Abstract
Two comparative experiments on the behavioural, audiometric and histological effects of kanamycin-induced cochleotoxicity in the Wistar rat are reported.
In the first experiment kanamycin 400–1,500 mg/kg/day was injected subcutaneously for 20 days and the morphological damage to the organ of Corti assessed. In the second experiment the progression of damage to the organ of Corti was examined in animals given kanamycin 700 mg/kg/day for 4–20 days. Behavioural audiometric studies of threshold shift were undertaken throughout both experiments.
In the first study, all the animals were killed after a recovery period of 20 days from the last injection, i.e., day 40, and in the second study groups of animals were killed at 4-day intervals between days 4 and 20 of dosing.
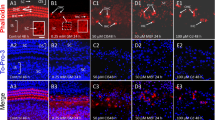
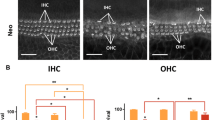
One cochlea from each animal was critical point-dried, dissected to expose the organ of Corti and examined by scanning electron microscopy. A vertical section through the contralateral cochlea was examined by light microscopy. The results of the morphological examination of the cochleas were collated with the behavioural audiometry.
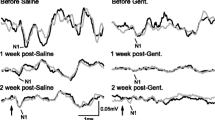
The morphological damage to the organ of Corti followed a stereotyped pattern of degeneration, the extent of which appeared to be determined both by the number and concentration of the kanamycin administrations. The collateral audiometric examinations indicated that extensive damage had taken place before a shift in the behavioural auditory threshold could be detected by observation of the Preyer reflex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson H, Wedenberg E (1965) A new method for hearing tests in the guinea pig. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 60: 375–393
Astbury PJ, Read NG Improved morphological technique for screening potentially ototoxic compounds in laboratory animals. Br J Audiol 16: 131–137
Baird JRC, Carter AJ (1979) Tests for effects of drugs on hearing and balance — a screen for assessing the ototoxic potential of aminoglycoside antibioties. Pharmacol Ther (B) 5: 579–583
Engström H, Ades HW, Anderson A (1966) Structural pattern of the organ of Corti. Almqvist and Wiksell, Stockholm
Glauert AM (1974) Practical methods in electron microscopy, 3 (1). North Holland Publishing Co, Amsterdam and Oxford/American Elsevier Publishing Co, New York
Hawkins Jr JE, Engstrom H (1964) Effect of kanamycin on cochlear cytoarchitecture. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl, 188
Humphrey CD, Pittman FE (1974) A simple methylene blue-azure II-basic fuchsin stain for epoxy embedded tissue sections. Stain Technol 49: 9–14
Hunter-Duvar IM, Mount RJ (1978) The organ of Corti following ototoxic antibiotic treatment. Becker RP, Johari O (eds) Scanning electron microscopy II: S.E.M. Inc, A M F O'Hare, Ill USA, pp 423–430
Kaneko Y, Terayama Y, Kawamoto K, Kasajima K, Ise I (1978) Singlecell layer membrane covering the degenerated cochlear duct after perilymphatic perfusion of streptomycin. Acta Otolaryngol 86: 375–384
Kohonen A (1965) Effect of some ototoxic drugs upon the pattern and innervation of cochlear sensory cells in the guinea pig. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 208
Leake-Jones PA, Vivion MC (1979) Cochlear pathology in cats following administration of neomycin sulfate. Johari O, Becker RP (eds) Scanning electron microscopy III: S.E.M. Inc, A M F O'Hare, Ill, USA, pp 983–991
Theopold HM (1977) Comparative surface studies of ototoxic effects of various aminoglycoside antibiotics on the organ of Corti in the guinea pig. Acta Otolaryngol 84: 57–64
Toyoda Y, Saito H, Matsuoka H, Takenaka H, Oshima W, Mizukoshi O (1977) Quantitative analysis of kanamycin ototoxicosis. Acta Otolaryngol 84: 202–212
Voelker FA, Henderson CM, Macklin AW, Tucker WE (1980). Evaluating the rat inner ear. A technique using scanning electron microscopy. Arch Otolaryngol 106: 613–617
Ward WD, Duvall AJ (1971) Behavioural and ultrastructural correlates of acoustic trauma. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 8: 881–896
Wersall J (1973) Problems and pitfalls in studies of cochlear hair cell pathology. Møller A (ed) Basic mechanisms in hearing. Academic Press, New York, pp 235–256
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Astbury, P.J., Read, N.G. Kanamycin induced ototoxicity in the laboratory rat. Arch Toxicol 50, 267–278 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00310859
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00310859