Summary
-
1.
The developmental processes in early larval instars and during larval molts differ markedly from those during the last larval instar and the pupal molt. This difference is reflected at the level of gene activities by the behaviour of the puffs of giant chromosomes. Puffing in salivary gland chromosomes of intermolt and molting third instar larvae of Chironomus tentans is the subject of this paper.
-
2.
The pattern of puffing in third instar larvae before molting does not differ from that in last instar larvae. Furthermore, the frequency of puffing of most loci is more or less identical during both larval stages.
-
3.
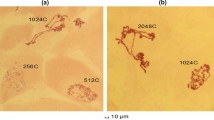
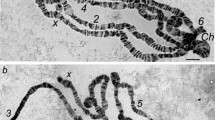
The appearance of puff I-18-C represents the first alteration in the puffing pattern after the onset of the larval molt. This puff reaches its maximal size at about the middle of the molting phase, remains very large for some time, then regresses and disappears one to two days after molting is completed. Puff IV-2-B appears later than I-18-C, reaches maximal size earlier, and completely regresses before the molt is finished.
-
4.
Most molt specific puffs which appear later during metamorphosis do not appear during the larval molt, but a few do. Furthermore, only during the larval molt does a puff in region III-4-A appear or, at least, become larger than at any other stage.
-
5.
No alterations were observed in the activity pattern of those puffs which are not specific for molting: The frequency of puffing of these loci is not lower during the molt than before, and locus I-17-B and others which regularly increase in size during the pupal molt, do not show any comparable enlargement during the larval molt.
-
6.
In contrast to the pupal molt, a high titer of juvenile hormone is characteristic of all larval molts. Similarities and differences in puffing events during the two types of molts are, therefore, discussed in terms of the action of juvenile hormone in modifying the cellular reactions to ecdysone. From the behaviour of puffs I-18-C and IV-2-B it is concluded that the primary action of ecdysone is the same in both larval and pupal molts and, therefore, is independent of the titer of juvenile hormone. It follows, then, that the juvenile hormone must interfere, probably indirectly, with some of the cellular reactions subsequent to the primary action of ecdysone,
-
7.
From the data of this and the foregoing papers in this series, the chronology of the activity of a large number of gene loci have become comprehensible. The modes of their puffing behaviour, although varying in detail, may be classified into only a few types (see Fig. 11) whose different relationships to the processes of larval development are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Becker, H. J.: Die Puffs der Speicheldrüsenchromosomen von Drosophila melanogaster. I. Beobachtungen zum Verhalten des Puffmusters im Normalstamm und bei zwei Mutanten, giant und lethal-giantlarvae. Chromosoma (Berl.) 10, 654–678 (1959); - Die Puffs der Speicheldrüsenchromosomen von Drosophila melanogaster. II. Die Auslösung der Puffbildung, ihre Spezifität und ihre Beziehung zur Funktion der Ringdrüse. Chromosoma (Berl.) 13, 341–384 (1963).
Beermann, W.: Chromomerenkonstanz und spezifische Modifikationen der Chromosomenstruktur in der Entwicklung und Organdifferenzierung von Chromosoma tentans. Chromosoma (Berl.) 5, 139–198 (1952); - Ein Balbiani-Ring als Locus einer Speicheldrüsen-Mutation. Chromosoma (Berl.) 12, 1–25 (1963).
Burdette, W. J., and M. W. Bullock: Ecdysone: Five biologically active fractions from Bombyx mori. Science 140, 1311 (1963).
Clever, U.: Genaktivitäten in den Riesenchromosomen von Chironomus tentans und ihre Beziehungen zur Entwicklung. I. Genaktivierung durch Ecdyson. Chromosoma (Berl.) 12, 607–675 (1961a); - Über das Reaktionssystem einer hormonalen Induktion. Verh. dtsch. zool. Ges. 1961b, 75–92; - Genaktivitäten in den Riesenchromosomen von Chironomus tentans... II. Das Verhalten der Puffs während des letzten Larvenstadiums und der Puppenhäutung. Chromosoma (Berl.) 13, 385–436 (1962a);- Genaktivitäten in den Riesenchromosomen von Chironomus tentans ... III. Das Aktivitätsmuster in Phasen der Entwicklungsruhe. J. Ins. Physiol. 8, 357–376 (1962b); - Von der Ecdysonkonzentration abhängige Genaktivitätsmuster in den Speicheldrüsenchromosomen von Chironomus tentans. Develop. Biol. 6, 73–98 (1963a); - Puffs in giant chromosomes of Diptera and the mechanism of its control. In: Histon biology and histon chemistry, ed. by J. Bonner and P. Ts'o. HoldenDay, San Francisco (im Druck, 1963b).
—, u. P. Karlson: Induktion von Puff-Veränderungen in den Speicheldrüsen-chromosomen von Chironomus tentans durch Ecdyson. Exp. Cell Res. 20, 623–626 (1960).
Davidson, E. H., V. G. Allfrey and A. E. Mirsky: Gene expression in differentiated cells. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 49, 53–60 (1963).
Gilbert, L. I.: Maintenance of the prothoracic gland by the juvenile hormone in insects. Nature (Lond.) 193, 1205–1207 (1962).
—, and H. A. Schneiderman: Some biochemical aspects of insect metamorphosis. Amer. Zool. 1, 11–51 (1961).
Jacob, F., and J. Monod: On th regulation of gene activity. Cold Spr. Harb. Symp. quant. Biol. 26, 193–211 (1961).
Mechelke, F.: Reversible Strukturmodifikationen der Speicheldrüsenchromosomen von Acricotopus lucidus. Chromosoma (Berl.) 5, 511–543 (1953).
Panitz, R.: Innersekretorische Wirkungen auf Strukturmodifikationen der Speicheldrüsenchromosomen von Acricotopus lucidus. Naturwissenschaften 47, 383 (1960).
Piepho, H.: Untersuchungen zur Entwicklungsphysiologie der Insektenmetamorphose. Über die Puppenhäutung der Wachsmotte Galleria mellonella. Wilhelm Roux' Arch. Entwick.-Mech. Org. 141, 500–583 (1942).
Schmialek, P.: Die Identifizierung zweier im Tenebrio-Kot und in Hefe vorkommender Substanzen mit Juvenilhormonwirkung. Z. Naturforsch. 16b, 461–464 (1961).
Schneiderman, H. A., and L. I. Gilbert: The chemistry and physiology of insect growth hormones. In: Cell, organism and milieu, pp. 157–184. New York: Ronald Press 1959.
Waddington, C. H.: New patterns in genetics and development. New York: Columbia University Press 1962.
Wigglesworth, V. B.: The physiology of insect metamorphosis. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1954; - Some observations on the juvenile hormone effect of farnesol. J. Ins. Physiol. 7, 73–78 (1961); - Endocrine regulation during development I. Hormones in relation to metamorphosis. Gen. comp. Endocr., Suppl. 1, 316–321 (1962).
Williams, C. M.: The juvenile hormone of insects. Nature (Lond.) 178, 212–213 (1956); - The juvenile hormone. II. Its role in the endocrine control of molting, pupation, and adult development in the Cecropia silkworm. Biol. Bull. 121, 572–585 (1961).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clever, U. Genaktivitäten in den Riesenchromosomen von Chironomus tentans und ihre Beziehungen zur Entwicklung. Chromosoma 14, 651–675 (1963). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00326517
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00326517