Abstract
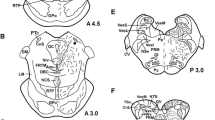
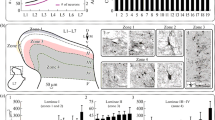
Intraspinal serotonin-positive cells and fibers were examined in the chicken lumbar spinal cord following removal of descending serotonin fibers by spinal transection. Co-localization of Leu-enkephalin immunoreactivity in intraspinal serotonin cells was also examined using a double immunofluorescence labeling technique. By one or two weeks after spinal transection, virtually all supraspinal serotonin fibers were eliminated. Intraspinal serotonin cells were located ventral or ventrolateral to the central canal corresponding to laminae VII, VIII, and IX, and the anterior funiculus. Intraspinal serotonin cells sent fibers to (1) the pia mater on the ventral or ventrolateral surface of the spinal cord; (2) vessels in the spinal cord; (3) sympathetic preganglionic column of Terni; (4) other intraspinal serotonin neurons; (5) the central canal. Some 30%–50% of the intraspinal serotonin cells co-localized with Leu-enkephalin. Intraspinal serotonin fibers co-containing Leu-enkephalin were observed in the pia mater located on the most lateral surface of the spinal cord.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JC (1981) Heavy metal intensification of DAB-based HRP reaction product. J Histochem Cytochem 29:775
Bowker RM (1986) Intrinsic 5HT-immunoreactive neurons in the spinal cord of the fetal non-human primate. Dev Brain Res 28:137–143
Bowker RM, Westlund KN, Coulter JD (1981) Origins of serotonergic projections to the spinal cord in rat: an immunocytochemical-retrograde transport study. Brain Res 226:187–199
Cabot JB, Wild JM, Choen DH (1979) Raphe inhibition of sympathetic preganglionic neurons. Science 203:184–186
Cabot JB, Reiner A, Bogan N (1982) Avian bulbospinal pathways: anterograde and retrograde studies of cells of origin, funicular trajectories and laminar terminations. Prog Brain Res 57: 79–108
Chan-Palay V, Jonsson G, Palay SL (1978) Serotonin and substance P coexist in neurons of the rat's central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 75:1582–1586
Edvinsson L, MacKenzie ET (1977) Amine mechanisms in the cerebral circulation. Pharmacol Rev 28:275–348
Gilbey MP, Coote JH, Macleod VH, Peterson DF (1981) Inhibition of sympathetic activity by stimulating in the raphe nuclei and the role of 5-hydroxytryptamine in this effect. Brain Res 226:131–142
Griffith SG, Lincoln J, Burnstock G (1982) Serotonin as a neurotransmitter in cerebral arteries. Brain Res 247:388–392
Harris-Warrick RM, McPhee JC, Filler JA (1985) Distribution of serotonergic neurons and processes in the lamprey spinal cord. Neuroscience 14:1141–1147
Hökfelt T, Ljungdahl A, Steinbusch H, Verhofstad A, Nilsson G, Brodin E, Pernow B, Goldstein M (1978) Immunohistochemical evidence of substance P-like immunoreactivity in some 5-hydroxytryptamine-containing neurons in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 3:517–538
Hosoya Y, Yaginuma H, Okado N, Kohno K (1992) Morphology of sympathetic preganglionic neurons innervating the superior cervical ganglion in the chicken: an immunohistochemical study using retrograde labeling of cholera toxin subunit B. Exp Brain Res 89:478–483
Johansson O, Hökfelt T, Pernow B, Jeffcoate SL, White N, Steinbusch HWM, Verhofstad AAJ, Emson PC, Spindel E (1982) Immunohistochemical support for three putative transmitters in one neuron: coexistence of 5-hydroxytryptamine, substance P- and thyrotropin-releasing hormone-like immunoreactivity in medullary neurons projecting to the spinal cord. Neuroscience 6:1857–1881
Johnson DG, De Nogueria C, Araujo GM (1981) A simple method of reducing the fading of immunofluorescence during microscopy. J Immunol Methods 43:349–350
Kojima M, Takeuchi Y, Goto M, Sano Y (1982) Immunohistochemical study on the distribution of serotonin fibers in the spinal cord of the dog. Cell Tissue Res 226:477–491
Kojima M, Takeuchi Y, Goto M, Sano Y (1983) Immunohistochemical study on the localization of serotonin fibers and terminals in the spinal cord of the monkey (Macaca fuscata). Cell Tissue Res 229:23–26
LaMotte CC, Johns DR, Lanerolle NC de (1982) Immunohistochemical evidence of indolamine neurons in monkey spinal cord. J Comp Neurol 206:359–370
Macdonald RL, Cohen DH (1970) Cells of origin of sympathetic pre- and postganglionic cardioacceleratory fibers in the pigeon. J Comp Neurol 140:343–358
Martin AH (1979) A cytoarchitechtonic scheme of the spinal cord of the domestic fowl, Gallus gallus domesticus: lumbar region. Acta Morphol Neerl-Scand 17:105–117
Millhorn DE, Hökfelt T, Verhofstad AAJ, Terenius L (1989) Individual cells in the raphe nuclei of the medulla oblongata in rat that contain immunoreactivities for both serotonin and enkephalin project to the spinal cord. Exp Brain Res 75:536–542
Newton BW, Hamill RW (1988) The morphology and distribution of rat serotoninergic intraspinal neurons: an immunohistochemical study. Brain Res Bull 20:349–360
