Abstract
In acute and subacute inhalation studies rats were exposed to methylchloroform. In the 4-h exposure the concentrations were approximately 220 and 440 ppm, and in the 3-month study (5×8 h/week) approximately 204 ppm (MAC= 200 ppm).
The behavior of methylchloroform and its metabolites (trichloroethanol and trichloroacetic acid) in the expired air, blood, and urine was investigated. A gaschromatographic method for the determination of methylchloroform is described. Most of the methylchloroform is eliminated unchanged via the lungs.
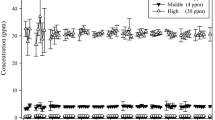
In the subchronic inhalation studies, methylchloroform concentrations within the range of the MAC were tolerated with no symptoms. During this time, the concentrations of methylchloroform and trichloroethanol in the blood and the concentration of trichloroacetic acid in the urine remained constant. The urinary trichloroethanol excretion increased until the 10th week, then it fell and remained constant at a level somewhat below the maximum concentration. Methylchloroform was not detectable in organ tissue. The results of the metabolic studies are discussed.
Zusammenfassung
In akuten und subakuten Inhalationsversuchen wurden Ratten Methylchloroform exponiert. Bei den 4stündigen Expositionen waren die Konzentrationen ca. 220 und 440 ppm, im 3 Monateversuche (wöchentlich 5×8 Std) ca. 204 ppm (MAK-Wert: 200 ppm). Das Verhalten von Methylchloroform und seiner Metabolite (Trichloräthanol und Trichloressigsäure) in Atemluft, Blut und Harn wurde untersucht. Eine gaschromatographische Methode zur Methylchloroformbestimmung wird angegeben. Methylchloroform wird hauptsächlich unverändert abgeatmet. Als Metabolite wurden Trichloroäthanol und Trichloressigsäure nachgewiesen. In den subchronischen Inhalationsversuchen wurden von den Ratten Methylchloroformkonzentrationen im MAK-Bereich symptomlos toleriert.
Während dieser Zeit blieben die Konzentrationen von Methylchloroform und Trichloräthanol im Blut- und von Trichloressigsäure im Harn konstant. Die Trichloräthanolmenge im Harn stieg bis zur 10. Woche an und stellte sich dann auf einem Niveau etwas unterhalb der maximalen Konzentration ein. Im Organgewebe konnte Methylchloroform nicht nachgewiesen werden. Die Ergebnisse der Stoffwechseluntersuchungen werden diskutiert.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, E. M., Spencer, H. C., Rowe, V. K., Irish, D. D.: Vapor toxicity of 1,1,1-Trichloroethane (methylchloroform) determined by experiments on laboratory animals. Arch. industr. Hyg. 1, 225 (1950)
Betke, K., Savelsberg, W.: Stufenphotometrische Hämoglobinbestimmung mittels Cyanhämoglobin. Biochem. Z. 320, 431 (1950)
Boettner, E. A., Muranko, H. J.: Animal breath data for estimating the exposure of humans to chlorinated hydrocarbons. Amer. industr. Hyg. Ass. J. 30, 437 (1969)
DFG-Kommission Gesundheitsschädliche Arbeitsstoffe. Toxikologisch arbeitsmedizinische Begründung von MAK-Werten. Weinheim: Verlag Chemie 1972
Fuller, G., Olshan, A. M., Puri, S. K., Lal, H.: Induction of hepatic drug metabolism in rats by methylchloroform inhalation. J. Pharmacol. exp. Therap. 175, 311 (1970)
Hake, C. L., Waggoner, T. B., Robertson, D. N., Rowe, V. K.: The metabolism of 1,1,1-Trichloroethane by the rat. Arch. environm. Hlth 1, 101 (1960)
Henry, R. J.: Clinical chemistry. Hoeber 1964
