Summary
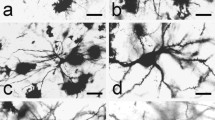
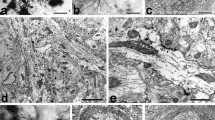
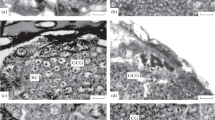
Complete neurones were impregnated in the brain of the pulmonate gastropod pond snail, Lymnaea stagnalis L. using the Golgi-Cox method. Mapping of small to medium sized neurones identified in living preparations by the position of the perikarya was possible. Simple monopolar and bifurcating monopolar neurones with varying lateral patterns of short fine fibres were common in the pond snail brain. Larger neurones have more complex and numerous branches originating from axons close to the perikarya than smaller ones. Stem processes originating on the cell body were observed on neurones above 30 μ in somal diameter. Possible sites for the location of chemical synapses were suggested. Functional types of neurones were difficult to separate on morphological grounds. Giant or very large neurones are small in number in pond snail ganglia, compared with medium or small neurones.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amoroso, E. C., Baxter, M. I., Chiquoine, A. D., Nisbet, R. H.: The fine structure of neurones and other elements in the giant African land snail Archachatina marginata. Proc. roy. Soc. B 160, 168–180 (1964).
Benjamin, P. R.: On the structure of the pulmonate osphradium. I. Cell types and their organisation. Z. Zellforsch. 117, 485–501 (1971).
Benjamin, P. R., Peat, A.: Myoneural junctions in the connective tissue sheath of a molluscan ganglion. Nature (Lond.) 219, 1371–1372 (1968a).
Benjamin, P. R., Peat, A.: A secretory role of the lipid bodies of molluscan neurons. J. comp. Neurol. 132, 617–630 (1968b).
Benjamin, P. R., Peat, A.: On the structure of the pulmonate osphradium II. Ultrastructure. Z. Zellforsch. 118, 168–189 (1971).
Bullock, T. H., Horridge, G. H.: Structure and function in the nervous systems of invertebrates. p. 81–110. San Francisco: W. H. Freeman 1965.
Coggeshall, R. E.: A light and electron microscope study of the abdominal ganglion of Aplysia californica. J. Neurophysiol. 30, 1267–1287 (1967).
Davis, W. J.: Functional significance of motoneuron size and soma position in swimmeret system of lobster. J. Neurophysiol. 34, 274–288 (1971).
Dowling, J. E., Werblin, F.: Organisation of the retina of the mudpuppy, Necturus maculosus I. Synaptic structure. J. Neurophysiol. 32, 315–338 (1969).
Frazier, W. T., Kandel, E. R., Kupfermann, I., Waziri, R., Coggeshall, R. E.: Morphological and functional properties of identified neurones in the abdominal ganglion of Aplysia californica. J. Neurophysiol. 30, 1288–1251 (1967).
Gerschenfeld, H. M.: Observations on the ultrastructure of synapses in some pulmonate molluscs. Z. Zellforsch. 60, 258–275 (1963).
Gilchrist, J.: Notes on the minute structure of the nervous system of the Mollusca. Linn. J. Zool. 26, 179–186 (1897–1898).
Gorman, A. L. F., Mirolli, M.: Axonal localisation of an excitatory postsynaptic potential in a molluscan neurone. J. exp. Biol. 53, 727–736 (1970).
Haller, B.: Die Intelligenzsphären des Molluskengehirns. Arch. mikr. Anat. 81, 233–322 (1913).
Hanström, B.: Über die sogenannten Intelligenzsphären des Molluskengehirns und die Innervation des Tentakels von Helix. Acta zool. (Stockh.) 6, 184–215 (1925).
Havet, J. L.: L'état moniliforme des neurones chez quelques animaux. Cellule 16, 35–46 (1899).
Henneman, E., Somjen, G., Carpenter, D. O.: Excitability and inhibitibility of motoneurons of different sizes. J. Neurophysiol. 28, 599–620 (1965).
