Summary
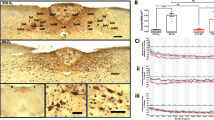
FOS and JUN proteins are transcription factors thought to be involved in coupling neuronal excitation to target gene expression. Cortical infarction of consistent size and location was produced by irradiating the rat brain with Xenon light through the intact skull for 20 min following systemic injection of the photo-sensitizing dye, rose bengal. To investigate the time course and distribution pattern of five cellular ummediate early gene (IEG)-encoded proteins after focal ischemia, the expression of c-FOS, FOS B, c-JUN, JUN B and JUN D was studied immunocytochemically in sham-operated control animals and at different postischemic time intervals up to 24 h. A separate group of animals was pretreated with the non-competitive N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) antagonist MK-801. Photochemically induced focal ischemia caused a rapid induction of FOS and JUN proteins in the entire ipsilateral cortex apart from the ischemic focus. Immunoreactivity in the ipsilateral subcortical gray and white matter and in the entire contralateral hemisphere was indistinguishable from control animals. Individual IEG-encoded proteins were sequentially induced with increased levels of immunoreactivity persisting for different time periods up to 24 h. c-FOS, FOS B, c-JUN and JUN B exhibited a characteristic distribution pattern as reflected by different staining intensities in individual cortical layers. The rapid IEG induction in the entire ipsilateral sensorimotor and limbic structure-associated cortices after photochemically induced infarction most likely reflects spreading depression caused by ischemia and mediated by NMDA receptors. This conclusion is supported by the finding that MK-801 pretreatment completely prevented the postischemic induction of FOS proteins and markedly attenuated the levels of JUN immunoreactivity in all cortical regions except in the peri-infarct area.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartel DP, Sheng M, Lau LF, Greenberg ME (1989) Growth factors and membrane depolarization activate distinct programs of early response gene expression: dissociation of fos and jun induction. Gene Dev 3:304–313
Bravo R (1990) Growth factor responsive genes in fibroblasts. Cell Growth Diff 1:305–309
Bures J, Buresova O, Krivanek J (1974) The mechanism and application of Leao's spreading depression of electroencephalographic activity. Academic Press, New York
Caubet JF (1989) c-fos proto-oncogene expression in the nervous system during mouse development. Mol Cell Biol 9:2269–2272
Chiu R, Angel P, Karin M (1989) JUN-B differs in its biological properties from, and is a negative regulator of, c-JUN. Cell 59:979–986
Cohen DR, Ferreira PCP, Gentz R, Franza BR, Curran T (1989) The product of a fos-related gene, fra-1, binds cooperatively to the AP-1 site with jun: transcription factor AP-1 is comprised of multiple protein complexes. Gene Dev 3:173–184
Dempsey RJ, Carney JM, Kindy MS (1990) Inducible ornithine decarboxylase expression in brain subject to vasogenic edema after transient ischemia: relationship to c-fos gene expression. Acta Neurochir (Wien) [Suppl] 51:189–191
Dietrich WD, Ginsberg MD, Busto R, Watson BD (1986) Photochemically induced cortical infarction in the rat. 1. Time course of hemodynamic consequences. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 6:184–194
Dietrich WD, Ginsberg MD, Busto R, Watson BD (1986) Photochemically induced cortical infarction in the rat. 2. Acute and subacute alterations in local glucose utilization. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 6:195–202
Dietrich WD, Watson BD, Busto R, Ginsberg MD, Bethea JR (1987) Photochemically induced cerebral infarction. I. Early microvascular alterations. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 72:315–325
Dietrich WD, Busto R, Watson BD, Scheinberg P, Ginsberg MD (1987) Photochemically induced cerebral infarction. II. Edema and blood-brain barrier disruption. Acta Neuropathol Berl 72:326–334
Dirnagl U, Tanabe J, Pulsinelli W (1990) Pre- and posttreatment with MK-801 but not pretreatment alone reduces neocortical damage after focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. Brain Res 527:62–68
