Abstract
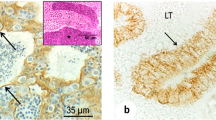
The localization and distribution of inhibin/activin subunits was evaluated in the testes of three nonhuman primate species (Macaca fascicularis, M. mulatta, M. arctoides), of young (31 to 43 years) and old (60 to 85 years) men, and of men with disturbed or arrested spermatogenesis using immunohistochemical techniques (peroxidase-anti-peroxidase and alkaline-phosphatase/ anti-alkaline-phosphatase technique). Specific polyclonal (anti-porcine inhibin α-1-32 and anti-bovine activin A) and monoclonal (anti-human inhibin α-1-32 and anti-human activin βA-82-114) antisera were employed. Among all nonhuman primate species and in men, inhibin/activin subunits were present in the cytoplasm of Sertoli cells and Leydig cells but not in germ cells. No relationship could be established between the staining pattern for inhibin/activin subunits and the completeness or the stage of the spermatogenic process. The staining for the βA-subunit in Sertoli cells appeared more intense in the testes of old men compared with that of young men. The majority of Leydig cells contained either the α-subunit and βA-subunit or the βA-subunit alone. The signal for the βA-subunit was remarkably intense in normal and hyperplastic human Leydig cells. These observations demonstrate the presence of inhibin/activin subunits in Sertoli cells and Leydig cells of adult primates and raise the possibility that these subunits or their respective dimers (inhibin A/activin A) might subserve a paracrine/ autocrine role in the adult primate testis. Also, the possibility of specific differences in the α-1-32 subunit and the βA-82-114 subunit region among certain primate species arises from the observation that the monoclonal antisera failed to detect the respective antigens in M. fascicularis and M. mulatta.
Access this article
We’re sorry, something doesn't seem to be working properly.
Please try refreshing the page. If that doesn't work, please contact support so we can address the problem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allenby G, Foster PMD, Sharpe RM (1991) Evidence that secretion of immunoreactive inhibin by seminiferous tubules from adult rat testis is regulated by specific germ cell types: correlation between in vivo and in vitro studies. Endocrinology 128:467–476
Bergh A, Cajander S (1990) Immunohistochemical localization of inhibin alpha in the testes of normal men and men with testicular disorders. Int J Androl 13:463–469
Betteridge A, Craven RP (1991) A two-site enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for inhibin. Biol Reprod 45:748–754
Bhasin S, Krummen LA, Swerdloff S, Morelos BS, Kim H, Zerega GS di, Ling N, Esch F, Shimasaki S, Toppari J (1989) Stage dependent expression of inhibin alpha and beta B subunits during the cycle of the rat seminiferous epithelium. Endocrinology 124:987–991
Bicsak TA, Vale W, Vaughan J, Tucker EM, Cappel S, Hsueh AJW (1987) Hormonal regulation of inhibin production by cultured Sertoli cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 49:211–217
Dissel-Emiliani FMF van, Grootenhuis AJ, Jong FH de, Rooij DG de (1989) Inhibin reduces spermatogonial numbers in testes of adult mice and Chinese hamsters. Endocrinology 125:1898–1903
Fingscheidt U, Nieschlag E (1989) The response of inhibin to chorionic gonadotrophins is decreased in senescent men compared with young men. J Endocrinol 123:R9-R11
Garde SV, Sheth AR (1988) Immunoperoxidase localization of prostatic inhibin peptide in human, monkey, dog and rat prostates. Anat Rec 223:181–184
Garde SV, Moodbidri SB, Phadke AM, Sheth AR (1988) Localization of inhibin in human testes by immunoperoxidase technique. Anat Rec 222:357–361
Groome NP (1991) Ultrasensitive two-site assays for inhibin A and activin A using monoclonal antibodies raised to synthetic peptides. J Immunol Meth 145:65–69
