Hodgkin, A.L., Huxley, A.F.: A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J. Physiol. (London) 117, 500–544 (1952)
Holden, A.V.: The response of excitable membrane models to a cyclic input. Biol. Cybernetics 21, 1–7 (1976)
Huxley, A.F.: Ion movements during nerve activity. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 81, 221–246 (1959)
Katz, B.: Electric excitation of nerve. London: Oxford University Press 1939
Mauro, A, Conti, F., Dodge, F., Schor, R.: Subthreshold behavior and phenomenological impedance of the squid giant axon. J. Gen. Physiol. 55, 497–523 (1970)
Minorsky, N.: Non-linear mechanics. Ann. Arbor: J.W. Edwards 1947
Monnier, A.M.: L'excitation électrique des tissus. Paris: Hermann 1934
Monnier, A.M.: The damping factor as a functional criterion in nerve physiology. Cold spring Harbor Symp. Quant. Biol. 17, 69–93 (1952)
Monnier, A.M., Coppee, G.: Nouvelles recherches sur la resonance des tissus excitables. I. Relation entre la rythmicite de la response nerveuse et la resonance. Arch. Int. Physiol. 48, 129–180 (1939)
Noble, D.: The relation of Rushton's “liminal length” for excitation to the resting and active conductances of excitable cells. J. Physiol. (London) 226, 573–591 (1972)
Noble, D.: Cardiac action potentials and pacemaker activity. Recent advances in physiology. Linden, R.J., (ed.), pp. 1–50, London: Churchill 1974
Rashevsky, N.: Outline of a physico-mathematical theory of excitation and inhibition. Protoplasma 20, 42–56 (1933)
Rushton, W.A.H.: Initiation of the propagated disturbance. Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. B 124, 210–243 (1937)
Stein, R.B.: The frequency of nerve action potentials generated by applied currents. Proc. Roy. Soc. London, Ser. B 167, 63–86 (1967)
Steinbach, H.B., Spiegelman, S., Kawata, N.: The effect of potassium and calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J. Cell. Comp. Physiol. 24, 147–154 (1944)
Young, G.: Note on excitation theories. Psychometrika 2, 103–106 (1937)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holden, A.V. Autorhythmicity and entrainment in excitable membranes. Biol. Cybernetics 38, 1–8 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00337395
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00337395