Abstract
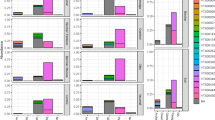
Earthworms recorded during 1989–1993 across 15 soil management treatments, comprising three different tillagexthree organic amendments (bare, farmyard manure, and rice straw) and six perennial ley treatments, belonged to two endogeic species, Octochaetona phillotti (Michaelsen) and Lampito mauritii Kinberg, while in a nearby undisturbed natural revegetation area three species were found, including the above two and Octonochaeta rosea (Stephenson). The earthworm biomass showed significant temporal and spatial variations and was higher during the post monsoon period than in the early rainy season. No worm biomass was recorded during the dry season. In the tillage and organic amendment treatments, the biomass was drastically reduced from September 1989 to September 1991 after the application of carbofuran and some herbicides, and was significantly reduced during these two years compared to that of 1992. The maximum monthly earthworm biomass ranged between 2.5 and 17.9 g m-2 across the treatments and increased several-fold in the nearby natural revegetation area (75.9 g m-2). It significantly increased in perennial ley treatments compared to annual treatments with organic amendments. Thus the earthworm biomass varied significantly (P<0.01) across the 15 treatments, indicating discernible effects of soil management.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Deibert EJ, Utter RA, Schwert DP (1991) Tillage system influence on earthworms (Lumbricidae) in North Dakota. N D Farm Res 48:10–12
Foissner W (1992) Comparative studies on the soil life in ecofarmed and conventionally farmed fields and grasslands of Austria. Agric Ecosyst Environ 40:207–218
Gerard BM, Hay RKM (1979) The effect on earthworms of ploughing, tine cultivation, direct drilling and nitrogen in a barley monoculture system. J Agric Sci 93:147–155
Haukka J (1988) Effects of various cultivation methods on earthworm biomass and communities on different soil types. Ann Agric Fenn 27:263–269
Haynes RJ (1980/1981) Effects of soil management practices on soil physical properties, earthworm population and tree root distributions in a commerical apple orchard. Soil Tillage Res 1:269–280
Lee KE (1985) Earthworms: Their ecology and relationship with soil and land use. Academic Press, Sydney Orlando San Diego New York London Toronto Montreal Tokyo
Parmelle RW, Beare MH, Cheng W, Hendrix PF, Rider SJ, Crossley DA Jr, Coleman DC (1990) Earthworms and enchytraeids in conventional and no-tillage agroecosystems: A biocide approach to assess their role in organic matter breakdown. Biol Fertil Soils 10:1–10
Remy EAD, Daynard TB (1982) Effects of tillage methods on earthworm population in monoculture corn. Can J Soil Sci 62: 699–703
Smith GD, Coughlan KJ, Yule DF, Laryea KB, Srivastava KL, Thomas NP, Cogle AL (1992) Soil management options to reduce runoff and erosion on a hardsetting Alfisol in the semiarid tropics. Soil Tillage Res 25:195–215
Zicsi A (1958) Einfluß der Trockenheit und der Bodenbearbeitung auf die Aktivität der Regenwürmer. Pedobiologia 9:141–146
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Visiting Scientist (under the Rockefeller Foundation Environmental Research Fellowship in International Agriculture)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vikram Reddy, M., Kiran Kumar, V.P., Ravinder Reddy, V. et al. Earthworm biomass response to soil management in semi-arid tropical Alfisol agroecosystems. Biol Fertil Soils 19, 317–321 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00336101
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00336101