Summary
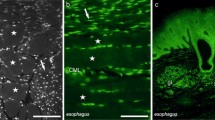
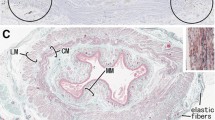
The anatomy and intrinsic innervation of the colon, rectum, internal anal sphincter, ano-coccygeus and recto-coccygeus have been studied in the cat with cholinesterase and catecholamine-fluorescence histochemical techniques. A variable pattern of intrinsic innervation by acetylcholinesterase-positive and adrenergic nerves along the length of the large bowel is described and is related to segmental variations in motor activity. A variation in the distribution of non-specific cholinesterase within the muscle layers is also described. Adrenergic nerves in proximal colon are arranged in the usual peri-ganglionic manner but there is also a rich direct adrenergic innervation of the longitudinal muscle in distal colon and rectum, and of circular muscle in lower rectum and internal anal sphincter. This distribution has not been reported in other species. Direct adrenergic innervation of muscle cells has been confirmed at ultrastructural level after treatment with 5-hydroxydopamine. Adrenergic neurones have not been detected in cat bowel. The ano- and recto-coccygeus muscles and internal anal sphincter possess a dense innervation of adrenergic and cholinesterase-positive nerves. It is suggested that the variation in intrinsic innervation along the large bowel should be considered in the interpretation of pharmacological and physiological experiments on this part of the gut.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åberg, G., Eränkö, O.: Localization of noradrenaline and acetylcholinesterase in the taenia of the guinea pig caecum. Acta physiol. scand. 69, 383–384 (1967).
Bayliss, W. M., Starling, E. H.: The movements and the innervation of the large intestine. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 26, 107–118 (1900).
Bishop, B., Garry, R. C., Roberts, T. D., Todd, J. K.: Control of the external sphincter of the anus in the cat. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 134, 229–240 (1956).
Boyd, G., Gillespie, J. S., Mackenna, B. R.: Origin of the cholinergic response of the rabbit intestine to stimulation of its extrinsic sympathetic nerves after exposure to sympathetic blocking agents. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 19, 258–270 (1962).
Cannon, W. B.: The movements of the intestines studied by means of the Röntgen rays. Amer. J. Physiol. 6, 251–277 (1901–1902).
Day, M. D., Rand, M. J.: Effect of guanethidine in revealing cholinergic sympathetic fibres. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 17, 245–260 (1961).
Elfvin, L. G.: The ultrastructure of the superior cervical sympathetic ganglion of the cat. II. The structure of the preganglionic end fibers and the synapses as studied by serial sections. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 8, 441–476 (1963).
Elliot, T. R., Barclay-Smith, E.: Antiperistalsis and other muscular activities of the colon. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 31, 272–304 (1904).
Eränkö, O.: The practical histochemical demonstration of catecholamines by formaldehyde-induced fluorescence. J. roy. micr. Soc. 87, 259–276 (1967).
Falck, B., Owman, C.: A detailed methodological description of the fluorescence method for the cellular demonstration of biogenic monoamines. Acta Univ. Lund. 11 No 7 (1965).
Fink, S., Friedman, G.: The differential effect of drugs on the proximal and distal colon. Amer. J. Med. 28, 534–540 (1960).
Furness, J. B.: The origin and distribution of adrenergic nerve fibres in the guinea pig colon. Histochemie 21, 295–306 (1969).
Furness, J. B., Costa, M.: Morphology and distribution of intrinsic adrenergic neurones in the proximal colon of the guinea-pig. Z. Zellforsch. 120, 346–363 (1971).
Gabella, G.: Glial cells in the myenteric plexus. Z. Naturforsch. 26, 244–245 (1971).
Gabella, G.: Fine structure of the myenteric plexus in the guinea-pig ileum. J. Anat. (Lond.) 111, 69–97 (1972).
Gabella, G., Costa, M.: Le fibre adrenergiche nel canale alimentare. G. Accad. Med. Torino 130, 1–12 (1968).
Garrett, J. R., Howard, E. R.: Effects of rectal distension on the internal anal sphincter of cats. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 222, 85–86P (1972).
Garrett, J. R., Howard, E. R., Nixon, H. H.: Autonomic nerves in rectum and colon in Hirschsprung's disease. Arch. Dis. Childh. 44, 406–417 (1969).
