Abstract
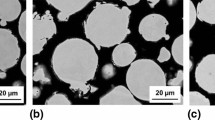
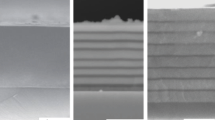
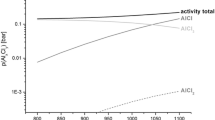
Metallic materials for application at high temperatures must form a slowly growing, dense oxide scale for their own protection. Up to about 1000°C, chromia-forming, at higher temperatures, alumina-forming Fe, Ni or Co based materials are used. In the present paper it is demonstrated how intact homogeneous scales on materials can be studied by AES sputter profiling and SNMS, but the main objective is to show phenomena at surfaces and interfaces which occur in complex atmospheres. In complex atmospheres, the formation of a protective scale is aggravated if several aggressive components of the gas atmosphere attack the free metal surface. This was demonstrated by AES for oxidizing and chlorinating atmospheres, in which chlorides and oxides grow simultaneously on the free metal surface. The chlorides are overgrown after some minutes by the stable oxide, but the formation of a dense, protective oxide scale is prevented. Similar effects have been observed by AES in oxidizing and nitriding atmospheres and also in oxidizing and sulfidizing atmospheres. The structure and the composition of the interface oxide/metal is decisive for the adherence of oxide scales. Stresses in the oxide scale can initiate detachment, diffusion processes in the alloy can lead to formation of voids and cavities beneath the oxide layer; both processes are favoured by segregation of sulfur from the alloy to the nascent metal surface as was shown by AES. For the investigation of the interface, this has to be laid bare by in-situ bending of the sample; this causes physical removal of the oxide scale. In addition to the surface of the oxide and the interface oxide/metal, grain boundaries of the alloys are also of interest; at these grain boundaries, dissolved non-metal atoms such as C, O, N, S ... can penetrate into the alloy. The grain boundaries can be analyzed by AES if the samples are fractured inside the UHV system. It can be shown, for example, that oxygen can penetrate into the grain boundaries of the intermetallic compounds NbAl3 and NiAl; this oxygen penetration leads to grain boundary oxidation or even disintegration of the material into fine oxidized metal particles. These examples should demonstrate that the application of surface analytical methods, especially of AES, can provide valuable information for improved understanding and control of the high temperature corrosion of metallic materials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Viefhaus H, Grabke HJ (1993) Final report on the ECSC project: Untersuchung von Zunderschichten und Anlaufschichten auf Stählen mit SNMS (7210/GD/105)
Viefhaus H, Hennesen K, Müller-Lorenz EM, Lucas M, Grabke HJ Surf Interf Anal (in press)
Reese E, Müller-Lorenz EM, Grabke HJ J Phys (in press)
Bramhoff D, Grabke HJ, Schmidt HP (1989) Werkst Korros 40:642–650
Flatley T, Birks N (1971) Werkst Korrosion, J Iron Steel Inst 209:523
Rahmel A, Gonzalez JA (1970) Werkst Korros 21:925, (1975) Oxid Met 9:401
Hussey RJ, Papaiacovou P, Grabke HJ (1986) Werkst Korros 37:578–587
Funkenbusch AW, Smeggil JG, Bornstein NS (1986) Metall Trans 16A:923
Smeggil JG, Funkenbusch AW, Bornstein NS (1986) Metail Trans 17A:923
Smialek JL (1987) Metall Trans 18A:163
Grabke HJ, Wiemer D, Viefhaus H (1991) Appl Surf Sci 47:243–250
Wiemer D, Grabke HJ, Viefhaus H (1991) Fresensius J Anal Chem 341:402–405
Schmutzler HJ, Viefhaus H, Grabke HJ (1992) Surf Interf Anal 18:581–584
Schmutzler HJ, Viefhaus H, Grabke HJ (1992) In: Nichtmetalle in Metallen '92. DGM Oberursel
Viefhaus H, Wittig J, Grabke HJ (1988) In: Hirschfeld D (ed) Nichtmetalle in Metallen '88, DGM, Oberursel p 245
Grabke HJ, Kurbatov G, Schmutzler HJ; Oxid Met (in preparation)
Steinhorst M, Grabke HJ (1990) Z Metallkd 81:732–738
Grabke HJ, Brumm M, Steinhorst M (1991) Fresenius J Anal Chem 341:378–382
Brumm MW, Grabke HJ, Wagemann B Corros Sci (in press)
Tolpygo V, Grabke HJ (1993) Scri Metall 28:747–775
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grabke, H.J. Interfacial phenomena in the oxidation and high temperature corrosion of metals and alloys. Fresenius J Anal Chem 349, 11–19 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00323217
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00323217