Dragunow M, Robertson HA (1988) Brain injury induces c-fos protein(s) in nerve and glia-like cells in adult mammalian brain. Brain Res 455:295–299
Dragunow M, Goulding M, Faull RLM, Ralph R, Mee E, Frith R (1990) Induction of c-fos mRNA and protein in neurons and glia after traumatic brain injury: pharmacological characterization. Exp Neurol 107:136–148
Dragunow M, Faull RLM, Lansen KLR (1990) MK-801, an antagonist of NMDA receptors, inhibits injury-induced c-fos protein accumulation in the rat brain. Neurosci Lett 109:128–133
Gass P, Herdegen T, Bravo R, Kiessling M (1992) Induction of immediate early gene encoded proteins in the rat hippocampus after bicuculline-induced seizures: differential expression of KROX-24, FOS and JUN proteins. Neuroscience 48:315–324
Ginsberg MD, Reivich M, Giandomenico A, Greenberg JH (1977) Local glucose utilization in acute focal cerebral ischemia: local dysmetabolism and diaschisis. Neurology 27:1042–1048
Grafstein B (1956) Mechanism of spreading cortical depression. J Neurophysiol 19:154–171
Gubits RM, Hazelton JL, Simantov R (1988) Variations of c-fos gene expression during rat brain development. Mol Brain Res 3:197–202
Gunn AJ, Dragunow M, Faull RLM, Gluckman R (1990) Effects of hypoxia-ischemia and seizures on neuronal and glial-like c-fos protein levels in the infant rat. Brain Res 531:105–116
Hengerer B, Lindholm D, Heumann R, Rüther U, Wagner EF, Thoenen H (1990) Lesion-induced increase in nerve growth factor mRNA is mediated by c-fos. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:3899–3903
Herdegen T, Kovary K, Leah JD, Bravo R (1991) Specific temporal and spatial distribution of JUN, FOS and KROX-24 proteins in spinal neurons following noxious transsynaptic stimulation. J Comp Neurol 313:178–191
Herdegen T, Kummer W, Fiallos CE, Leah JD, Bravo R (1991) Expression of c-JUN, JUN B and JUN D proteins in rat nervous system following transection of vagus nerve and cervical sympathetic trunk. Neuroscience 45:413–422
Hernandez-Caceres J, Macias-Gonzalez R, Brozek G, Bures J (1987) Systemic ketamine blocks cortical spreading depression but does not delay the onset of terminal anoxic depolarization in rats. Brain Res 437:360–364
Herrera DG, Robertson HA (1989) Unilateral induction of c-fos protein in cortex following cortical devascularization. Brain Res 503:205–213
Herrera DG, Robertson HA (1990) Application of potassium chloride to the brain surface induces the c-fos proto-oncogene: reversal by MK-801. Brain Res 510:166–170
Herschman HR (1991) Primary response genes induced by growth factors and tumor promotors. Annu Rev Biochem 60:281–319
Hunt SP, Pini A, Evan G (1987) Induction of c-fos like protein in spinal cord neurons following sensory stimulation. Nature 328:632–634
Jorgensen MB, Johansen FF, Diemer NH (1991) Post-ischemic and kainic acid-induced c-fos protein expression in the rat hippocampus. Acta Neurol Scand 84:352–356
Kiessling M, Herchenhan E, Eggert HR (1990) Cerebrovascular and metabolic effects on the rat brain of focal Nd: YAG laser irradiation. J Neurosurg 73:909–917
Kovary K, Bravo R (1991) Expression of different JUN and FOS proteins during the G0 to G1 transition in mouse fibroblasts: in vitro and in vivo associations. Mol Cell Biol 11:2451–2459
Kovary K, Bravo R (1991) The JUN and FOS protein families are both required for cell cycle progression in fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol 11:4466–4472
Leao AAP (1944) Spreading depression of activity in the cerebral cortex. J Neurophysiol 7:359–390
Marrannes R, Willems R, de Prins E, Wauquier A (1988) Evidence for a role of the N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor in cortical spreading depression. Brain Res 457:226–240
Mies G, Ishimaru S, Xie Y, Seo K, Hossmann KA (1991) Ischemic thresholds of cerebral protein synthesis and energy state following middle cerebral artery occulusion in rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 11:753–761
Morgan JI, Curran T (1991) Stimulus-transcription coupling in the nervous system: involvement of the inducible proto-oncogenes fos and jun. Annu Rev Neurosci 14:421–451
Morgan JI, Curran T (1991) Proto-oncogene transcription factors and epilepsy. TIPS 12:343–349
