Summary
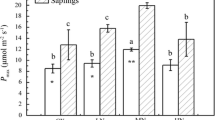
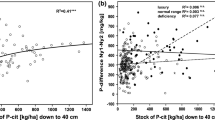
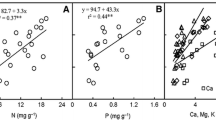
Photosynthetic rates and nutrient contents of spruce needles were measured in a region with high levels of air pollution in NE Bavaria, Germany (FRG), and compared to spruce grown under clean air conditions at Craigieburn, in the South Island of New Zealand (NZ). The absolute rates of CO2 uptake, the slope of the CO2 response curve at 240 μl l−1 internal CO2 concentration, and the change of photosynthetic rates with needle age at ambient and saturated CO2 concentrations were virtually identical at both measuring sites. These results confirm an earlier conclusion, that there is no long-term effect of atmospheric pollutants directly on photosynthetic CO2 uptake rates with persistent exposure at the FRG site to high levels of anthropogenic air pollution. Photosynthetic capacity at saturating CO2 concentration was three times higher in the NZ spruce. Needles with high photosynthetic capacity in NZ had lower nitrogen and higher calcium concentrations per unit dry weight but higher concentrations of nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, magnesium and calcium per unit leaf area, and twice the specific leaf weight.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (1988) Critical levels of air pollution. Umweltbundesamt, Berlin, 1988
Benecke U, Schulze E-D, Matyssek R, Havranek WM (1981) Environmental control of CO2 Assimilation and leaf conductance in Larix decidua Mill. I. A comparison of contrasting natural environments. Oecologia 50:54–61
Eiden R (1989) Air pollution and deposition. In: Schulze E-D, Lange OL, Oren R (eds) Air pollution and forest decline. A study on spruce (Picea abies) on acid soils. Ecological studies Vol 77. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York pp 57–106
Fuchs M, Schulze E-D, Fuchs MI (1977) Spatial distribution of photosynthetic capacity and performance in a mountain spruce forest of Northern Germany. II. Climatic control of carbon dioxide uptake. Oecologia 29:329–340
Keerkeer SF (1985) Atmospheric hydrogen sulfide and sulfur dioxide. MSc Thesis, University of Auckland, New Zealand
Krause GHM (1988) Impact of air pollutants on above-ground plant parts of forest trees. In: Mathy P (ed) Air Pollution and ecosystems. Reidel Publishing Comp Dordrecht, pp 168–217
Laisk A, Pfanz H, Heber U (1988) SO2 fluxes into different cellular compartments of leaves photosynthesizing in a polluted atmosphere. II. Consequences of SO2 uptake as revealed by computer analysis. Planta 1973:241–252
Lange OL, Gebel J, Schulze E-D, Walz H (1985) Eine Methode zur raschen Charakterisierung der photosynthetischen Leistungsfähigkeit von Bäumen unter Freilandbedingungen — Anwendung zur Analyse “neuartiger Waldschäden” an Fichte. Forstwiss Cbl 104:186–198
Lange OL, Führer G, Gebel J (1986) Rapid field determination of photosynthetic capacity of cut spruce twigs (Picea abies) at saturating ambient CO2. Trees 1:70–77
Lange OL, Weikert RM, Wedler M, Gebel J, Heber U (1989) Photosynthese und Nährstoffversorgung von Fichten aus einem Waldschadensgebiet auf basenarmem Untergrund. Allg Forst Z 54–63
Lange OL, Heber U, Schulze E-D, Ziegler H (1989b) Atmospheric pollutants and plant metabolism. In: Schulze E-D, Lange OL, Oren R (eds) Air pollution and forest decline. A study on spruce (Picea abies) on acid soils. Ecological studies Vol 77. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York pp 238–276
Meyer J, Schneider BU, Werk KS, Oren R, Schulze E-D (1988) Performance of two Picea abies (L.) Karst. stands at different stages of decline. V. Root tip and ectomycorrhiza development and their relations to above ground and soil nutrients. Oecologia 77:7–13
Oren R, Schulze E-D, Werk KS, Meyer J, Schneider BU, Heilmeier H (1988a) Performance of two Picea abies (L.) Karst. stands at different stages of decline. I. Carbon relations and stand growth. Oecologia 75:25–37
Oren R, Werk KS, Schulze E-D, Meyer J, Schneider BU, Schramel P (1988b) Performance of two Picea abies (L.) Karst. stands at different stages of decline. VI. Nutrient concentration. Oecologia 77:151–162
Oren R, Schulze E-D, Werk KS, Meyer J (1988c) Performance of two Picea abies (L.) Karst. stands at different stages of decline. VII. Nutrient relations and growth. Oecologia 77:163–173
Oren R, Schulze E-D (1989) Nutritional disharmony and forest decline: A conceptual model. In: Schulze E-D, Lange OL, Oren R (eds) Air pollution and forest decline. A study on spruce (Picea abies) on acid soils. Ecological studies Vol 77. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York pp 425–443
Reich PB, Amundson RG (1985) Ambient levels of ozone reduced net photosynthesis in tree and crop species. Science 230:566–570
Schulze E-D (1986) Carbon dioxide and water vapor exchange in response to drought in the atmosphere and in the soil. Ann Rev Plant Physiol 37:247–274
Schulze E-D (1989) Air pollution and forest decline in a spruce (Picea abies) forest. Science 244:776–783
VDI, Verein Deutscher Ingenieure (1983) Maximale Immissionswerte für Schwefeldioxid. VDI-Richtlinien 2310, p 2
Werk KS, Oren R, Schulze E-D, Zimmermann R, Meyer J (1988) Performance of two Picea abies (L.) Karst. stands at different stages of decline. III. Canopy transpiration of green trees. Oecologia 76:519–524
Zimmermann R (1985) Untersuchungen zur Photosyntheseleistung, Transpiration und Nadelbiomasseverteilung von zwei geschädigten Fichtenforsten in den höheren Lagen des Fichtelgebirges. Dipl. Thesis, University of Bayreuth
Zimmermann R (1989) Photosynthese und Transpiration von Picea abies (L.) Karst. bei unterschiedlichem Ernährungszustand im Fichtelgebirge (Nordostbayern) Dr. Thesis, Bayreuth
Zimmermann R, Oren R, Schulze E-D, Werk KS (1988) Performance of two Picea abies (L.) Karst. stands at different stages of decline. II. Photosynthesis and leaf conductance. Oecologia 76:513–516
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schulze, E.D., McCracken, I., Zimmermann, R. et al. Performance of two Picea abies (L.) Karst. stands at different stages of decline. Oecologia 82, 158–161 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00323529
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00323529