Abstract
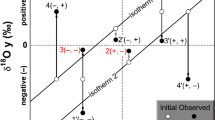
The pilot hole of the Continental Deep Borehole (KTB) drilling project is located in the Bavarian Oberpfalz at the western margin of the Bohemian Massif. The 4-km deep borehole penetrated various paragneisses and minor orthogneisses with intercalations of amphibolites and metagabbros. The different lithologies have systematically different whole-rock oxygen isotope values and give little evidence for large scale water-rock interaction. Minor fluid interaction is well documented during retrograde metamorphism by non-equilibrium fractionations between refractory minerals (quartz, garnet and hornblende) and altered minerals (chlorite/biolite and feldspar). Ubiquitous vein mineralisation indicates fluid-induced retrogression at temperatures between 150°C and 400°C. The δD values of hydroxylbearing minerals are very uniform in all lithologic units. The calculated hydrogen isotope composition of the fluid in equilibrium with matrix and vein minerals increases from -45‰ for metabasic rocks, to -20‰ for gneisses, to about -5‰ for vein minerals. The oxygen isotope composition of the fluid has been buffered by the rock and decreases with decreasing temperature because of increasing fractionations at low temperatures and low water-rock ratios. Modern fluids sampled from open cavities within the borehole have isotopic compositions that suggest a continuous fluid evolution during retrogression in a closed system. The δ13C values of calcite and graphite also indicate closed system mixing processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borchardt R, Zulauf G, Emmermann R, Hoefs J, Simon K (1990) Abfolge und Bildungsbedinggungen von Sekundärmineralen in der KTB-Vorbohrung. In: Emmermann R, Giese P (eds) KTB Report 90-4, NLfB. Hannover, pp 76–88
Bottinga Y (1969) Calculated fractionation factors for carbon and hydrogen isotope exchange in the system calcite-CO2-graphite-methane-hydrogen and water vapor. Geochim Cosmochim Acta. 33:49–64
Bottinga Y, Javoy M (1973) Comments on oxygen isotope geothermometry. Earth Planet Sci Lett 20:250–265
Chacko T, Mayeda TK, Clayton RN, Goldsmith JR (1991) Oxygen and carbon isotope fractionations between CO2 and calcite. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 55:2867–2882
Chiba H, Kusakabe M, Hirano S, Matsuo S, Somiya S (1981) Oxygen isotope fractination factors between anhydrite and water from 100°C and 550°C. Earth Planet Sci Lett 53:55–62
Cole DR, Ohmoto H (1986) Kinetics of isotope exchange at elevated temperatures and pressures. In: Valley JW, Taylor HP, O'Neil JR (eds) Stable isotopes in high temperature geological processes. (Reviews in Mineralogy 16) Mineral Soc Am Washington DC, pp 41–90
Cole DR, Ohmoto H, Jacobs GK (1992) Isotopic exchange in mineral-fluid systems: III, rates and mechanism of oxygen isotope exchange in the system granite-H2O±NaCl±KCl at hydrothermal conditions. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 56:445–466
Craig H (1961) Isotopic variations in meteoric, waters. Science 133:1702–1703
Dodson MH (1973) Closure temperature in cooling geochronological and petrological systems. Contrib Mineral Petrol 40:259–274
Fortier SM, Giletti BJ (1991) Volume self-diffusion of oxygen in biotite, muscovite, and phlogopite micas. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 55:1319–1330
Frape SK, Fritz P (1982) The chemistry and isotopic composition of saline groundwaters from the Canadian Shield. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 48:1617–1627
Frape SK, Fritz P (1987) Geochemical trends from groundwaters from the Canadian Shield. In: Fritz P, Frape SK (eds) Saline water and gases in crystalline rocks. Geol Assoc Can Spec Pap 33: 19–38
