Summary
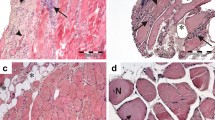
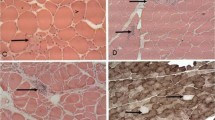
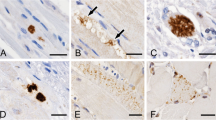
In 10 of 10 inclusion-body myositis (IBM) patients, including 1 hereditary case, vacuolated muscle fibers contained large or small cytoplasmic inclusions immunoreactive for (α1-ACT). All IBM muscle biopsies had characteristic cytoplasmic tubulo-filaments by electron microscopy. None of 17 control muscle biopsies contained the (α1-ACT) immunoreactive inclusions characteristic of IBM. In vacuolated muscle fibers, (α1-ACT) immunoreactive inclusions colocalized with β-amyloid protein and ubiquitin immunoreactivities. Our study provides the first demonstration of (α1-ACT) accumulations in abnormal human muscle, and it suggest that, as in Alzheimer's disease and Down's syndrome, (α1-ACT) may be involved in the pathogenesis of IBM.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham CR, Selkoe DJ, Potter H (1988) Immunochemical identification of the serine protease inhibitor α1-anthichymptrypsin in the brain amyloid deposits of Alzheimer's disease. Cell 52: 487–501
Abraham CR, Shirahama T, Potter H (1990) α1-Antichymotrypsin is associated solely with amyloid deposits containing the β-protein. Amyloid and cell localization of 381-3. Neurobiol Aging 11: 123–129
Abraham CR, Driscoll J, Potter H, Van Nostrand WE, Tempst P (1991) A calcium-activated protease from Alzheimer's disease brain cleaves at the N terminus of the amyloid β-protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 174: 790–796
Askanas V, Bornemann A, Engel WK (1990) Immunocytochemical localization of desmin at human neuromuscular junctions. Neurology 40: 949–953
Askanas V, Serdaroglu P, Engel WK, Alvarez RB (1991) Immunolocalization of ubiquitin in muscle biopsies of patients with inclusion body myositis and oculopharyngeal muscular dystrophy. Neurosci Lett 130: 73–76
Askanas V, Serdaroglu P, Engel WK, Alvarez RB (1992) Immunocytochemical localization of ubiquitin in inclusion body myositis allows its light microscopic distinction from polymyositis. Neurology 42: 460–461
Askanas V, Engel WK, Alvarez RB, Glenner GG (1992) β-Amyloid protein immunoreactivity in muscle of patients with inclusion-body myositis. Lancet 339: 560–561
Askanas V, Engel WK, Alvarez RB (1992) Light and electron microscopic localization of β-amyloid protein in muscle biopsies of patients with inclusion-body myositis. Am J Pathol 141: 31–36
Carpenter S, Karpati G, Heller I, Eisen A (1978) Inclusion body myositis: a distinct variety of idiopathic inflammatory myopathy. Neurology 28: 8–17
Carrell RW, Travis J, (1987) Serpins: the superfamily of plasma serine protease inhibitors. In: Barret A, Salvesen G (eds) Protease inhibitors. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 403–420
Cataldo AM, Nixon RA (1990) Enzymatically active lysosomal proteases are associated with amyloid deposits in Alzheimer brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 3861–3865
Chou S-M (1967) Myxovirus-like structures in a case of human chronic polymyositis. Science 158: 1453–1455
Cole AJ, Kuzniecky R, Karpati G, Carpenter S, Andermann E, Andermann F (1988) Familial myopathy with changes resembling inclusion body myositis and periventricular leukoencephalopathy. Brain 111: 1025–1037
Dalakas MC (1991) Polymyositis, dermatomyositis, and inclusion body myositis. N Engl J Med 325: 1487–1498
Engel WK (1967) Muscle biopsies in neuromuscular diseases. Pediatr Clin North Am 14: 963–996
Engel WK, Cunningham GG (1963) Rapid examination of muscle-tissue. An improved trichrome method for freshfrozen biopsy sections. Neurology 13: 919–923
