Summary
The influence of puromycin on the incorporation of leucin-3H into cells of choroid plexus of nine day old chicken embryos is studied.
Puromycin causes a strong inhibition of the incorporation of leucin-3H into the cultures. Compared with controls, the inhibition of the uptake of the labelled substance is more pronounced in the cytoplasm than in the nucleus.
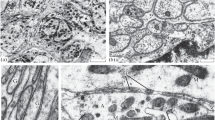
Immediately after puromycin is added to the tissue culture medium an accumulation of “multivesicular bodies” and—to a certain degree—of lysosomes appears in the cells of the choroid plexus. Both organells disappear almost completely during the cultivation period.
A second incubation with labelled leucin after puromycin shows that the observed effects are reversible and that puromycin acts only as long as it is present in the culture medium.
The embryonic cells of choroid plexus develop normally even though treated with puromycin.
Zusammenfassung
Der Einfluß von Puromycin auf die Inkorporierung von Leucin-3H wird an kultivierten Plexus chorioideus-Zellen 9 Tage alter Hühnerembryonen untersucht. Die Kulturen zeigen unter Einwirkung von Puromycin eine deutliche Hemmung der Aufnahme von Leucin-3H. Die Aufnahme der markierten Substanz ins Cytoplasma wird im Vergleich zu Kontrolluntersuchungen prozentual mehr gehemmt als die Aufnahme des Leucins in den Kern.
Unmittelbar nach dem Zusatz von Puromycin zum Nährmedium treten in den kultivierten Plexus chorioideus-Zellen Ansammlungen von „multivesicular bodies“ und z. T. auch zahlreiche Lysosomen auf. Beide Organellen verschwinden im Verlauf der weiteren Kultivierung wieder fast vollständig aus den Zellen.
Eine neuerliche Zugabe von markiertem Leucin nach der Puromycingabe zeigt, daß die beobachteten Wirkungen reversibel sind und daß die Puromycinwirkung nicht länger anhält, als diese Substanz im Nährmedium vorhanden ist.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Ansevin, K. D.: The effects of RNA-synthesis inhibition and of protein synthesis inhibition on embryonic induction and cell differentiation in Rana pipiens. J. Morph. 117, 171–184 (1965).
Buddecke, E.: Grundriß der Biochemie. Berlin: Walter de Gruyter & Co. 1970.
Caro, L., Tubergen, R. P.: High-resolution autoradiography. J. Cell Biol. 15, 173–188 (1962).
Dalton, A. J.: A chrome-osmium fixative for electron microscopy. Anat. Rec. 121, 281 (1955).
Flexner, L. B., Flexner, J. B., Roberts, R. B.: Memory in mice analyzed with antibiotics. Science 155, 1377–1383 (1967).
—, Stellar, E.: Memory in mice as affected by intracerebral Puromycin. Science 141, 57–59 (1963).
Gambetti, P., Gonatas, N. K., Flexner, L. B.: Puromycin: Action on neuronal mitochondria. Science 161, 900–902 (1968).
Grunz, H.: Hemmung der Reaggregation dissoziierter Amphibienzellen durch Inhibitoren der RNS- und Proteinsynthese. Wilhelm Roux' Archiv 163, 184–196 (1969).
Holland, J. J.: Effects of Puromycin on RNA-synthesis in mammalian cells. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 50, 436–443 (1963).
Hopkins, J. W.: Amino acid activation and transfer to ribonucleic acids in the cell nucleus. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 45, 1461–1470 (1959).
Kahri, A. I.: Effects of Actinomycin D and Puromycin on the ACTH-induced ultrastructural transformation of mitochondria of cortical cells of rat adrenals in tissue culture. J. Cell Biol. 36, 181–195 (1968).
Liebermann, J., Ove, P.: Isolation and study of mutants from mammalian cells in culture. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 45, 867–877 (1959).
Meller, K., Breipohl, W., Wagner, H. H.: Die Inkorporation von Leucin-H3 in Plexus chorioideus-Zellen in der Gewebekultur. Z. Zellforsch. 104, 116–126 (1970).
—, Wagner, H. H.: Die Feinstruktur des Plexus chorioideus in Gewebekulturen. Z. Zellforsch. 86, 98–110 (1968).
—, Breipohl, W.: Das Verhalten trypsinierter Plexus chorioideus-Zellen in Gewebekulturen. Eine elektronenmikroskopische Untersuchung. Z. Zellforsch. 97, 392–402 (1969).
Moigne, A. Le, Gabriel, A.: Mise en évidence du caractère ≪activé≫ des cellules indifférenciées du parenchyme chez de jeunes Planaires en croissance. C. R. Acad. Sci. (Paris) Sér. D 163, 1070–1073 (1969).
Stephens, R. E., Colé, M. B., Jr., Carlson, J. G.: Inhibition of DNA synthesis by Actinomycin D and Puromycin in grasshopper neuroblasts. J. Cell Biol. 43, 139a (1969).
Yamorlinsky, M. B., Haba, G. L. de la: Inhibition by puromycin of amino acid incorporation into protein. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 45, 1721–1729 (1959).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Mit Unterstützung durch die Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Me 276/5) und den Sonderforschungsbereich 33 Göttingen.
Die unreifen Plexus chorioideus-zellen entwickeln sich trotz der Puromycingaben normal.
Das morphologische Differenzierungsergebnis wird nicht verändert.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meller, K., Breipohl, W. Elektronenmikroskopische und histoautoradiographische Befunde zur Puromycinwirkung auf ausreifende Plexus chorioideus-Zellen in vitro. Z. Zellforsch. 118, 428–438 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00331195
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00331195