Summary
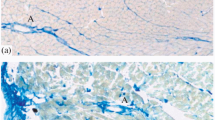
There is limited information on the distribution of nerve fibers containing substance P (SP) in the heart conduction system. Therefore, in the present study, the various parts of the conduction system of the bovine heart were examined by the use of an SP-antiserum and immunohistochemistry. Nerve fibers showing SP-like immunoreactivity (SP-LI) occurred in the proximities of conduction cells in all parts of the conduction system, but were present in greatly larger numbers in the AV bundle than in the other parts. The nerve fibers showed a predilection for certain regions of the bundles of conduction cells (Purkinje fiber bundles) in the AV bundle and the bundle branches and their ramifications. Nerve fibers showing SP-LI also occurred in the walls of the arteries and in association with some the ganglionic cells located in the regions of the conduction system. None of the ganglionic cells exhibited SP-LI. The observations are discussed in relation to what is known of the function of SP in the heart and of the distribution of sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve fibers in the conduction system. As SP is regarded as a marker of afferent fibers the observations support the view that afferent nerve fibers are present throughout the conduction system. It is likely that the existence of a significant SP-innervation in the conduction system is of importance for the function of this part of the heart.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson RH (1972) The disposition, morphology and innervation of cardiac specialized tissue in the guinea pig. J Anat 111:453–468
Blair DM, Davies F (1935) Observations on the conducting system of the heart. J Anat 69:303–325
Bojsen-Möller F, Tranum-Jensen J (1971) On nerves and nerve endings in the conducting system of the moderator band (septomarginal trabecula). J Anat 108:387–395
Brum JM, Go VLW, Sufan Q, Lane G, Reilly W, Bove AA (1986) Substance P distribution and effects in the canine epicardial coronary arteries. Regul Pept 14:41–55
Burcher E, Alterhög JH, Pernow B, Rosell S (1977) Cardiovascular effects of substance P: effects on the heart and regional blood flow in the dog. In: von Euler ES, Pernow B (eds) Substance P. Raven Press, New York, pp 261–268
Chahl LA, Walker SB (1981) Responses of the rat cardiovascular system to substance P, neurotensin and bombesin. Life Sci 29:2009–2015
Dalsgård C-J, Franco-Cereceda A, Saria A, Lundberg JM, Theodorsson-Norheim E, Hökfelt T (1986) Distribution and origin of substance P-and neuropeptide Y—immunoreactive nerves in the guinea pig heart. Cell Tissue Res 243:477–485
Davies F, Francis ETB, King TS (1952) Neurological studies of the cardiac ventricles of mammals. J Anat 86:130–143
Delbro D (1987) Substance P-induced tachycardia in the ahaesthetized rat. Acta Physiol Scand 130:41–45
Forsgren S (1986) The distribution of sympathetic nerve fibres in the AV node and AV bundle of the bovine heart. Histochem J 18:625–638
Forsgren S (1988) The distribution of terminal sympathetic nerve fibers in bundle branches and false tendons of the bovine heart. An immunohistochemical and catecholamine histofluorescence study. Anat Embryol 177:437–443
Franco-Cereceda A, Henke H, Lundberg JM, Petermann JB, Hökfelt T, Fischer JA (1987) Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in capsaicin-sensitive substance P-immunoreactive sensory neurons in animals and man: Distribution and release by capsaicin. Peptides 8:399–410
Furness JB, Papka RE, Della NG, Costa M, Eskay RL (1982) Substance P-like immunoreactivity in nerves associated with the vascular system of guinea pigs. Neurosci 7:447–459
Gamse R, Holzer P, Lembeck F (1981) Decrease of substance P in primary afferent neurones and impairment of neurogenic plasma extravasation by capsaicin. Neurosci 6:437–441
Hayashi K (1962) An electron microscope study on the conduction system of the cow heart. Jpn Circ J 26:765–842
Helke CJ, O'Donohue TL, Jacobitz DM (1980) Substance P as a baro- and chemoreceptor afferent neurotransmitter: immunocytochemical and neurochemical evidence in the rat. Peptides 1:1–9
Henry JL (1977) Substance P and pain: a possible relation to afferent transmission. In: von Euler ES, Pernow B (eds) Substance P. Raven Press, New York, pp 231–240
Kubota Y, Takagi H, Morishima Y, Powell JF, Smith AD (1985) Synaptic interaction between catecholaminergic neurons and substance P-immunoreactive axons in the caudal part of the nucleus of the solitary tract of the rat: demonstration by the electron microscopical mirror technique. Brain Res 333:188–192
Lembeck F, Holzer P (1979) Substance P as neurogenic mediator of antidromic vasodilation and neurogenic plasma extravasation. NS Arch Pharmac 310:175–183