Garry, R. C., Gillespie, J. S.: The responses of the musculature of the colon of the rabbit to stimulation in vitro, of the parasympathetic and of the sympathetic outflows. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 128, 557–576 (1955).
Gillespie, J. S., Mackenna, B. R.: The inhibitory action of the sympathetic nerves on the smooth muscle of the rabbit gut—its reversal by reserpine and restoration by catecholamines and by Dopa. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 156, 17–34 (1961).
Gillespie, J. S., Maxwell, J. D.: Adrenergic innervation of sphincteric and non-sphincteric smooth muscle in the rat intestine. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 19, 676–681 (1971).
Gomori, G.: Microscopic histochemistry. Chicago: Chicago University Press 1952.
Henderson, J. R.: The use of silver for intensifying sulfide deposits in the cholinesterase technique. Stain Technol. 42, 101–102 (1967).
Hollinshead, W. H.: Embryology and surgical anatomy of the colon. Dis. Colon Rect. 5, 23–27 (1926).
Howard, E. R., Garrett, J. R.: Electron microscopy of myenteric nerves in Hirschsprung's disease and in normal bowel. Gut II, 1007–1014 (1970).
Hultén, L.: Extrinsic nervous control of colonic motility and blood flow. Acta physiol. scand., Suppl. 335 (1969).
Hunter, R. H.: A note on the development of the ascending colon. J. Anat. (Lond.) 62, 297–300 (1928).
Jacobowitz, D.: Histochemical studies of the autonomic innervation of the gut. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 149, 358–364 (1965).
Kamijo, K., Hiatt, R. B., Koelle, G. B.: Congenital megacolon. A comparison of the spastic and hypertrophied segments with respect to cholinesterase activities and sensitivities to acetyl choline, D. F. P. and the barium ion. Gastroenterology 24, 173–185 (1953).
Langley, J. N., Anderson, H. K.: On the innervation of the pelvic and adjoining viscera. Part I. The lower portion of the intestine. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 18, 67–105 (1895).
Langley, J. N., Anderson, H. K.: The innervation of the pelvic and adjoining viscera. Part VII. Anatomical observations. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 20, 372–406 (1896).
Lannon, J., Weller, E. J.: Parasympathetic supply of the distal colon. Brit. J. Surg. 34, 373–378 (1947).
M'Fadden, G. D. F., Loughridge, J. S., Milroy, T. H.: The nerve control of the distal colon. Quart. J. exp. Physiol. 25, 315–327 (1935).
McKirdy, H. C., Jones, J. V., Ballard, K. J.: Cholinesterase histochemistry of the rabbit distal colon. Histochemie 29, 287–295 (1972).
Norberg, K. A.: Adrenergic innervation of the intestinal wall studied by fluorescence microscopy. Int. J. Neuropharmacol. 3, 379–382 (1964).
Reynolds, E. S.: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol. 17, 208–212 (1963).
Rodríguez, E. M.: Fixation of the central nervous system by perfusion of the cerebral ventricules with a threefold aldehyde mixture. Brain Res. 15, 395–412 (1970).
Schofield, G. C.: Anatomy of muscular and neural tissues in the alimentary canal. In: Handbook of physiology, sect. 6, vol. 4., p. 1579–1627. Ed. C. F. Code. Washington (1968).
Tranzer, J. P., Thoenen, H.: Electronmicroscopic localization of 5-hydroxydopamine (3, 4, 5-trihydroxy-phenyl-ethylamine), a new “false” sympathetic transmitter. Experientia (Basel) 23, 743 (1967).
Trumble, H. C.: The plan of visceral nerves in the lumbar and sacral outflows of the autonomic nervous system. Brit. J. Surg. 21, 664–676 (1933–1934).
Wright, R. D., Florey, H. W., Jennings, M. A.: The secretion of the colon of the cat. (A) The effects of nerve stimulation and certain drugs. (B) An investigation of the enzymes of the juice. Quart. J. exp. Physiol. 28, 207–229 (1938).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by a grant from the King's College Hospital Voluntary Research Trust. We wish to thank Dr. J. P. Tranzer and F. Hoffman-La Roche & Co. Ltd., Basle, for the gift of 5-hydroxydopamine.
We also thank Miss M. K. Egan and Mr. K. J. Davies for their technical assistance.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Howard, E.R., Garrett, J.R. The intrinsic myenteric innervation of the hind-gut and accessory muscles of defaecation in the cat. Z.Zellforsch 136, 31–44 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307678
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307678