Abstract
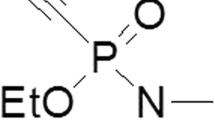
The inhibitory effect of paraquat on cholinesterase activity was investigated in comparison with four paraquat derivatives, six monoquaternary ammoniums and six anticholinergic drugs. Inhibitor concentrations to cause 50% inhibition (I50) and Hill coefficients for three enzymes, human erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase (AChE), Electrophorus electricus AChE and human plasma butyrylcholinesterase (BuChE) were measured. The results obtained were as follows. The I50 for erythrocyte AChE was similar to the I50 for eel AChE. Secondary to edrophonium, diethylparaquat, paraquat, morfamquat and monoquat showed lower I50 for AChE, and possessed higher inhibition selectivity (IS), expressed as the ratio of I50 for BuChE to I50 for erythrocyte AChE. However, diquat showed higher I50 for AChE and lower IS, similar to the other monoquaternary ammoniums. A negative correlation was observed between log [I50 for erythrocyte AChE] and log [IS], among paraquat and its derivatives, monoquaternary ammoniums and anticholinergic drugs, respectively. With respect to Hill coefficients, these inhibitors could be classified into four groups, [1] competitive inhibitors: diquat, edrophonium, choline, tetramethylammonium and trimethylphenylammonium, [2] inhibitors showing negative cooperativity: paraquat, diethylparaquat, morfamquat, d- tubocurarine, atropine, gallamine and nicotine, [3] moderate type inhibitors: monoquat, hexamethonium and decamethonium. [4] the other type inhibitors showing positive cooperativity for erythrocyte AChE: tetraethylammonium and ethyltrimethylammonium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Augustinsson KB (1960) Butyryl- and propionylcholinesterases and related types of eserine-sensitive esterases. In: Boyer PD, Lardy H, Myrbäck K (eds) The Enzymes 2nd ed, vol 4. Academic Press, New York, pp 521–540
Autor AP (1977) Biochemical mechanism of paraquat toxicity. Academic Press, New York
Changeux J-P (1966) Responses of acetylcholinesterase from Torpedo marmorata to salts and curarizing drugs. Mol Pharmacol 2: 369–392
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V Jr, Featherstone RB (1961) A new rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7: 88–95
Gornall AG, Bardaeill CJ, David MM (1949) Determination of serum proteins by means of the biuret reaction. J Biol Chem 177: 751–766
Loftfield RB, Eigner EA (1969) Molecular order of participation of inhibitors (or activators) in biological systems. Science 164: 305–308
Pasi A (1978) The toxicology of paraquat, diquat and morfamquat. Hans Huber Publishers, Switzerland
Roufogalis BD, Quist EE (1972) Relative binding sites of pharmacologically active ligands on bovine erythrocyte acetylcholinesterase. Mol Pharmacol 8: 41–49
Seto Y, Shinohara T (1987) Inhibitory effects of paraquat and its related compounds on the acetylcholinesterase activities of human erythrocytes and electric eel Electrophoms electricus. Agric Biol Chem 51: 2131–2138
Shinohara T, Seto Y (1986) In vitro inhibition of acetylcholinesterase by paraquat. Agric Biol Chem 50: 255–256
Wilson IB (1960) Acetylcholinesterase. In: Boyer PD, Lardy H, Myrbäck K (eds) The Enzymes 2nd ed vol 4. Academic Press, New York, pp 501–520
Wilson IB, Quan C (1958) Acetylcholinesterase studies on molecular complementariness. Arch Biochem Biophys 73: 131–143
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seto, Y., Shinohara, T. Structure-activity relationship of reversible cholinesterase inhibitors including paraquat. Arch Toxicol 62, 37–40 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00316254
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00316254