Morgan JI, Cohen DR, Hempstead JL, Curran T (1987) Mapping patterns of c-FOS expression in the central nervous system after seizure. Science 237:192–196
Nakabeppu Y, Ryder K, Nathans D (1988) DNA binding activities of three different jun proteins: stimulation by Fos. Cell 55:907–915
Naranjo JR, Mellström B, Achaval M, Sassone-Corsi P (1991) Molecular pathways of pain: fos/jun-mediated activation of a noncanonical AP-1 site in the prodynorphin gene. Neuron 6:607–617
Nedergaard M (1988) Mechanisms of brain damage in focal cerebral ischemia. Acta Neurol Scand 77:81–101
Nowak TS Jr (1990) Protein synthesis and the heatshock/stress response after ischemia. Cerebrovasc Brain Metab Rev 2:345–366
Nowak TS Jr, Ikeda J, Nakajima T (1990) 70-kDa heat-shock protein and c-fos gene expression after transient ischemia. Stroke 21:107–111
Ozyurt E, Graham D, Woodruff G, McCulloch J (1988) Protective effect of the glutamate antagonist MK-801 in focal cerebral ischemia in the cat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 8:138–143
Park C, Nehls B, Graham D, Teasdale G, McCulloch J (1988) The glutamate antagonist MK-801 reduces focal ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann Neurol 24:543–551
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, Sydney
Popovici T, Represa A, Crepel V, Barbin G, Beaudoin M, Ben-Ari Y (1990) Effects of kainic acid-induced seizures and ischemia on c-fos-like proteins in the rat brain. Brain Res 536:183–194
Riabowol KT (1988) Microinjection of fos-specific antibodies blocks DNA synthesis in fibroblast cells. Mol Cell Biol 8:1670–1676
Ryseck RP, Bravo R (1991) c-JUN, JUN B, and JUN D differ in their binding affinities to the AP-1 and CRE consensus sequences: effect of FOS proteins. Oncogene 6:533–542
Sagar SM, Sharp FR, Curran T (1988) Expression of c-fos protein in the brain: metabolic mapping at the cellular level. Science 240:1328–1331
Sheng M, Greenberg ME (1990) The regulation and function of c-fos and other immediate early genes in the nervous system. Neuron 4:477–485
Sokoloff L, Reivich M, Kennedy C, Des Rosiers MH, Patlak CS, Pettigrew KD, Sakurada O, Shinohara M (1977) The [14C] deoxyglucose method for the measurement of local cerebral glucose utilization: theory, procedure and normal values in the conscious and anesthetized albino rat. J Neurochem 28:897–916
Sonnenberg JL, Rauscher FJ III, Morgan JI, Curran T (1989) Regulation of proenkephalin by fos and jun. Science 246:1622–1625
Uemura Y, Kowall NW, Moskowitz MA (1991) Focal ischemia in rats causes time-dependent expression of c-fos protein immunoreactivity in widespread regions of ipsilateral cortex. Brain Res 552:99–105
Uemura Y, Kowall NW, Beal MF (1991) Global ischemia induces NMDA receptor-mediated c-fos expression in neurons resistant to injury in gerbil hippocampus. Brain Res 542:343–347
Van Harrefeld A, Kooiman M (1965) Amino acid release from the cerebral cortex during spreading depression and asphyxation. J Neurochem 12:431–439
Van Reempts J, Van Deuren B, Van de Ven M, Cornelissen F, Borgers M (1987) Flunarizine reduces cerebral infarct size after photochemically induced thrombosis in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Stroke 18:1113–1119
Watson BD, Dietrich WD, Busto R, Wachtel M, Ginsberg MD (1985) Induction of reproducible brain infarction by photochemically initiated thrombosis. Ann Neurol 17:497–504
Wisden W, Errington ML, Williams S, Dunnet SB, Waters C, Hitchcock D, Evan G, Bliss TV, Hunt SP (1990) Differential expression of immediate early genes in the hippocampus and spinal cord. Neuron 4:603–614
Zerial M, Toschi L, Ryseck RP, Schuermann M, Muller R, Bravo R (1989) The product of a novel growth factor activated gene, fos B, interacts with JUN proteins enhancing their DNA binding activity. EMBO J 8:805–813
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gass, P., Spranger, M., Herdegen, T. et al. Induction of FOS and JUN proteins after focal ischemia in the rat: differential effect of the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist MK-801. Acta Neuropathol 84, 545–553 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00304474
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00304474