Friedrich G, Vogtmann-Becker J, Kotnik M, Redecke P, Herzig P, Kontny A, van Delden S, Keyssner S (1989) Bildungsbe-dingungen von Chlorit in metamorphen Gesteinen der Oberpfalz. In: Emmermann R, Giese P (eds) KTB Report 89-3, NLfB, Hannover, p 439
Fritz P, Frape SK (1982) Saline groundwaters in the Canadian shield—a first overview. Chem Geol 36:179–190
Fritz P, Lodemann M (1990) Die salinaren Tiefenwässer der KTB-Vorbohrung. Die Geowissenschaften 9:281–285
Frost BR (1979) Mineral equilibria involving mixed volatiles in a C-O-H fluid phase: the stabilities of graphite and siderite. Am J Sci 279:1033–1059
Gascoyne M, Davison CC, Ross JD, Pearson R (1987) Saline groundwaters and brines in plutons in the Canadian Shield. In: Fritz P, Frape SK (eds) Saline water and gases in crystalline rocks. Geol Assoc Can Spec Pap 33:53–68
Giletti BJ (1986) Diffusion effects on oxygen isotope temperatures of slowly cooled igneous and metamorphic rocks. Earth Planet Sci Lett 77:218–228
Giletti BJ, Anderson TF (1975) Studies in diffusion—II: oxygen in phlogopite mica. Earth Planet Sci Lett 28:225–233
Giletti BJ, Yund RA (1984) Oxygen diffusion in quartz. J Geophys Res 89:4039–4046
Giletti BJ, Semet MP, Yund RA (1978) Studies in diffusion—III: oxygen in feldspars: an ion microprobe determination. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 42:45–57
Graham CM (1983) Experimental hydrogen isotope studies, III: diffusion of hydrogen in hydrous minerals, and stable isotope exchange in metamorphic rocks. Contrib Mineral Petrol 76:216–228
Graham CM, Sheppard SMF (1980) Experimental hydrogen isotope study II: fractionation in the system epidote-NaCl-H2O, epidote-CaCl2-H2O and epidote-seawater, and the hydrogen isotope composition of natural epidotes. Earth Planet Sci Lett 49:237–251
Graham CM, Harmon RS, Sheppard SMF (1984) Experimental hydrogen isotope studies: hydrogen isotope exchange between amphibole and water. Am Mineral 69:128–138
Graham CM, Viglano JA, Harmon RS (1987) An experimental study of hydrogen isotope exchange between aluminous chlorite and water, and of hydrogen diffusion in chlorite. Am Mineral 72:566–579
Grimmeisen W, Hoernes S (1990) Syn-and postmetamorphe Fluid-Gesteins-Wechselwirkungen. In: Emmermann R, Giese P (eds) KTB Report 90-4, NLfB, Hannover, p 581
Guha J, Kanwar R (1987) Vug brines—fluid inclusions: a key to the understanding of secondary gold enrichment processes and the evolution of deep brines in the Canadian Shield. In: Fritz P, Frape SK (eds) Saline water and gases in crystalline rocks. Geol Assoc Can Spec Pap 33:95–102
Hoefs J (1987) Stable isotope geochemistry, 3rd. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Jenkin GRT, Fallick AE, Leake BE (1992) A stable isotope study of retrograde alteration in SW Connemara, Ireland. Contrib Mineral Petrol 110:269–288
Jöreskog KG, Klovan JE, Reyment RA (1976) Geological factor analysis: methods in geomathematics 1. Elsevier Scientific Publishing Company, Amsterdam
Kamineni DC (1987) Halogen-bearing minerals in plutonic rocks: a possible source of chlorine in saline groundwater in the Canadian Shield. In: Fritz P, Frape SK (eds) Saline water and gases in crystalline rocks. Geol Assoc Can Spec Pap 33:69–79
Karlsson HR, Clayton RN (1990) Oxygen isotope fractionation between analcime and water: an experimental study. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 54:1359–1368
Kelly WC, Rye RO, Livnat A (1986) Saline minewaters of the Keweenaw Peninsula, northern Michigan; their nature, origin and relation to similar deep waters in Precambrian crystalline rocks of the Canadian Shield. Am J Sci 286:281–308
