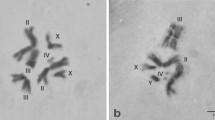
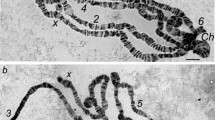
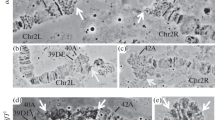
Abstract
Polyteny is an effective mechanism for accelerating growth and enhancing gene expression in eukaryotes. The purpose of investigation was to study the genetic variability of polyteny degree of giant chromosomes in the salivary glands of Drosophila melanogaster Meig. in relation to the differential fitness of different genotypes. 16 strains, lines and hybrids of fruit flies were studied. This study demonstrates the significant influence of hereditary factors on the level of polytenization of giant chromosomes in Drosophila. This is manifested in the differences between strains and lines, the effect of inbreeding, chromosome isogenization, hybridization, adaptively significant selection, sexual differences, and varying degrees of individual variability of a trait in different strains, lines, and hybrids. The genetic component in the variability of the degree of chromosome polyteny in Drosophila salivary glands was 45.3%, the effect of sex was 9.5%. It has been shown that genetic distances during inbreeding, outbreeding or hybridization, which largely determine the selective value of different genotypes, also affect polyteny patterns. Genetic, humoral, and epigenetic aspects of endocycle regulation, which may underlie the variations in the degree of chromosome polyteny, as well as the biological significance of the phenomenon of endopolyploidy, are discussed.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- C V :
-
Coefficient of variation
- ES:
-
Ecdysterone
- HSP:
-
Heat shock proteins
- IIS:
-
Insulin/insulin-like growth factor
- JH:
-
Juvenile hormone
- SSD:
-
Sexual size dimorphism
- EGFR/MAPK:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor/mitogen-activated protein kinase
- Hpo/Yki:
-
Hippo/Yorkie
- JAK/STAT:
-
Janus kinases/signal transducer and activator of transcription proteins
- JNK:
-
C-Jun N-terminal kinases
- PI3K/TOR:
-
Phosphoinositide-3-kinase/target of rapamycin
References
Anisimov AP (2005) Endopolyploidy as a morphogenetic factor of development. Cell Biol Int 29:993–1004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellbi.2005.10.013
Bainard LD, Bainard JD, Newmaster SG, Klironomos JN (2011) Mycorrhizal symbiosis stimulates endoreduplication in angiosperms. Plant Cell Environ 34:1577–1585. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2011.02354.x
Bandura JL, Zielke N (2017) Polyploidy in animal development and desease. In: Li X-Q (ed) Somatic Genome Variation: Animals, Plants, and Microorganisms, Chapter 1. Wiley-Blackwell, New York, pp 3–44
Bennett MD (1982) Nucleotypic basis of the spatial ordering of chromosomes in eukaryotes and the implications of the order for genome evolution and phenotypic variation. In: Dover GA, Flavell RB (eds) Genome evolution. Academic Press, London, pp 239–261
Bomblies K (2020) Wheneverything changes at once: finding a newnormal after genome duplication. Proc R Soc B 287:20202154. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2020.2154
Britton JS, Edgar BA (1998) Environmental control of the cell cycle in Drosophila: nutrition activated mitotic and endoreduplicative cells by distinct mechanisms. Development 125:2149–2158
Brodskiy V, Uryvayeva IV (1981) Cell polyploidy: proliferation and differentiation. Nauka, Moscow (In Russian)
Chen J, Niu N, Zhang J, Qi L, Shen W, Donkena KV, Feng Z, Liu J (2019) Polyploid giant cancer cells (PGCCs): the evil roots of cancer. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 19(5):360–367. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568009618666180703154233
Cheniclet C, Rong WY, Causse M, Frangne N, Bolling L, Carde J-P, Renaudin J-P (2005) Cell expansion and endoreduplication show a large genetic variability in pericarp and contribute strongly to tomato fruit growth. Plant Physiol 139:1984–1994. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.068767
