Summary
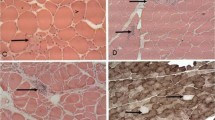
We report on two patients, who had myalgias while receiving long-term zidovudine treatment for an HIV infection, in whom muscle biopsy findings included a partial cytochrome c oxidase (CCO) deficiency, a feature of zidovudine myopathy, and tubular aggregates, a finding hitherto unreported in HIV-infected patients. The CCO deficit was observed in 28% and 24% of muscle fibers, respectively. Tubular aggregates were the prominent histopathological feature in patient 1, and were detected by systematic electron microscopy in patient 2. Inflammation and myonecrosis were not detected. In patient 1, the typical mitochondrial and myofibrillar changes of zidovudine myopathy were present and 12% of fibers showed tubular aggregates. The aggregates were not stained at CCO reaction, and 96% of myofibers enclosing tubular aggregates showed a decreased CCO activity. This suggested more than a chance association between mitochondrial dysfunction and the formation of tubular aggregates. We conclude that tubular aggregates are detected in some patients treated by zidovudine, and that the finding could be related to the long-term administration of the drug.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnaudo E, Dalakas M, Shanske S, Moraes CT, DiMauro S, Schon EA (1991) Depletion of muscle mitochondrial DNA in AIDS patients with zidovudine-induced myopathy. Lancet 337:508–510
Belec L, Di Costanzo B, Georges AJ, Gherardi R (1991) HIV infection in African patients with tropical pyomyositis. AIDS 5:234
Belec L, Mhiri C, Di Costanzo B, Gherardi R (1992) The HIV wasting syndrome. Muscle Nerve 15:856–857
Carpenter S, Karpati G (1984) Pathology of skeletal muscle. Churchill Livingstone, New York
Chariot P, Gherardi R (1991) Partial cytochrome c oxidase deficiency and cytoplasmic bodies in patients with zidovudine myopathy. Neuromusc Disord 1:357–363
Chui LA, Neustein H, Munsat TL (1975) Tubular aggregates in subclinical alcoholic myopathy. Neurology 25:405–412
Dalakas MC, Illa I, Pezeshkpour GH, Laukaitis JP, Cohen B, Griffin JL (1990) Mitochondrial myopathy caused by longterm zidovudine therapy. N Engl J Med 322:1098–1105
Danon MJ, Carpenter S, Harati Y (1989) Muscle pain associated with tubular aggregates and structures resembling cylindral spirals. Muscle Nerve 12:265–272
del Villar Negro A, Merino Angulo J, Rivera Pomar JM, Aguirre Errasti C (1982) Tubular aggregates in skeletal muscle of chronic alcoholic patients. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 56:250–254
Engel WK, Bishop DW, Cunningham GC (1970) Tubular aggregates in type II muscle fibers; ultrastructural and histochemical correlation. J Ultrastruct Res 31:507–525
Fardeau M, Tome FMS, Simons P (1979) Muscle and nerve changes induced by perhexiline maleate in man and mice. Muscle Nerve 2:24–36
Figarella-Branger D, Prellissier JF, Pérez-Castillo AM, Desnuelle C, Pouget J, Serratrice G (1991) Myopathie lentement progressive avec accumulation d'agrégats tubulaires. Rev Neurol (Paris) 147:586–594
Gherardi R, Mhiri C, Baudrimont M, Roullet E, Berry JP, Poirier J (1991) Iron pigment deposits, small vessel vasculitis and erythrophagocytosis in the muscle of HIV-infected patients. Hum Pathol 22:1187–1194
Gherardi R, Baudrimont M, Lionnet F, Salord JM, Duvivier C, Michon C, Wolff M, Marche C (1992) Skeletal muscle toxoplasmosis in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: a clinical and pathological study. Ann Neurol 32:535–542
Herzberg NH, Zorn I, Zwart R, Portegies P, Bolhuis PA (1992) Major growth reduction and minor decrease in mitochondrial enzyme activity in cultured human muscle cells after exposure to zidovudine. Muscle Nerve 15:706–710
Illa I, Nath A, Dalakas M (1991) Immunocytochemical and virological characteristics of HIV-associated inflammatory myopathies: similarities with seronegative polymyositis. Ann Neurol 29:474–481
Jay C, Ropka M, Hench K, Grady C, Dalakas M (1992) Prospective study of myopathy during prolonged low-dose AZT: clinical correlates of AZT mitochondrial myopathy and HIV-associated myopathy (abstract). Neurology 42 [Suppl 3]:145
Meijer AEFH (1988) Histochemical features of tubular aggregates in diseased human skeletal muscle fibres. J Neurol Sci 86:73–82
Mhiri C, Baudrimont M, Bonne G, Geny C, Degoul F, Marsac C, Roullet E, Gherardi R (1991) Zidovudine myopathy: a distinctive disorder associated with mitochondrial dysfunction. Ann Neurol 29:606–614
Nonaka I, Koga Y, Kikuchi A, Goto Y (1991) Mitochondrial encephalomyopathies and cytochrome c oxidase deficiency: muscle culture study. Acta Neuropathol 82:286–294
Reyes MG, Casanova J, Varricchio F, Sequeira W, Fresco K (1992) Zidovudine myopathy. Neurology 42:1252
Richter RW, Person J, Bruun B, Challenor YB, Brust JCM, Baden MM (1973) Neurological complications of addiction to heroin. Bull NY Acad Med 49:3–21
Rosenberg NL, Neville HE, Ringel MD (1985) Tubular aggregates. Their association with neuromuscular diseases, including the syndrome of myalgia/cramps. Arch Neurol 42:973–976
Schiaffino S, Severin E, Cantini M, Sartore S (1977) Tubular aggregates induced by anoxia in isolated rat skeletal muscle. Lab Invest 37:223–228
Schröder JM, Becker PE (1972) Anomalien des T-Systems und des sarkoplasmatischen Reticulums bei der Myotonie, Paramyotonie and Adynamie. Virchows Arch [A] 357:319–344
Simpson MV, Chin CD, Keilbaugh SA, Lin TS, Prusoff WH (1989) Studies on the inhibition of mitochondrial DNA replication by 3′-azido-3′-deoxythymidine and other dideoxynuleoside analogs which inhibit HIV-1 replication. Biochem Pharmacol 38:1033–1036
Tomelleri G, Orrico D, Tonin P, Tilia G, Spadaro M, Monaco S, Bonetti B, Rizzuto N (1991) Muscle pathology in AZT long-term treatment (abstract). Clin Neuropathol 10:166–167
Widrow CA, Kellie SM, Saltzman BR, Mathur-Wagh U (1991) Pyomyositis in patients with the human immunodeficiency virus: an unusual form of disseminated bacterial infection. Am J Med 91:129–136
Yarchoan R, Mitsuya H, Myers CE, Broder S (1989) Clinical pharmacology of 3′-azido-2′,3′-dideoxythymidine (zidovudine) and related dideoxynuclosides. N Engl J Med 321:726–738
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chariot, P., Benbrik, E., Schaeffer, A. et al. Tubular aggregates and partial cytochrome c oxidase deficiency in skeletal muscle of patients with AIDS treated with zidovudine. Acta Neuropathol 85, 431–436 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00334455
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00334455