Hughes, G. M., Tauc, L.: The path of the giant cell axons in Aplysia depilans. Nature (Lond.) 191, 404–405 (1961).
Kerkut, G. A.: Biochemical aspects of invertebrate nerve cells. In: Invertebrate nervous systems (ed. C. A. G. Wiersma). Chicago: Chicago University Press 1967.
Kerkut, G. A., French, M. C., Walker, R. J.: The location of axonal pathways of identifiable neurones of Helix aspersa using the dye Procion yellow M-4R. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 32, 681–690 (1970).
Kolb, H.: Organisation of the outer plexiform layer of the primate retina: Electron microscopy of Golgi-impregnated cells. Phil. Trans. B. 258, 261–283 (1970).
Kupfermann, I., Kandel, E. R.: Neuronal controls of a behavioural response mediated by the abdominal ganglion of Aplysia. Science 164, 847–850 (1969).
Lever, J., Kok, M., Meuleman, E. A., Joosse, J.: On the location of Gomori-positive neurosecretory cells in the central ganglia of Limnaea stagnalis. Proc. kon. med. Akad. Wet. C64, 640–647 (1961).
Lewis, E. R., Everhart, T. E., Zeevi, Y.: Studying neural organisation in Aplysia with the scanning electron microscope. Science 165, 1140–1143 (1969).
Pantin, C. F. A.: Notes on microscopical techniques for zoologists. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1964.
Pearson, L.: The corpora pedunculata of Sphinx ligustri L. and other Lepidoptera: an anatomical study. Phil. Trans B 259, 477–516 (1971).
Ramón-Moliner, E.: The Golgi-Cox technique. In: Contemporary research methods in neuroanatomy (ed. W. J. H. Nauta and Ebbesson, S. O. E.), p. 32–55. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1970.
Rosenbluth, J.: The visceral ganglion of Aplysia californica. Z. Zellforsch. 60, 213–236 (1963).
Scheibel, M. E., Scheibel, A. B.: The rapid Golgi method. Indian summer or renaissance? In: Contemporary research methods in neuroanatomy (ed. W. J. H. Nauta and Ebbeson, S. O. E.), p. 1–11. Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: Springer 1970.
Sholl, D. A.: Dendritic organisation in the neurons of the visual and motor cortices of the cat. J. Anat. (Lond.) 87, 387–406 (1953).
Strausfeld, N. J., Blest, A. D.: Golgi studies on insects 1. The optic lobes of Lepidoptera. Phil. Trans. B 258, 81–134 (1970).
Stretton, A. O. W., Kravitz, E. A.: Neuronal geometry: Determination with the technique of intracellular dye injection. Science 162, 132–134 (1968).
Strumwasser, F., Jacklet, J. W., Alvarez, R. B.: A seasonal rhythm in the neuronal extract of behavioural egg-laying in Aplysia. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 29, 197–206 (1969).
Tauc, L.: Physiology of the nervous system. In: Physiology of the Mollusca (ed. K. M. Wilbur and Yonge, C. M.), p. 387–454. New York: Academic Press 1966.
Veratti, E.: Ricerche sul sistema nervoso dei Limax. Mem. 1st. Lombardo 18, 163–179 (1900).
Wendelaar Bonga, S. E.: Ultrastructure and histochemistry of neurosecretory cells and neurohaemal areas in the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis (L.) Z. Zellforsch. 108, 190–224 (1970).
Willows, A. O. D.: Behavioural acts elicited by stimulation of single, identifiable brain cells Science 157, 570–574 (1967).
Willows, A. O. D., Hoyle, G.: Neuronal network triggering a fixed action pattern. Science 166, 1549–1551 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors wish to thank Mr. Colin Atherton for photographic assistance and the U.K. Science Research Council for a grant to P. R. B.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Benjamin, P.R., Ings, C.T. Golgi-Cox studies on the central nervous system of a gastropod mollusc. Z.Zellforsch 128, 564–582 (1972). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00306989
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00306989