Abstract
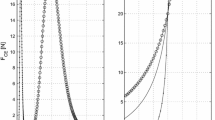
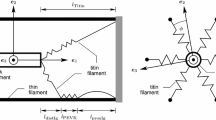
Post-tetanic potentiation (PTP) in single motor units was simulated using a simple visco-elastic model. Single isometric twitches and unfused tetani were obtained using a wide range of physiological input rates. Values of model parameters were chosen to simulate contraction times close to those of fast and slow muscle fibers. PTP has been attributed either to i) an augmented plateau level of active state or ii) an increase in time constant of active state decay. Our results show that a prolonged decay time of active state can account for most of the experimental data obtained in amphibian and mammalian preparations. In particular, potentiation is more marked in unfused tetani than in single twitches. Moreover the model accounts for PTP even in the case of a reduction of active state plateau due to fatigue.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldissera, F., Parmiggiani, F.: After hyperpolarization conductance time-course and repetitive firing in a motoneurone model with early inactivation of the slow potassium conductance system. Biol. Cybern.34, 233–240 (1979)
Bawa, P., Mannard, A., Stein, R.B.: Predictions and experimental tests of a visco-elastic muscle model using elastic and inertial loads. Biol. Cybern.22, 139–145 (1976)
Brust, M.: Relative resistence to dystrophy of slow skeletal muscle of the mouse. Am. J. Physiol.210, 445–451 (1966)
Brust, M.: Fatigue and caffeine effects in fast-twitch and slow-twitch muscles of the mouse. Pflügers Arch.367, 189–220 (1976)
Buller, A.J., Lewis, D.M.: The rate of tension development in isometric tetanic contractions of mammalian fast and slow skeletal muscle. J. Physiol.176, 337–354 (1965)
Buller, A.J., Ranatunga, K.W., Smith, J.M.: The influence on the contractile characteristics of mammalian fast and slow twitch skeletal muscles. J. Physiol.176, 82P (1968)
Burke, R.E., Rudomin, P., Zajac III, F.E.: The effect of activation history on tension production by individual muscle units. Brain Res.109, 515–529 (1976)
Close, R.I.: Dynamic properties of mammalian skeletal muscle. Physiol. Rev.52, 129–197 (1972)
Close, R., Hoh, J.F.Y.: The after-effects of repetitive stimulation on the isometric twitch contraction of rat fast skeletal muscle. J. Physiol.197, 461–477 (1968)
Connolly, R., Gough, W., Winegrad, S.: Characteristics of the isometric twitch of skeletal muscle immediately after a tetanus. J. Gen. Physiol.57, 697–709 (1971)
Cooper, S., Eccles, J.C.: The isometric responses of mammalian muscles. J. Physiol.69, 377–385 (1930)
Desmedt, J.E., Hainaut, K.: Excitation-contraction coupling in single muscle fibers and the calcium channel in sarcoplasmic reticulum. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci.307, 433 (1978)
Ebashi, S.: Excitation-contraction coupling. Ann. Rev. Physiol.38, 293–313 (1976)
Hanson, J.: The effects of repetitive stimulation on the action potential and the twitch of rat muscle. Acta Physiol. Scand.90, 387–400 (1974)
Hatze, H.: A myocybernetic control model of skeletal muscle. Biol. Cybern.25, 103–119 (1977)
Hill, A.V.: The heat of shortening and the dynamic constants of muscle. Proc. R. Soc. (London) B126, 136–195 (1938)
Kernell, D.: The limits of firing frequency in cat lumbosacral motoneurones possessing different time course of afterhyperpolarization. Acta Physiol. Scand.65, 87–100 (1965)
Kernell, D., Ducati, A., Sjöholm, H.: Properties of motor units in the first deep lumbrical muscle of cat's foot. Brain Res.98, 37–55 (1975)
Kernell, D., Sjöholm, H.: Repetitive impulse firing comparisons between neurone models based on “voltage clamp equations” and spinal motoneurones. Acta Physiol. Scand.87, 40–56 (1973)
Nyström, B.: Effect of direct tetanization on twitch tension in developing cat leg muscles. Acta Physiol. Scand.74, 319–330 (1968)
Parmiggiani, F., Stein, R.B.: Nonlinear summation of contractions of cat muscle. II. The later facilitation and stiffness changes. J. Gen. Physiol.78, 295–311 (1981)
Ramsey, R.W., Streets, S.F.: Muscle function as studied in single muscle fibres. Biol. Symp.3, 9–34 (1941)
Ranatunga, K.W.: Influence of temperature on the characteristics of summation of isometric mechanical responses of mammalian skeletal muscle. Exp. Neurol.54, 513–532 (1977)
Ranatunga, K.W.: Characteristics of tension recruitment and mechanical activation in mammalian skeletal muscle. Exp. Neurol.61, 175–184 (1978)
Ranatunga, K.W.: Potentiation of the isometric twitch and mechanisms of tension recruitment in mammalian skeletal muscle. Exp. Neurol.63, 266–276 (1979)
Ranatunga, K.W.: Influence of temperature on isometric tension development in mouse fast-and slow-twitch skeletal muscle. Exp. Neurol.70, 211–219 (1980)
Richtie, J.M., Wikie, D.R.: The effect of previous stimulation on the active state of muscle. J. Physiol.130, 488–496 (1955)
Stein, R.B., Oğuztöreli, M.N.: Tremor and other oscillations in neuromuscular systems. Biol. Cybern.22, 145–157 (1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ducati, A., Parmiggiani, F. & Schieppati, M. Simulation of post-tetanic potentiation and fatigue in muscle using a visco-elastic model. Biol. Cybernetics 44, 129–133 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317972
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00317972