Holzer, H., Hahn, J., Schneider, S.: Zum Mechanismus des aneroben Glucose- und Fructose-Abbaues im Mäuse-Ascites-Carcinom. Biochem. Z. 326, 351 (1955)
Ikeda, M., Ohtsujl, H.: A comperative study of the excretion of Fujiwara reaction positive substances in urine of humans and rodents given trichloro- or tetrachloro-derivatives of ethane and ethylene. Brit. J. industr. Med. 29, 99 (1972)
Kimmerle, G., Eben, A.: Metabolism, excretion and toxicology of trichloro-ethylene after inhalation. 1. Experimental exposure on rats. Arch. Toxikol. 30, 115 (1973)
Lal, H., Shah, H.: Effect of prolonged Methylchloroform inhalation on drug-induced CNS activity. Toxicol. appl. Pharmacol. 10, 389 (1967)
Lal, H., Shah, H.: Reduced sleeping time and increased microsomal oxidation of hexobarbital after methylchloroform inhalation in mice. Pharmacologist 10, 153 (1968)
Lal, H., Olshan, A., Puri, S., Shah, H. C., Fuller, G. C.: Enhancement of hepatic drug metabolism in rats after Methyl-Chloroform (MC) inhalation. Toxicol. appl. Pharmacol. 14, 625 (1969)
Lal, H., Shah, H. C.: Effect of methylchloroform inhalation on barbiturate hypnosis and hepatic drug metabolism in male mice. Toxicol. appl. Pharmacol. 17, 625 (1970)
Popper, H., Mandel, E., Mayer, H.: Zur Kreatininbestimmung im Blut. Biochem. Z. 291, 354 (1937)
Prendergast, J. A., Jones, R. A., Jenkins, L. J., Siegel, J.: Effects on experimental animals of long-term inhalation of trichloroethylene, carbon tetrachloride, 1,1,1-trichloroethane, dichlorodifluoromethane and 1,1-dichloroethylene. Toxicol. appl. Pharmacol. 10, 270 (1967)
Reitman, St., Frankel, S.: A colorimetric method for the determination of serum glutamic oxalacetic and glutamic pyruvic transaminase. Amer. J. clin. Pathol. 28, 56 (1957)
Schmidt, F. H.: Enzymatische Methoden zur Bestimmung von Blut- und Harnzucker unter Berücksichtigung von Vergleichsuntersuchungen mit klassischen Methoden. Internist 4, 554 (1963)
Stewart, R. D., Gay, H. H., Erley, D. S., Hake, C. L., Schaffer, A. W.: Human exposure to 1,1,1-trichloroethane vapor: relationship of expired air and blood concentration to exposure and toxicity. Amer. industr. Hyg. Ass. J. 22, 252 (1961)
Stewart, R. D., Gay, H. H., Schaffer, A. W., Erley, D. S., Rowe, V. K.: Experimental human exposure to methylchloroform vapor. Arch. environm. Hlth 19, 467 (1969)
Tanaka, S., Ikeda, M.: A method for determination of trichloroethanol and trichloroacetic acid in urine. Brit. J. industr. Med. 25, 214 (1968)
Torkelson, T. R., Oyen, F., McCollister, D. D., Rowe, V. K.: Toxicity of 1,1,1-trichloroethane as determined on laboratory animals and human subjects. Amer. industr. Hyg. Ass. J. 19, 353 (1958)
Wilcoxon, F.: Individual comparison by ranking methods. Biometrics 1, 80 (1945)
With, T. K.: Bestimmung von Bilirubin in kleinen Blutmengen (Cutanblut). Hoppe Seylers Z. physiol. Chem. 278, 129 (1943)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
We wish to express our thanks to Mrs. U. Gloy, Mrs. M. Gebauer, Mr. F. Tepper and Mr. U. Jansen for their technical assistance: Special thanks are given to Dr. G. Luckhaus for the histo-pathological investigations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eben, A., Kimmerle, G. Metabolism, excretion and toxicology of methylchloroform in acute and subacute exposed rats. Arch. Toxicol. 31, 233–242 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00311056
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00311056