Abstract
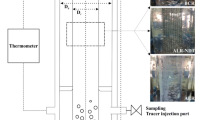
Protein enrichment of sago starch of three different diameters was investigated both in flask culture and under forced aeration in a packed-bed fermenter using two strains of Rhizopus. Protein production by R. oligosporus UQM 145F was superior to Rhizopus sp. UQM 186F in the flask culture without aeration, with both preferring larger diameter (3 to 4 mm) spherical sago-beads. In the packed-bed fermenter with forced aeration, Rhizopus sp. UQM 186F led to more rapid protein production compared to R. ollgosporus UQM 145F and produced equivalent final yields (about 10% protein on a dry wt basis).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AOAC 1984 Official Methods of Analysis, 13th edn, Washington, DC: Association of the Official Analytical Chemists.
Carrizalez, V. & Jaffe, W. 1986 Solid-state fermentation: an appropriate biotechnology for developing countries. Interciencia 11, 9–15.
Czajkowska, D. & Ilnicka-Olejniczak, O. 1988 Biosynthesis of protein by microscopic fungi in solid-state fermentation. I. Selection of Aspergillus strain for enrichment of starchy materials in protein. Acta Biotechnologica 8, 407–413.
Daubresse, P., Ntibashirwa, S., Gheysen, A. & Meyer, J.A. 1987 A process for the protein enrichment of cassava by solid substrate fermentation in rural conditions. Biotechnology and bioengineering 29, 962–968.
Durand, A. & Chereau, D. 1987 A new pilot reactor for solid-state fermentation: application to the protein enrichment of sugar beet pulp. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 31, 476–481.
Flach, M. 1983 The sagopalm plant protection paper 47. pp. 1–85. FAO: Rome.
Forage, A.J. 1979 Utilization of agricultural and food processing wastes containing carbohydrates. Chemical Society Review 8, 309–314.
Gerhardt, P. 1981 Manual of Methods for General Bacteriology. pp. 358–359. Washington, DC: American Society of Microbiology.
Hesseltine, C.W. 1972 Solid-state fermentations. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 14, 517–532.
Huang, S.Y., Wang, H.H., Wei, C.-J., Malaney, G.W. & Tanner, R.D. 1985 Kinetic responses of the koji solid-state fermentation process. Topics in Enzyme and Fermentation Biotechnology 10, 88–108.
Hutagalung, R.I. & Tan, P.H. 1976 Utilization of nutritionally improved cassava by nutrient supplementation and microbial enrichment in poultry and pigs. In Proceedings of the Fourth Symposium of the International Society of Tropical Root Crops eds Cock, J., MacIntyre, R. & Graham, M. pp. 255–262. Cali: CIAT.
Laukevics, J.J., Apsite, A.F., Viesturs, U.S. & Tengerdy, R.P. 1985 Steric hindrance of growth of filamentous fungi in solid substrate fermentation of wheat straw. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 27, 1687–1691.
Mitchell, D.A., Greenfield, P.F. & Doelle, H.W. 1986 A model substrate for solid-state fermentation. Biotechnology Letters 8, 827–832.
Mitchell, D.A., Doelle, H.W. & Greenfield, P.F. 1988 Agar plate growth studies of Rhizopus oligosporus and Aspergillus oryzae to determine their suitability for solid-state fermentation. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 8, 1–5.
Moo-Young, M., Moreira, A.R. & Tengerdy, R.P. 1983 Principles of solid-substrate fermentation. In The Filamentous Fungi, eds Smith, J.E., Berry, D.R. & Kristiansen, B. pp. 117–144. London: Edward Arnold.
Mudgett, R.E. 1986 Solid-state fermentation. In Manual of Industrial Microbiology, eds Demain, A.L. & Solomon, N.A. pp. 66–83. Washington, DC: American Society of Microbiology.
Narahara, H., Koyama, Y., Yoshida, Pichyangkura, S., Ueda, R. & Taguchi, H. 1982 Growth and enzyme production in a solid-state culture of Aspergillus oryzae. Journal of Fermentation Technology 60, 311–319.
Raimbault, M. & Alazard, D. 1980 Culture method to study fungal growth in solid fermentation. European Journal of Applied Microbiology 9, 199–209.
Raimbault, M., Revah, S., Pina, F. & Villalobos, P. 1985 Protein enrichment of cassava by solid substrate fermentation using molds isolated from traditional foods. Journal of Fermentation Technology 63, 395–399.
Ramos-Valdivia, A., De la Torre, M. & Cassas-Campelo, C. 1983 Solid-state fermentation of cassava with Rhizopus. oligosporus NRRL 2710. In Production and Feeding of Single Cell Protein, ed. Ferranti, M.P. pp. 104–111. London: Applied Science Publishers.
Senez, J.C. 1985 Microbial food and feed. In Biotechnology and Bioprocess Engineering, ed. Ghose, T.K. pp. 309–319. New Delhi, India: Indian Institute of Technology.
Sukara, E. 1987 Production of single cell protein from cassava by microfungi. PhD Thesis. Brisbane: University of Queensland.
Sukara, E. & Doelle, H.W. 1988 Cassava starch fermentation pattern of Rhizopus oligosporus. MIRCEN Journal of Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 4, 463–471.
Waliszewska, A., Garcia, H.S. & Waliszewski, K. 1983 Nutritional evaluation of Rhizopus oligosporus biomass propagated on potato. Nutritional Report International 28, 197–202.
Wang, H.L. & Hesseltine, C.W. 1982 Oriental fermented foods. In Prescott and Dunn's Industrial Microbiology, 4th edn, ed. Reed, G. pp. 492–538. Westport, Connecticut: AVI Publishing Company.
Yang, S.S. 1988 Protein enrichment of sweet potato residue with amylolytic yeasts by solid-state fermentation. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 32, 886–890.
Additional information
E. Gumbira-Sa'id, P.F. Greenfield and D.A. Mitchell are with the Department of Chemical Engineering, and H.W. Doelle is with the Department of Microbiology, University of Queensland, Queensland 4072, Australia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gumbira-Sa'id, E., Doelle, H.W., Greenfield, P.F. et al. Protein enrichment of sago starch by solid-state fermentation with Rhizopus spp.. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology 7, 419–427 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00329411
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00329411