Chevalier C, Nafati M, Mathieu-Rivet E, Bourdon M, Frangne N, Cheniclet C, Renaudin J-P, Gevaudant F, Hernould M (2011) Elucidating the functional role of endoreduplication in tomato fruit development. Ann Bot 107:1159–1169. https://doi.org/10.1093/aob/mcq257
Cookson SJ, Radziejowski A, Granier C (2006) Cell and leaf size plasticity in Arabidopsis: what is the role of endoreduplication. Plant Cell Environ 29:1273–1283. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2006.01506.x
Costa CAM, Wang X-F, Ellsworth C, Deng W-M (2021) Polyploidy in development and tumor models in Drosophila. Semin Cancer Biol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.09.011
Deng W, Althauser C, Ruohola-Baker H (2001) Notch-delta signaling induces a transition from mitotic cell cycle to endocycle in Drosophila follicle cells. Development 128(23):4737–4746. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.128.23.4737
Dyka LD, Shakina LA, Strashnyuk VYu, Shckorbatov YuG (2016) Effects of 36,6 GHz and static magnetic field on degree of endoreduplication in Drosophila melanogaster polytene chromosomes. Int J Radiat Biol 92:222–227. https://doi.org/10.3109/09553002.2016.1137105
Edgar BA, Orr-Weaver TI (2001) Endoreduplication cell cycle: more for less. Cell 105:297–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00334-8
Edgar BA, Zielke N, Gutierrez C (2014) Endocycles: a recurrent evolutionary innovation for post-mitotic cell growth. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15:197–210. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3756
FlyBase. https://flybase.org
Fox DT, Duronio RJ (2013) Endoreplication and polyploidy: insights into development and disease. Development 140:3–12. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.080531
Frakova V, Koprivy L, Palova M, Kolarčik V, Martonfi P (2021) Evaluation of endopolyploidy patterns in selected Capsicum and Nicotiana species (Solanaceae). Biologia 76:2079–2092. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-021-00704-1
Gandarillas A, Molinuevo R, Sanz-Gómez N (2018) Mammalian endoreplication emerges to reveal a potential developmental timer. Cell Death Differ 25:471–476. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-017-0040-0
Genard M, Bertin N, Borel C, Bussieres P, Gautier H, Habib R, Lechaudel M, Lecomte A, Lescourret F, Lobit P, Quilot B (2007) Towards a virtual fruit focusing on quality: modeling features and potential uses. J Exp Bot 58:917–930. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/erl287
Grendler J, Lowgren S, Mills M, Losick VP (2019) Wound-induced polyploidization is driven by Myc and supports tissue repair in the presence of DNA damage. Development. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.173005
Gruntenko NE, Rauschenbach IYU (2008) Interplay of JH, 20E and biogenic amines under normal and stress conditions and its effect on reproduction. J Insect Physiol 54(6):902–908. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinsphys.2008.04.004
Gruntenko NE, Wilson TG, Monastirioti M, Rauschenbach IY (2000) Stress-reactivity and juvenile hormone degradation in Drosophila melanogaster strains having stress-related mutations. Insect Biochem Molec Biol 30:775–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0965-1748(00)00049-7
Gruntenko NE, Karpova EK, Alekseev AA, Chentsova NA, Bogomolova EV, Faddeeva NV, Saprykina ZV, Bownes M, Rauschenbach IYU (2007) Effects of octopamine on juvenile hormone metabolism, dopamine and 20-hydroxyecdysone contents and reproduction in Drosophila. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 65:85–94. https://doi.org/10.1002/arch.20187
Guo W, Wu Z, Song J, Jiang F, Wang Z, Deng S, Walker VK, Zhou S (2014) Juvenile hormone-receptor complex acts on mcm4 and mcm7 to promote polyploidy and vitellogenesis in the migratory locust. PLoS Genet. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1004702
Hesse M (1969) Anatomische und Karyologische Untersuchungen an der Galle von Mayetiola pose auf Poa nemoralis. Österr Bot Ztschr 117:411–425