Groome NP, Lawrence M (1991) Preparation of monoclonal antibodies reactive with the beta A subunit of ovarian inhibin. Hybridoma 10:309–311
Groome NP, Hancock J, Betteridge A, Lawrence M, Craven R (1990) Monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies reactive with the 1–32 amino-terminal peptide of the alpha subunit of human ovarian inhibin. Hybridoma 9:31–33
Handelsman DJ, Spaliviero JA, Phippard AF (1990) Highly vectorial secretion of inhibin by primate Sertoli cells in vitro. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 71:1235–1238
Hsueh AJW, Dahl KD, Vaughan J, Tucker E, Rivier J, Bardin CW, Vale WW (1987) Heterodimers and homodimers of inhibin subunits have different paracrine action in the modulation of luteinizing hormone-stimulated androgen biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:5082–5086
Jong FH de, Grootenhuis AJ, Klaij A, Beurden WMO van (1990) Inhibin and related proteins: Colocalization, regulation and effects. In: Porter JC, Jezova D (eds) Circulating regulatory factors and neuroendocrine function. Plenum Press, New York, pp 271–293
Keiman D, Madigan MB, Bardin CW, Chen CLC (1989) Expression and regulation of testicular inhibin alpha subunit gene expression in vivo and in vitro. Mol Endocrinol 3:29–35
Knight PG, Muttukrishna S, Groome N, Webley GE (1992) Evidence that most of the radioimmunoassayable inhibin secreted by the corpus luteum of the common marmoset monkey is of a non-dimeric form. Biol Reprod 47:554–560
Kretser DM de, Robertson DM (1989) The isolation and physiology of inhibin and related proteins. Biol Reprod 40:33–47
Krummen LA, Wong WL, Garg S, Gibson U, Mann E, Mather JP (1992) Activin A is produced in vitro by interstitial cells derived from immature, but not adult rat testis. 7th European Workshop of Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology of the Testis, Elmau. Miniposter no 76
Ling N, Ying SY, Ueno N, Shimasaki S, Hotta M, Guillemin SR (1986) Pituitary FSH is released by a heterodimer of the beta subunits from two forms of inhibin. Nature 321:779–782
Ling T, Calkins H, Morris PL, Vale WW, Bardin CW (1989) Regulation of Leydig cell function in primary culture by inhibin and activin. Endocrinology 125:2134–2140
Mather JP, Krummer LA (1992) Inhibin, activin and growth factors: paracrine regulators of testicular function. In: Nieschlag E, Habenicht UF (eds) Spermatogenesis — fertilization — contraception. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 170–200
Mather JP, Kenneth MA, Woodruff TK, Rice GC, Phillips DM (1990) Activin stimulates spermatogonial proliferation in germ-Sertoli cell cocultures from immature rat testis. Endocrinology 127:3206–3214
Meunier H, Revier C, Evans RM, Vale W (1988) Gonadal and extragonadal expression of inhibin alpha, beta A and beta B subunits in various tissue predicts diverse functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:247–251
Ogawa K, Kurohmaru M, Shiota K, Takahashi M, Nishida T, Hayashi Y (1981) Histochemical localization of inhibin and activin alpha, beta A and beta B subunits in rats gonads. J Vet Med Sci 53:207–212
Pineau C, Sharpe RM, Saunders PTK, Gerard N, Jegou B (1990) Regulation of Sertoli cell inhibin production and of inhibin alpha subunit mRNA levels by specific germ cell types. Mol Cell Endocrinol 72:13–22
Rabinovici J, Goldsmith PC, Roberts VJ, Vaughan J, Vale W, Jaffe RB (1991) Localization and secretion of inhibin/activin subunits in human and subhuman primate fetal gonads. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 73:1141–1149
Risbridger GP, Clements J, Robertson DM, Drummond AE, Muir J, Burger HG, Kretser DM de (1989) Immuno- and bioactive inhibin and inhibin alpha subunit expression in rat Leydig cell culture. Mol Cell Endocrinol 66:119–122
