Summary
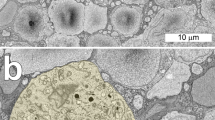
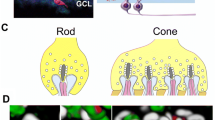
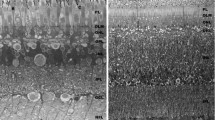
Dopaminergic interplexiform cells in retinae of glass catfish were investigated using an antiserum against tyrosine hydroxylase and peroxidase-anti-peroxidase (PAP) visualization. In whole-mount preparations, we observed a homogeneous distribution of cell bodies throughout the retina without any indication of regional specializations. At the ultrastructural level, we studied the morphology of labelled telodendria within the outer plexiform layer. Apart from contacts with horizontal cells and bipolar cell dendrites, we report for the first time direct contacts with cone pepdicles and rod spherules. Quantitative evaluation of short series of sections showed that all cone pedicles, and a major part of the rod terminals, were approached in this way. The dopaminergic pathway terminating on photoreceptors is discussed in the context of pharmacological effects of this transmitter in the distal retina during light adaptation, i.e., cone contraction, spinule formation and horizontal cell coupling.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Besharse JC, Iuvone PM, Pierce ME (1988) Regulation of rhythmic photoreceptor metabolism: a role for post-receptoral neurons. In: Osborne N, Chader G (eds) Progress in retinal research, vol 7. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 7–61
Burnside A, Nagle W (1983) Retinomotor movements of photoreceptor and retinal pigment epithelium: mechanism and regulation. In: Osborne N, Chader G (eds) Progress in retinal research, vol 2. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 67–190
Dearry A, Burnside B (1986) Dopaminergic regulation of cone retinomotor movement in isolated teleost retinas: 1. Induction of cone contraction is mediated by D2-receptors. J Neurochem 46:1006–1021
Dowling JE, Ehinger B (1978) The interplexiform cell system 1. Synapses of the dopaminergic neurons in the goldfish retina. Proc R Soc Lond (Biol) 201:7–26
Ehinger B, Falck B, Laties AM (1969) Adrenergic neurons in teleost retina. Z Zellforsch 97:285–297
Frederick JM, Rayborn ME, Laties AM, Lam DM-K, Hollyfield JG (1982) Dopaminergic neurons in the human retina. J Comp Neurol 210:65–79
Hedden WL Jr, Dowling JE (1978) The interplexiform cell system. II. Effects of dopamine on goldfish retinal neurons. Proc R Soc Lond (Biol) 201:27–55
Jensen RJ, Daw NW (1986) Effects of dopamine and its antagonists on the receptive field properties of ganglion cells in the rabbit retina. Neuroscience 17:837–855
Kirsch M, Wagner H-J, Djamgoz MBA (1989) Dopamine controls light-adaptive spinule formation and feedback activity of horizontal cells in teleost retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci [Suppl] 30:19
Kirsch M, Wagner H-J, Behrends UD (1990a) Dopamine sensitive spinule formation in teleost horizontal cells is mediated by D1 receptors. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 31:333
Kirsch M, Wagner H-J, Djamgoz MBA (1990b) Dopamine and plasticity of horizontal cell function in teleost retina: Regulation of a spectral mechanism through D1 receptors. Vis Res (in press)
Knapp AG, Dowling JE (1985) Responsiveness and receptive field size of carp horizontal cells are reduced by prolonged darkness and dopamine. Science 229:1107–1109
Kurz-Isler G, Wolburg H (1988) Light dependent dynamics of gap junctions between horizontal cells in the retina of the crucian carp. Cell Tissue Res 251:641–649
Linberg KA, Fisher SK (1986) An ultrastructural study of interplexiform cell synapses in the human retina. J Comp Neurol 243:561–576
Mangel SC, Dowling JE (1987) The interplexiform-horizontal cell system of the fish retina: effects of dopamine, light stimulation and time in the dark. Proc R Soc Lond (Biol) 231:91–121
Negishi K, Teranishi T, Kato S (1981) 5,7-Dihydroxytryptamine destroys indoleamine-accumulating cell bodies in carp retina. Acta Histochem Cytochem 14:654–660
Pfenninger KH (1973) Synaptic morphology and cytochemistry. Progr Histochem Cytochem 5:1–86
Piccolino M, Neyton J, Gerschenfeld HM (1984) Decrease of gap junction permeability induced by dopamine and cyclic adenosine 3′:5′-monophosphate in horizontal cells of turtle retina. J Neurosci 4:2477–2488
Stell WK, Lightfoot D (1975) Color-specific interconnections of cones and horizontal cells in the retina of the goldfish. J Comp Neurol 159:473–502
Sternberger LA (1979) Immunocytochemistry, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Teranishi T, Negishi K, Kato S (1983) Dopamine modulates S-potential amplitude and dye-coupling between horizontal cells in carp retina. Nature 301:243–246
Teranishi T, Negishi K, Kato S (1984) Regulatory effects of dopamine on spatial properties of horizontal cells in carp retina. J Neurosci 4:1271–1280
Wagner H-J (1980) Light dependent plasticity of the morphology of horizontal cell terminals in cone pedicles of fish retinas. J Neurocytol 9:573–590
Wagner H-J (1990) Retinal structure of fishes. In: Douglas RH, Djamgoz MBA (ed) The visual system of fish. Blackwell, Oxford, pp 109–156
Wässle H, Riemann HJ (1978) The mosaic of nerve cells in the mammalian retina. Proc R Soc Lond (Biol) 200:441–461
Weiler R, Kohler K, Kirsch M, Wagner H-J (1988a) Glutamate and dopamine induce synaptic plasticity in horizontal cell dendrites of fish retina. Neurosci Lett 87:205–209
Weiler R, Kohler K, Kolbinger W, Wolburg H, Kurz-Isler G, Wagner H-J (1988b) Dopaminergic neuromodulation in the retinas of lower vertebrates. Neurosci Res [Suppl] 8:S183-S196
Welsh JH, Osborn CM (1937) Diurnal changes in the retina of the catfish, Ameiurus nebulosus. J Comp Neurol 66:439–459
Wulle I, Wagner H-J (1990) Dopaminerge Neurone in der Fischretina: Immunhistochemische Untersuchungen der Morphologie, Verteilung und Synaptologie. Verh Anat Ges (in press)
Yazulla S, Zucker CL (1988) Synaptic organization of dopaminergic interplexiform cells in the goldfish retina. Vis Neurosci 1:13–29
Zucker CL, Dowling JE (1987) Centrifugal fibres synapse on dopaminergic interplexiform cells in the teleost retina. Nature 300:166–168
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wagner, H.J., Wulle, I. Dopaminergic interplexiform cells contact photoreceptor terminals in catfish retina. Cell Tissue Res 261, 359–365 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00318678
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00318678