Houle D (1989) Allozyme-associated heterosis in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 123(4):789–801. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/123.4.789
Iovleva OV, Myl’nikov SV (2007) Consequences of selection in highly inbred Drosophila strains. Russ J Genet 43(10):1108–1119. https://doi.org/10.1134/S102279540710004
Jensen C, Ørsted M, Kristensen TN (2018) Effects of genetic distance on heterosis in a Drosophila melanogaster model system. Genetica 146(4–5):345–359. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-018-0026-y
Kaidanov LZ, Mylnikov SV, Galkin AP, Iovleva OV, Kuznetsova OV, Zimina NV (1997) Genetic effects of destabilizing selection for adaptive traits of Drosophila melanogaster strains. Russ J Genet 33:935–941
Kiknadze II, Gruzdev AD (1970) Change in chromosome length related to polyteny in the chironomid salivary gland. Tsitologia 12:953–960
Kim M, Santos KD, Moon N-S (2021) Proper CycE–Cdk2 activity in endocycling tissues requires regulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor Dacapo by dE2F1b in Drosophila. Genetics 217(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1093/genetics/iyaa029
Kirillova A, Han L, Liu H, Kühn B (2021) Polyploid cardiomyocytes: implications for heart regeneration. Development 148:199401. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.199401
Kobayashi H (2019) Variations of endoreduplication and its potential contribution to endosperm development in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Prod Sci 22:227–241. https://doi.org/10.1080/1343943x.2019.1570281
Larkins BA, Dilkes BP, Dante RA, Coelho CM, Woo Y, Liu Y (2001) Investigating hows and why of DNA endoreduplication. J Exp Bot 52:183–194. https://doi.org/10.1093/jexbot/52.355.183
Lee HO, Davidson JM, Duronio RJ (2009) Endoreduplication: polyploidy with a purpose. Genes Dev 23:2461–2477. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1829209
Lei J, Chen IW, Wright GA, Pillai S, Zhu-Salzman K (2020) Electron beam irradiation induces DNA endoreplication in holometabolous juvenile insects: a rapid flow cytometry-based diagnosis. J Pest Sci 93:1131–1142. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10340-020-01235-5
Li S, Liu L, Li T, Lan T, Wang Y, Zhang Z, Liu J, Xu S, Zhang X, Zhu J, Xue J, Guo D (2019) The distribution pattern of endopolyploidy in maize. Theor Appl Genet 132:1487–1503. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-019-03294-4
Mal’ceva NI, Gyurkovics H, Zhimulev IF (1995) General characteristics of the polytene chromosomes from ovarian pseudonurse cells of the Drosophila melanogaster otu11 and fs(2)B mutants. Chromosome Res 3:191–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00710713
Marguerat S, Bähler J (2012) Coordinating genome expression with cell size. Trends Genet 28:560–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2012.07.003
Mehrotra S, Maqbool SB, Kolpakas A, Murnen K, Calvi BR (2008) Endocycling cells do not apoptose in response to DNA rereplication genotoxic stress. Genes Dev 22:3158–3171. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1710208
Moein S, Adibi R, da Silva ML, Nardi NB, Gheisari Y (2020) Cancer regeneration: polyploid cells are the key drivers of tumor progression. BBA Rev Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbcan.2020.188408
Moriyama M, Osanai K, Ohyoshi T, Wang HB, Iwanaga M, Kawasaki H (2016) Ecdysteroid promotes cell cycle progression in the Bombyx wing disc through activation of c-Myc. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 70:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2015.11.008
Nagl W (1976) DNA endoreduplication and polyteny understood as evolutionary strategies. Nature 261:614–615
Nesterkina M, Bilokon S, Alieksieieva T, Chubyk I, Kravchenko I (2018) The influence of monoterpenoids and phenol derivatives on Drosophila melanogaster viability. J Asia-Pac Entomol 21:793–796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aspen.2018.06.004
