Summary
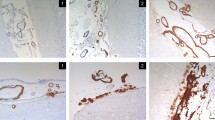
To clarify the pathogenesis of cerebrovascular amyloid deposits, histological and immunocytochemical studies were performed on the central nervous system (CNS) in ten casès with type I familial amyloid polyneuropathy (FAP). They commonly suffered from peripheral somatic and autonomic nerve disorders without any CNS dysfunctions. However, all cases showed CNS amyloid deposits, mainly on the leptomeningeal vessels and pia-arachnoid membranes, with arteries and arterioles in the subarachnoidal space being the predominant site of cerebral amyloid accumulation. Using immunocytochemical staining methods with antibodies to amyloid β-protein, human cystatin C and transthyretin (prealbumin), all of these amyloid deposits were specifically immunolabeled by the anti-human transthyretin antibody. However, there were no transthyretin-related amyloid deposits in the brain parenchyma. It is concluded that CNS transthyretin-immunoreactive amyloid deposition with cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA) is a common pathological finding in this disease. Moreover, the patients with type I FAP are known to have an amyloid protein precursor (a variant of transthyretin) in serum. This transthyretin type of CAA, therefore, seems to be an example of cerebrovascular amyloid deposits derived from a serum precursor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allsop D, Landon M, Kidd M, Lowe JS, Reynolds GP, Gardner A (1986) Monoclonal antibodies raised against a subsequence of senile plaque core protein react with plaque cores, plaque periphery and cerebrovascular amyloid in Alzheimer's disease. Neurosci Lett 68:252–256
Allsop D, Ikeda S, Bruce M, Glenner GG (1988) Cerebrovascular amyloid in scrapie-affected sheep reacts with antibodies to prion protein. Neurosci Lett 92: 234–239
Andrade C (1952) A peculiar form of peripheral neuropathy: familiar atypical generalized amyloidosis with special involvement of the peripheral nerves. Brain 75:408–427
Benson MD, Cohen AS (1977) Generalized amyloid in a family of Swedish origin. A study of 426 family members in seven generations of a new kinship with neuropathy, nephropathy, and central nervous system involvement. Ann Intern Med 86: 419–424
Castaño EM, Frangione B, (1988) Human amyloidosis, Alzheimer disease and related disorders. Lab Invest 58: 122–132
Ghiso J, Jensson O, Frangione B (1986) Amyloid fibrils in hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis of Icelandic type is a variant of ψ-trace basic protein (cystatin C). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:2974–2978
Gilbert JJ, Vinters HV (1983) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy: incidence and complications in the aging brain. I. Cerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 14:915–923
Glenner GG, Wong CW (1984) Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 120:885–890
Glenner GG, Wong CW, Quaranta V, Eanes ED (1984) The amyloid deposits in Alzheimer's disease: their nature and pathogenesis. Appl Pathol 2:357–369
Gudmundsson G, Hallgrímsson J, Jónasson TÁ, Bjarnason Ó (1972) Hereditary cerebral haemorrhage with amyloidosis. Brain 95:387–404
Hanyu N, Ikeda S, Nakadai A, Yanagisawa N, Powell HC (1989) Peripheral nerve pathological findings in familial amyloid polyneuropathy: a correlative study of proximal sciatic nerve and sural nerve lesions. Ann Neurol 25:340–350
Hofer P-Å, Andersson R (1975) Postmortem findings in primary familial amyloidosis with polyneuropathy. A study based on six cases from northern Sweden. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand [A] 83:309–322
Horta JDAS, Filipe I, Duarte S (1964) Portuguese polyneuritic familial type of amyloidosis. Pathol Microbiol 27:809–825
Ikeda S, Hanyu N, Hongo M, Yoshioka J, Oguchi H, Yanagisawa N, Kobayashi T, Tsukagoshi H, Ito N, Yokota T (1987) Hereditary gereralized amyloidosis with polyneuropathy. Clinicopathological study of 65 Japanese patients. Brain 110: 315–337
Ikeda S, Allsop D, Glenner GG (1989) Morphology and distribution of plaque and related deposits in the brains of Alzheimer's disease and control cases. An immunohistochemical study using amyloid β-protein antibody. Lab Invest 60: 113–122