Losay J, Mroz E, Tregear GW, Leeman SE, Gamble WJ (1977) Action of substance P on the coronary blood flow in the isolated dog heart. In: von Euler US, Pernow B (eds) Substance P. Raven Press, New York, pp 287–294
Lundberg JM, Franco-Cereceda A, Hua Y, Hökfelt T, Fischer JA (1985) Co-existence of substance P and calcitonin generelated peptide-like immunoreactivities in sensory nerves in relation to cardiovascular and bronchoconstrictor effects of capsaicin. Eur J Pharmacol 108:315–319
Malliani A, Lombardi F, Pagari M (1986) Sensory innervation of the heart. Prog Brain Res 67:39–48
Moravec-Mochet M, Moravec J, Hatt PY (1977) Presence of synaptic and muscular-spindle like structures in the atrio-ventricular junction of the rat heart. An electron microscopic study. J Ultrastruct Res 58:196–209
Moravec J, Moravec M (1987) Intrinsic nerve plexus of mammalian heart: Morphological basis of cardiac rhythmical activity? Int Rev Cytol 106:89–148
Munnell JF (1982) Sensory component in the terminal innervation of the ovine cardiac conduction system. Am J Anat 163:337–350
Otsuka M, Yanagisawa M (1987) Does substance P act as a pain transmitter? Trends Pharmacol Sci 8:506–510
Papka RE, Furness JB, Della NG, Costa M (1981) Depletion by capsaicin of substance P-immunoreactivity and acetylcholinesterase activity from nerve fibers in the guinea pig heart. Neurosci Lett 27:47–53
Papka RE, Urban L (1987) Distribution, origin and sensitivity to capsaicin of primary afferent substance P—immunoreactive nerves in the heart. Acta Physiol Hungarica 69:459–468
Patterson SI, Hanley MR (1987) Autoradiographic evidence for β-adrenergic receptors on capsaicin-sensitive primary afferent terminals in rat spinal cord. Neurosci Lett 78:17–21
Petty M, Reid J (1982) The cardiovascular effects of centrally administered substance P in the anaesthetized rabbit. Eur J Pharmacol 82:9–14
Rechardt L, Aalto-Setälä K, Purjeranta M, Pelto-Huikko M, Kyösola K (1986) Peptidergic innervation of human atrial myocardium: an electron microscopical and immunocytochemical study. J Autonom Nerv Syst 17:21–32
Reinecke M, Weihe E, Forssmann WG (1980) Substance P-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the heart. Neurosci Lett 20:265–269
Reinecke M, Forssmann WG (1984) Regulatory peptides (SP, NT, VIP, PHI, ENK) of autonomic nerves in the guinea pig heart. Clin Exp—Theory and Practise 6:1867–1871
Thaemert JC (1973) Fine structure of the atrioventricular node as viewed in serial sections. Am J Anat 136:43–66
Truex RC (1961) Comparative anatomy and functional considerations of the cardiac conduction system. In: de Carvalho A, de Mello WC, Hoffman BM (eds) The specialized tissues of the heart. Amsterdam, Elsevier Publ Co, pp 22–43
Weihe E, Reinecke M (1981) Peptidergic innervation of the mammalian sinus nodes: Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, neurotensin, substance P. Neurosci Lett 26:283–288
Weihe E, Reinecke M, Opherk D, Forssmann WG (1981) Peptidergic innervation (substance P) in the human heart. J Molec Cell Cardiol 13:331–333
Weihe E (1987) Peripheral innervation of the heart. In: von Arnim T, Maseri A (eds) Silent Ischemia. Steinkopff Verlag, Darmstadt, pp 7–18
Wharton J, Polak M, McGregor GP, Bishop AE, Bloom SR (1981) The distribution of substance P-like immunoreactive nerves in the guinea pig heart. Neurosci 6:2193–2204
Wharton J, Gulbenkian S, Mulderry PK, Ghatei MA, McGregor GP, Bloom SR, Polak JM (1986) Capsaicin induces a depletion of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)-immunoreactive nerves in the cardiovascular system of the guinea pig and rat. J Autonom Nerv Syst 16:289–309
Wharton J, Gulbenkian S (1987) Peptides in the mammalian cardiovascular system. Experientia 43:821–832
Viragh S, Challice CE (1973) The impulse generation and conduction system of the heart. In: Challice CE, Viragh S (eds) Ultrastructure of the Mammalian Heart. Academic Press, New York London, pp 127–178
Urban L, Papka RE (1985) Origin of small primary afferent substance P-immunoreactive nerve fibers in the guinea pig heart. J Autonom Nerv Syst 12:321–331
Yamauchi A (1973) Ultrastructure of the innervation of the mammalian heart. Challice CE, Viragh S (eds). Ultrastructure of the Mammalian Heart. Academic Press, New York London, pp 127–178
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Forsgren, S. The distribution of nerve fibers showing substance P-like immunoreactivity in the conduction system of the bovine heart: dense innervation in the atrioventricular bundle. Anat Embryol 179, 485–490 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00319591
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00319591