Nesterkina M, Bilokon S, Alieksieieva T, Chebotar S, Kravchenko I (2020) Toxic effect and genotoxicity of carvacrol ethers in Drosophila melanogaster. Mutat Res/fundam Mol Mech Mutagen. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2020.111713
Nozaki T, Matsuura K (2019) Evolutionary relationship of fat body endoreduplication and queen fecundity in termites. Ecol Evol 9(20):11684–11694. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.5664
Ørsted M, Malmendal A, Muñoz J, Torsten Kristensen TN (2018) Metabolic and functional phenotypic profiling of Drosophila melanogaster reveals reduced sex differentiation under stressful environmental conditions. Biol J Lin Soc 123(1):155–162. https://doi.org/10.1093/biolinnean/blx120
Øvrebø JI, Edgar BA (2018) Polyploidy in tissue homeostasis and regeneration. Development. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.156034
Pavan C, da Cunha AB, Morsoletto C (1971) Virus-chromosome relationships in cells of Rhynchosciara (Diptera, Sciaridae). Caryologia 24(3):371–389
Peterson NG, Fox DT (2021) Communal living: the role of polyploidy and syncytia in tissue biology. Chromosome Res 29:245–260. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-021-09664-3
Pezzoli C, Laporta D, Giorgi G, Guerra D, Cavicchi S (1986) Fitness components in a vestigial mutant strain of Drosophila melanogaster. Italian J Zool 53(4):351–354. https://doi.org/10.1080/11250008609355520
Qian W, Li Z, Song W, Zhao T, Wang W, Peng J, Wei L, Xia Q, Cheng D (2020) A novel transcriptional cascade is involved in Fzr-mediated endoreplication. Nucleic Acids Res 48(8):4214–4229. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa158
Rangel J, Strauss K, Seedorf K, Hjelmen CE, Johnston JS (2015) Endopolyploidy changes with age-related polyethism in the honey bee, Apis mellifera. PLoS ONE. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0122208
Rarog MA, Strashnyuk VYu, Kondrat’eva AO, Dmitruk TV, Vorob’eva LI, Shakhbazov VG (1999) Effect of culture density on expressivity of character eyeless and polyteny of giant chromosomes in Drosophila melanogaster. Russ J Genet 35:766–769
Rarog MA, Vorob'eva LI, Strashnyuk VYu (2004) Influence of parental age on endoreduplication of giant chromosomes and some quantitative traits in Drosophila melanogaster descendants. Russ J Dev Biol 35(1):37–41. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:RUDO.0000015124.26423.8f
Rauschenbach IY, Gruntenko NE, Khlebodarova TM, Mazurov MM, Grenback LG, Sukhanova MJH, Shumnaja LV, Zakharov IK, Hammock BD (1996) The role of the degradation system of the juvenile hormone in the reproduction of Drosophila under stress. J Insect Physiol 42(8):735–742. https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-1910(96)00027-3
Ren D, Song J, Ni M, Kang L, Guo W (2020) Regulatory mechanisms of cell polyploidy in Insects. Front Cell Dev Biol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.00361
Rodman TC (1967) DNA replication in salivary gland nuclei of Drosophila melanogaster at successive larval and prepupal stages. Genetics 55:375–386
Rotelli MD, Policastro RA, Bolling AM, Killion AW, Weinberg AJ, Dixon MJ, Zentner GE, Walczak CE, Lilly M, Calvi BR (2019) A cyclin A-Myb-MuvB-Aurora B network regulates the choice between mitotic cycles and polyploid endoreplication cycles. PLoS Genet. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1008253
Sawala A, Gould AP (2018) Sex-lethal in neurons controls female body growth in Drosophila. Fly 12(2):133–141. https://doi.org/10.1080/19336934.2018.1502535
Shakina LA, Strashnyuk VYu (2011) Genetic, molecular, and humoral endocycle-regulating mechanisms. Russ J Genet 47:1151–1160
Skorobagatko DA, Shakina LA, Strashnyuk VYu, Mazilov AA (2015) Lethal and recombinative action of γ-radiation in genetically unstable Drosophila melanogaster Bar strain. Radiatsionnaya Biol Radioekol 55:145–154. https://doi.org/10.7868/S0869803115020137
Skorobagatko DA, Mazilov AA, Strashnyuk VYu (2020) Endoreduplication in Drosophila melanogaster progeny after exposure to acute γ-irradiation. Radiat Environ Biophys 59:211–220. https://doi.org/10.1101/376145