Fardeau M, Askanas V, Tomé FMS, Engel WK, Alvarez R, McFerrin J, Chevallay M (1990) Hereditary neuromuscular disorder with inclusion body myositis-like filamentous inclusions: clinical, pathological, and tissue culture studies. Neurology 40: 120
Joachim CL, Mori H, Selkoe DJ (1989) Amyloid β-protein deposition in tissues other than brain in Alzheimer's disease. Nature 341: 226–230
Justice DL, Rhodes RH, Tökés ZA (1987) Immunohistochemical demonstration of proteinase inhibitor alpha-1-antichymotrypsin in normal human central nervous system. J Cell Biochem 34: 227–238
Lotz BP, Engel AG, Nishino H, Stevens JC, Litchy WJ (1989) Inclusion body myositis: observations in 40 patients. Brain 112: 727–747
Massa R, Weller B, Karpati G, Shonbridge E, Carpenter S (1991) Familial inclusion body myositis among Kurdish-Iranian Jews. Arch Neurol 48: 519–522
Mendell JR, Sahenk Z, Gales T, Paul L (1991) Amyloid filaments in inclusion body myositis. Arch Neurol 48: 1229–1234
Morii M, Travis J (1983) Amino acid sequence at the reactive site of human α1-antichymotrypsin. J Biol Chem 258: 12749–12752
Nelson RB, Siman R (1990) Clipsin, a chymotrypsin-like protease in rat brain which is irreversibly inhibited by 382-2. J Biol Chem 265: 3836–3843
Neville HE, Baumbach LL, Ringel SP, Russo LS, Sujansky E, Garcia CA (1992) Familial inclusion-body myositis: evidence for autosomal dominant inheritance. Neurology 42: 897–902
Rozemuller JM, Stam FC, Eikelenboom P (1990) Acute phase proteins are present in amorphous plaques in the cerebral but not in the cerebellar cortex of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett 119: 75–78
Serdaroglu P, Askanas V, Engel WK (1992) Immunocytochemical localization of ubiquitin at human neuromuscular junctions. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 18: 232–236
Tabaton M, Cammarata S, Maucardi G, Manetto V, Autilio-Gambetti L, Perry G, Gambetti P (1991) Ultrastructural localization of β-amyloid, τ and ubiquitin epitopes in extracellular neurofibrillary tangles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 2089–2102
Tagliavini F, Giaccone G, Frangione B, Bugiani O (1988) Preamyloid deposits in the cerebral cortex of patients with Alzheimer's disease and nondemented individuals. Neurosci Lett 93: 191–196
Tomé FMS, Fardeau M, Lebon P, Chevallay M (1981) Inclusion body myositis. Acta neuropathol (Berl) [Suppl VII]: 287–291
Travis J, Morii M (1981) Human α1-antichymotrypsin. Methods Enzymol 80: 767–771
Travis J, Salvesen GS (1983) Human plasma proteinase inhibitors. Annu Rev Biochem 52: 655–709
Travis J, Bowen J, Baugh R (1978) Human α1-antichymotrypsin: interaction with chymostrypsin-like proteinases. Biochemistry 17: 5651–5656
Wong CW, Quaranta V, Glenner GG (1985) Neuritic plaques and cerebrovascular amyloid in Alzheimer's disease are antigenically related. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82: 8729–8732
Yamaguchi H, Hirai S, Morimatsu M, Shoji M, Harigaya Y (1988) Diffuse type of senile plaques in the brains of Alzheimer-type dementia. Acta Neuropathol 77: 113–119
Yunis EJ, Samaha FJ (1971) Inclusion body myositis. Lab Invest 25: 240–248
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by the Norma Bard Research Fund. M.B. is a Research Postdoctoral Fellow
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bilak, M., Askanas, V. & Engel, W.K. Strong immunoreactivity of α1 co-localizes with β-amyloid protein and ubiquitin in vacuolated muscle fibers of inclusion-body myositis. Acta Neuropathol 85, 378–382 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00334447
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00334447