Ishihara T, Nagasawa T, Yokota T, Gondo T, Takahashi M, Uchino F (1989) Amyloid protein of vessels in leptomeninges, cortices, choroid plexuses, and pituitary glands from patients with systemic amyloidosis. Hum Pathol 20:891–895
Kitamoto T, Ogomori K, Tateishi J, Prusiner SB (1987) Formic acid pretreatment enhances immunostaining of cerebral and systemic amyloids. Lab Invest 57:230–236
Krücke W (1963) Zur pathologischen Anatomie der Paramyloidose. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) [Suppl II]: 74–93
Löfberg H, Grubb AO, Nilsson EK, Jensson O, Gudmundsson G, Blöndal H, Arnason A, Thorsteinsson L (1987) Immunohistochemical characterization of the amyloid deposits and quantitation of pertinent cerebrospinal fluid proteins in hereditary cerebral hemorrhage with amyloidosis. Stroke 18:431–440
Luyendijk W, Bots GTAM, Vegter-van der Vlis M, Went LN, Frangione B (1988) Hereditary cerebral haemorrhage caused by cortical amyloid angiopathy. J Neurol Sci 85:267–280
Mandybur TI (1975) The incidence of cerebral amyloid angiopathy in Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 25:120–126
Maruyama K, Ikeda S, Ishihara T, Allsop D, Yanagisawa N (1990) Immunohistochemical characterization of cerebrovascular amyloid in 46 autopsied cases using antibodies to β protein and cystatin C. Stroke 21:397–403
Masters CL, Multhaup G, Simms G, Pottgiesser J, Martins RN, Beyreuther K (1985) Neuronal origin of a cerebral amyloid: neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease contain the same protein as the amyloid of plaque cores and blood vessels. EMBO J 4:2757–2763
Nakazato M, Kangawa K, Minamino N, Tawara S, Matsuo H, Araki S (1984) Identification of a prealbumin variant in the serum of a Japanese patient with familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 122:712–718
Okazaki H, Reagan TJ, Campbell RJ (1979) Clinicopathologic studies of primary cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Mayo Clin Proc 54:22–31
Prusiner SB, DeArmond SJ (1987) Prions causing nervous system degeneration. Lab Invest 56:349–363
Sakaki Y, Sasaki H, Yoshioka K, Furuya H (1989) Genetic analysis of familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy, an autosomal dominant disease. Clin Chim Acta 185:291–298
Sasaki H, Sakaki Y, Matsuo H, Goto I, Kuroiwa Y, Sahashi I, Takahashi A, Shinoda T, Isobe T, Takagi Y (1984) Diagnosts of familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy by recombinant DNA techniques. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 125:636–642
Suzuki T, Azuma T, Tsujino S, Mizuno R, Kishimoto S, Wada Y, Hayashi A, Ikeda S, Yanagisawa N (1987) Diagnosis of familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy: Isolation of variant prealbumin. Neurology 37:708–711
Tagliavini F, Ghiso J, Timmers WF, Giaccone G, Bugiani O, Frangione B (1990) Coexistence of Alzheimer's amyloid precursor protein and amyloid protein in cerebral vessel walls. Lab Invest 62:761–767
Tawara S, Nakazato M, Kangawa K, Matsuo H, Araki S (1983) Identification of amyloid prealbumin variant in familial amyloidotic polyneuropathy (Japanese type). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 116:880–888
Tomonaga M (1981) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy in the elderly. J Am Geriatr Soc 29:151–157
Vinters HV, Gilbert JJ (1983) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy: review. Stroke 18:311–324
Vinters HV, Gilbert JJ (1983) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy: incidence and complications in the aging brain. II. The distribution of amyloid vascular changes. Stroke 14:924–928
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by a grant-in-aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Science and Culture and grants from the Intractable Disease Division, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Primary Amyloidois Research Committee, and Kanae Foundation of New Medicine, Japan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ushiyama, M., Ikeda, S. & Yanagisawa, N. Transthyretin-type cerebral amyloid angiopathy in type I familial amyloid polyneuropathy. Acta Neuropathol 81, 524–528 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00310133
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00310133