Stormo BM (2017) Fox DT Polyteny: still a giant player in chromosome research. Chromosome Res 25(3–4):201–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10577-017-9562-z
Strashnyuk VY, Vorobyova LI, Shakhbazov VG (1985) The contribution of heterozygosity for chromosome 2 to the heterosis effect in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetika 21(11):1828–1833
Strashnyuk VYu, Taglina OV, Shakhbazov VG (1991) In vitro examination of ecdyson-dependent activity of the ontogenetic puffs in Drosophila salivary glands in regard to heterosis effect and adaptive significant selection. Genetika 27(9):1512–1518
Strashnyuk VYu, Nepeivoda SN, Shakhbazov VG (1995) Cytomorphometric analysis of Drosophila melanogaster Meig. polytene chromosomes in relation to heterosis, selection for adaptively valuable traits, and sex. Russ J Genet 31:17–21
Strashnyuk VYu, Al-Hamed S, Nepeivoda SN, Shakhbazov VG (1997) Cytogenetic and cytobiophysical investigation of mechanisms of temperature adaptation and heterosis in Drosophila melanogaster Meig. Russ J Genet 33:793–799
Sugimoto-Shirasu K, Roberts K (2003) “Big it up”: endoreduplication and cell-size control in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:544–553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2003.09.009
Tikhomirova MM (1990) Genetic analysis. LSU Publition, Leningrad
Totskiĭ VN, Khaustova ND, Levchuk LV, Morgun SV (1998) Genotypic basis of low viability in vestigial mutants of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetika 34(9):1233–1238
Wang X-F, Liu J-X, Ma Z-Y, Shen Y, Zhang H-R, Zhou Z-Z, Suzuki E, Liu Q-X, Hirose S (2020) Evolutionarily conserved roles for Apontic in induction and subsequent decline of cyclin E expression. Iscience. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2020.101369
Wehr Mathews K, Cavegn M, Zwicky M (2017) Sexual dimorphism of body size is controlled by dosage of the X-chromosomal gene Myc and by the sex-determining gene tra in Drosophila. Genetics 205(3):1215–1228. https://doi.org/10.1534/genetics.116.192260
Wos G, Mackova L, Kubíkova K, Kolar F (2022) Ploidy and local environment drive intraspecific variation in endoreduplication in Arabidopsis arenosa. Am J Bot 109(2):259–271. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajb2.1818
Wu Z, Guo W, Yang L, He Q, Zhou S (2018) Juvenile hormone promotes locust fat body cell polyploidization and vitellogenesis by activating the transcription of Cdk6 and E2f1. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 102:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ibmb.2018.09.002
Zhuravleva LA, Strashnyuk VYu, Shakhbazov VG (2004) The influence of culture density on the polyteny degree of giant chromosomes in inbred lines and hybrids of Drosophila melanogaster. Cytol Genetics 38:46–51
Zielke N, Kim KJ, Tran V, Shibutani ST, Bravo MJ, Nagarajan S, van Straaten M, Woods B, von Dassow G, Rottig C, Lehner CF, Grewal SS, Duronio RJ, Edgar BA (2011) Control of Drosophila endocycles by E2F and CRL4CDT2. Nature 480:123–127. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10579
Zielke N, Edgar BA, DePamphilis ML (2013) Endoreplication. Cold Spring Harbor Perspect Biol. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a012948
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine (Project State Registration Number: 0117U004836).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the conception and design. All authors participated in data collection and analysis. VYS wrote the first draft of the manuscript. All authors commented on previous versions, read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Strashnyuk, V.Y., Shakina, L.A. & Skorobagatko, D.A. Variability of polyteny of giant chromosomes in Drosophila melanogaster salivary glands. Genetica 151, 75–86 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-022-00168-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-022-00168-4