Newton BW, Maley B, Hamill RW (1986) Immunohistochemical demonstration of serotonin neurons in autonomic regions of the rat spinal cord. Brain Res 376:155–163
Newton BW, Burkhart AH, Hamill RW (1989) Immunohistochemical distribution of serotonin in spinal autonomic nuclei. II. Early and late postnatal ontogeny in the rat. J Comp Neurol 279:82–103
Ochi J, Hosoya Y (1974) Fluorescence microscopic differentiation of monoamines in the hypothalamus and spinal cord of the lamprey, using a new filter system. Histochemistry 40: 263–266
Okado N, Ishihara R, Ito R, Homma S, Kohno K (1991a) Immunohistochemical study of tyrosine-hydroxylase-positive cells and fibers in the chicken spinal cord. Neurosci Res 11:108–118
Okado N, Matsukawa M, Noritake S, Ozaki S, Hamada S, Arita M, Kudo N (1991b) Species differences in the distribution and coexistence ratio of serotonin and substance P in the monkey, cat, rat and chick spinal cord. Neurosci Lett 132:155–158
Okado N, Sako H, Homma S, Ishikawa K (1992) Development of serotoninergic system in the brain and spinal cord of the chick. Prog Neurobiol 38:93–123
Ozaki S, Kudo N, Okado N (1992) Immunohistochemical study on development of serotonin-, substance P- and enkephalin-positive fibers in the rat spinal motor nucleus. J Comp Neurol 325:462–470
Parent A, Northcutt RG (1982) The monoamine-containing neurons in the brain of the garfish, Lepisosteus osseus. Brain Res Bull 9:189–204
Rajaofetra N, Passagia J-G, Marlier L, Poulat P, Pellas F, Sandillon F, Verschuere B, Gouy D, Geffard M, Privat A (1992) Serotoninergic, noradrenergic, and peptidergic innervation of Onuf's nucleus of normal and transected spinal cords of baboons (Papio papio). J Comp Neurol 318:1–17
Reddy VK, Cassini P, Ho RH, Martin GF (1990) Origins and terminations of bulbospinal axons that contain serotonin and either enkephalin or substance-P in the North American opossum. J Comp Neurol 294:96–108
Ritchie TC, Roos LJ, Williams BJ, Leonard RB (1984) The descending and intrinsic serotoninergic innervation of an elasmobranch spinal cord. J Comp Neurol 224:395–406
Sako H, Kojima T, Okado N (1986a) Immunohistochemical study on the development of serotoninergic neurons in the chick: II. distribution of cell bodies and fibers in the spinal cord. J Comp Neurol 253:79–91
Sako H, Kojima T, Okado N (1986b) Immunohistochemical study on the development of serotoninergic neurons in the chick: I. Distribution of cell bodies and fibers in the brain. J Comp Neurol 253:61–78
Sano Y, Takeuchi Y, Yamada H, Ueda S, Goto S (1982) Immunohistochemical studies on the serotoninergic innervation of the pia mater. Histochemistry 76:277–280
Tashiro T, Satoda T, Takahashi O, Matsushima R, Mizuno R (1988) Distribution of axons exhibiting both enkephalin- and serotonin-like immunoreactivities in the lumbar cord segments: an immunohistochemical study in the cat. Brain Res 440:357–362
Tashiro T, Satoda T, Matsushima R, Mizuno N (1990) Distribution of axons showing both enkephalin- and serotonin-like immunoreactivities in the lumbar cord segments of the Japanese monkey (Macaca fuscata). Brain Res 512:143–146
Van Dongen PAM, Hökfelt T, Grillner S, Rehfeld JF, Verhofstad AJ (1985a) A cholecystokinin-like peptide is present in 5-hydroxytryptamine neurons in the spinal cord of the lamprey. Acta Physiol Scand 125:557–560
Van Dongen PAM, Hökfelt T, Grillner S, Verhofstad AAJ, Steinbusch HWM, Cuello AC, Terenius L (1985b) Immunohistochemical demonstration of some putative neurotransmitters in the lamprey spinal cord and spinal ganglia: 5-hydroxytryptamine-, tachykinin-, and neuropeptide-Y-immunoreactive neurons and fibers. J Comp Neurol 234:501–522
Wallace JA, Allgood PC, Hoffman TJ, Mondragon RM, Maez RR (1986) Analysis of the change in number of serotonergic neurons in the chick spinal cord during embryonic development. Brain Res Bull 17:297–305
Wessendorf MW, Elde R (1987) The coexistence of serotonin- and substance P-like immunoreactivity in the spinal cord of the rat as shown by immunofluorescent double labeling. J Neurosci 7:2353–2363
Yamada T, Placzek M, Tanaka H, Dodd J, Jessell TM (1991) Control of cell pattern in the developing nervous system: polarizing activity of the floor plate and notochord. Cell 64:635–647
Zamboni L, DeMartino C (1967) Buffered picric acid-formaldehyde: a new rapid fixation for electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 35:148A
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Permanent address: This study was supported by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Priority Area from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture, Japan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamada, S., Ogawa, M. & Okado, N. Immunohistochemical examination of intraspinal serotonin neurons and fibers in the chicken lumbar spinal cord and coexistence with Leu-enkephalin. Cell Tissue Res 282, 387–397 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00318871
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00318871