Ligang Z, Jingxiu L, Huanbo Z, Zhensheng C (1989) Oxygen isotope fractionation in the quartz-water-salt system. Econ Geol 84:1643–1650
Nordstrom DK, Olsson T (1987) Fluid inclusions as a source of dissolved salts in deep granitic groundwaters. In: Fritz P, Frape SK (eds) Saline water and gases in crystalline rocks. Geol Assoc Can Spec Pap 33:111–119
O'Brien PJ (1991) High pressure metamorphism in the NW Bohemian Massif: comparisons and contrasts between the Moldanubian, Münchberg Massif, ZEV, ZTT and Erzgebirge. In: Emmermann R, Lauterjung J (eds) KTB Report 91-1, NLfB, Hannover, pp 1–12
O'Brien PJ, Röhr C, Okrusch M, Patzak M (1992) Eclogite facies relics and a multistage breakdown in metabasites of the KTB pilot hole, NE Bavaria: implications for the Variscan tectonometamorphic evolution of the NW Bohemian Massif. Contrib Mineral Petrol 112:261–278
O'Neil JR, Taylor HP (1967) The oxygen isotope and cation exchange chemistry of feldspars. Am Mineral 52:1414–1437
O'Neil JR, Truesdell AH (1991) Oxygen isotope fractionation studies of solute-water interactions. In: Taylor HP, O'Neil JR, Kaplan IR (eds) Stable isotope geochemistry: a tribute to Samuel Epstein. Geochem Soc Spec Publ 3, pp 17–25
O'Neil JR, Clayton RN, Maycda TK (1969) Oxygen isotope fractionation in divalent metal carbonates. J Chem Phys 51:5547–5558
Patzak M, Okrusch M, Röhr Ch (1991) Die Metabasite der KTB-Vorbohrung: Petrographie, Geochemie, Mineralchemie und Metamorphoseentwicklung. In: Emmermann R, Lauterjung J (eds) KTB Report 91-1. NLfB, Hannover, pp 63–81
Reinhardt J, Kleeman U, Blümel P, Schreyer W (1989) Geothermobarometry of metapelites as a key to the pressure and temperature history of the ZEV, NE Bavaria. In: Emmermann R, Giese P (eds) KTB Report 89-3, NLfB, Hannover, pp 24–32
Reutel C (1992) Krustenfluide in Gesteinen und Lagerstätten am Westrand der Böhmischen Masse. Göttinger Arb Geol Paläontol 53
Reutel C, Skrotzki W, Vollbrecht A (1989) TEM and RMP studies of graphites of the pilot borebole and the associated field. In: Emmermann R, Giese P (eds) KTB Report 89-3, NLfB, Hannover, p 445
Richet P, Bottinga Y, Javoy M (1977) A review of hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, oxygen, sulphur, and chlorine stable isotope fractionation among gaseous molecules. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 5:65–110
Richter R, Hoernes S (1988) The application of the increment method in comparison with experimentally derived and calculated O-isotope fractionations. Chem Erde 48:1–18
Scheele N, Hoefs J (1992) Carbon isotope fractionation between calcite, graphite and CO2: an experimental study. Contrib Mineral Petrol 112:35–45
Weber K, Vollbrecht A (1989) The crustal structure at the KTB drilling site, Oberpfalz. In: Emmermann R, Wohlenberg J (eds) The German continental deep drilling program (KTB)—exploration of the deep continental crust. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 5–36
Wimmenaueu W (1991) Geochemie der metamorphen Sedimentgesteine in der Kontinentalen Tiefbohrung und ihrem Umfeld. In: Emmermann R, Lauterjung J (eds) KTB Report 91-1, NLfB, Hannover, pp 106–135
Zulauf G (1991) Zur spät-bis postvariszischen Krustenentwicklung in der nördlichen Oberpfalz. In: Emmermann R, Lauterjung J (eds) KTB Report 91-1, NLfB, Hannover, pp 41–62
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simon, K., Hoefs, J. O, H, C isotope study of rocks from the KTB pilot hole: crustal profile and constraints on fluid evolution. Contr. Mineral. and Petrol. 114, 42–52 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307864
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307864