Risbridger GP, Robertson DM, Kretser DM de (1990) Current perspective of inhibin biology. Acta Endocrinol 122:673–682
Rivier C, Cajander S, Vaughan J, Hsueh AJW, Vale W (1989) Age-dependent changes in physiological action, content, and immunostaining of inhibin in male rats. Endocrinology 123:120–126
Roberts V, Meunier H, Sawchenko PE, Vale W (1989) Differential production and regulation of inhibin subunits in rat testicular cell types. Endocrinology 125:2350–2359
Romeis B (1968) Mikroskopische Technik Oldenburg, München, Wien, p 651
Saito S, Roche PC, McCormick DJ, Ryan RJ (1989) Synthetic peptide segments of inhibin-alpha and beta-subunits preparation and characterization of polyclonal antibodies. Endocrinology 125:898–905
Schlatt S, Weinbauer GF, Nieschlag E (1991) Inhibin-like and gonadotropin-like immunoreactivity in pituitary cells of male monkeys (Macaca fascicularis, Macaca mulatta). Cell Tissue Res 265:203–209
Shaha C, Morris PL, Chen CL, Vale W, Bardin CW (1989) Immunostainable inhibin subunits are in multiple types of testicular cells. Endocrinology 125:1941–1950
Sharpe RM, Kerr JB, Maddocks S (1988) Evidence for a role of the Leydig cell in control of the intratesticular secretion of inhibin. Mol Cell Endocrinol 60:243–247
Simpson BJB, Risbridger GP, Hedger MP, Kretser DM de (1991) The role of calcium in luteinizing hormone/human chorionic gonadotrophin stimulation of Leydig cell immunoreactive inhibin secretion in vitro. Mol Cell Endocrinol 75:49–56
Teerds KJ, Rollij DG de, Jong FH de, Rommerts FFG (1991) Rapid development of Leydig cell tumors in Wistar rat substrain. J Androl 12:171–179
Vale W, Rivier J, Vaughan J, McClintock R, Corrigan A, Woo W, Karr D, Spiess J (1986) Purification and characterization of a FSH releasing protein from porcine ovarian follicular fluid. Nature 321:776–779
Weinbauer GF, Surmann FJ, Akhtar FB, Shah GV, Vickery BH, Nieschlag E (1984) Reversible inhibition of testicular function by a gonadotropin-releasing hormone antagonist in monkeys (Macaca fascicularis). Fertil Steril 42:906–914
Weinbauer GF, Galhotra MM, Nieschlag E (1985) Focal testicular destruction following intratesticular injection of glycerol in rats. Int J Androl 8:365–375
Weinbauer GF, Drobnitzky F, Galhotra MM, Nieschlag E (1987) Intra-testicular injection of glycerol as a model for studying the quantitative relationship between spermatogenic damage and serum FSH. J Endocrinol 115:83–90
Weinbauer GF, Bartlett JMS, Fingscheidt U, Tsonis CG, Kretser DM de, Nieschlag E (1989) Evidence for a major role of inhibin in the feedback control of FSH in the male rat. J Reprod Fert 85:355–362
Winter JP de, Timmerman MA, Vanderstichele HMJ, Klaji IA, Grootenhuis AJ, Rommerts FFG, Jong FH de (1991) Testicular Leydig cell tumors can secrete bioactive inhibin. Mol Cell Endocrinol 83:105–115
Woodruff TK, Borree TJ, Attie KM, Cox ET, Rice GC, Mather JP (1992) Stage-specific binding of inhibin and activin to subpopulations of rat germ cells. Endocrinology 130:871–881
Yamoto M, Minami S, Nakano R, Kobayashi M (1992) Immunohisto-chemical localization of inhibin/activin subunits in human ovarian follicles during the menstrual cycle. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 74:989–993
Ying SY (1988) Inhibins, activins and follistatins. Gonadal proteins modulating the secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone. Endocr Rev 9:267–293
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vliegen, M.K., Schlatt, S., Weinbauer, G.F. et al. Localization of inhibin/activin subunits in the testis of adult nonhuman primates and men. Cell Tissue Res 273, 261–268 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00312827
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00312827