Summary
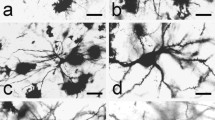
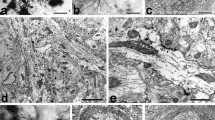
The cellular composition of the primate claustrum was analyzed using serially sectioned Golgi impregnated neurons. The tissue used in this study was embedded in a soft resin mixture and cut with 25 mm long glass knives. The resin embedding allowed the sections to be cut serially at a thickness of only 3 μm. A camera lucida was employed for drawing the cellular processes from selected impregnated neurons; these drawings were later incorporated into a single composite picture of the neuron. Three types of neurons were observed in the primate claustrum. The largest of these neurons (Type I) had a cell body and spine-laden dendritic arborization that varied in size and shape according to the neuron's position in the claustrum. The axons of Type I neurons were successfully impregnated in 25-day-old animals and were found to form collaterals within the claustrum. The collaterals from the axons of these cells appeared to leave the claustrum through both the external and extreme capsules. A second neuron found in the claustrum (Type II) had a round cell body with smooth beaded dendrites which radiated in all directions. The axon of the Type II neuron appeared to give off numerous collaterals that were not observed to leave the claustrum. A third type of neuron (Type III) had a small pear shaped cell body and a sparse dendritic tree. The axon and its collaterals appeared to remain within the dendritic circumference of the Type III neuron.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brodmann K (1925) Vergleichende Lokalisationslehre der Großhirnrinde. Verlag JA Barth, Leipzig.
Carey G, Fitzpatrick D, Diamond IT (1979) Layer I of striate cortex of Tupaia glis and Galago senegalensis: Projections from thalamus and claustrum revealed by retrograde transport of horseradish peroxidase. J Comp Neurol 186:393–438
Carman JB, Cowan WM, Powell TPS (1963) The organization of corticostriate connexions in the rabbit. Brain 86:525–562
Caviness VS Jr, Yorke CH Jr (1976) Interhemispheric neocortical connections of the corpus callosum in the reeler mutant mouse: A study based on anterograde and retrograde methods. J Comp Neurol 170:449–460
Devor M, Caviness VS Jr, Derer P (1975) A normally laminated afferent projection to an abnormally laminated cortex: Some olfactory connections in the reeler mouse. J Comp Neurol 164:471–482
Druga R (1966a) The claustrum of the cat (Felis domestica). Folia Morphol (Praha) 14:7–16
Druga R (1966b) Cortico-claustral connections. I. Fronto-claustral connections. Folia Morphol (Praha) 14:391–399
Druga R (1971) Projection of prepyriform cortex into claustrum (an experimental study using Nauta's method). Folia Morphol (Praha) 20:163–165
Druga R (1974) The claustrum and the transitional neo-paleocortical area of the hedgehog (Erinaceus europaeus). Anat Anz Bd 135:442–454
Filimonoff IN (1966) The claustrum, its origin and development. J Hirnforsch 8:503–528
Flindt-Egebak P, Olsen RB (1979) Some efferent connections of the feline claustrum. Neuroscience Letters Suppl 1, 159:159
Irvine DRF, Brugge JF (1980) Afferent and efferent connections between the claustrum and parietal association cortex in cat: A horseradish peroxidase and autoradiographic study. Neuroscience Letters 20:5–10
Kieveit J, Kuypers HGJM (1975) Subcortical afferents to the frontal lobe in the Rhesus monkey studied by means of retrograde horseradish peroxidase transport. Brain Res 85:261–266
Landau E (1923) Zur Kenntnis der Beziehung des Claustrums zum Nucleus Amygdalae und zur Area piriformis im speziellum zum Tractus olfactorius. Schweiz Arch f Neur u Psychiat, 13:391–404
LeVay S, Sherk H (1980) Visual area in the cat claustrom. 2. Structure, receptive fields and outputs. Soc Neurosci Abstr Vol 6, p 482
Loo IT (1931) The forebrain of the opossum, Didelphis virginiana. J Comp Neurol 52:1–148
Mannen H (1966) Contribution to the quantitative study of nervous tissue. A new method for measurement of the volume and surface area of neurons. J Comp Neurol 126:75–90
Mannen H (1975) Reconstruction of axonal trojectory of individual neurons in the spinal cord using Golgi-stained serial sections. J Comp Neurol 159:357–374
Meynert Th (1872) a) Vom Gehirne des Säugetiere. In: Stricker S (ed) Handbuch der Lehre von den Geweben des Menschen und der Tiere, Bd I, (1871), Bd II; W Engelmann, Leipzig
Narkiewicz O (1964) Degenerations in the claustrum after regional neocortical ablations in the cat. J Comp Neurol 123:335–356
Narkiewicz O (1972) Fronto-claustral interrelations in cats and dogs. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Warsaw) 32:141–150
Norita M, Hirata Y (1976) Some electron microscope findings of the claustrum of the cat. Arch Histol Jpn 39:33–49
Norita M (1977) Demonstration of bilateral claustro-cortical connections in the cat with the method of retrograde horseradish peroxidase. Arch Histol Jpn 40:1–10
Peters A, Fairén A (1978) Smooth and sparsely spined stellate cells in the visual cortex of the rat: A study using a combined Golgi-electron microscope technique. J Comp Neurol 181:129–172
Pilleri G (1961) Zur Struktur des Claustrum bei Didelphis marsupialis (Linné). Acta Anat 45:310–314
Rae AS (1954) The form and structure of the human claustrum. J Comp Neurol 100:15–40
Rakic P (1972) Extrinsic cytological determinations of basket and stellate cell dendritic pattern in the cerebellar molecular layer. J Comp Neurol 146:335–354
Riche D, Lanoir J (1978) Some claustro-cortical connections in the cat and baboon as studied by retrograde horseradish peroxidase transport. J Comp Neurol 177:435–444
Roberts TS, Akert K (1963) Insular and opercular cortex and its thalamic projection in Macaca mulatta. Schweizer Archiv für Neurologie, Neurochirurgie und Psychiatrie, Band 92:1–43
Romeis B (1968) Mikroskopische Technik. R Oldenbourg, München-Wien
Squatritio S, Battaglini PP, Galletti C, Riva Sanseverino E (1980a) Autoradiographic evidence for projections from cortical visual areas 17, 18, 19 and the Clare-Bishop area to the ipsilateral claustrum in the cat. Neuroscience Letters 19:265–270
Squatritio S, Battaglini PP, Galletti C, Riva Sanseverino E (1980b) Projections from the visual cortex to the contralateral claustrum of the cat revealed by an anterograde axonal transport method. Neuroscience Letters 19:271–275
Szentágothai J (1978) The neuron network of the cerebral cortex: A functional interpretation. Proc R Soc Lond B 201:219–248
Valverde F (1970) The Golgi method. A tool for comparative structural analysis. In: Nauta WJH, Ebbesson SOE (eds) Contemporary research methods in neuroanatomy. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg-New York, 12–31
Vaughn JE, Sims TJ (1978) Axonal growth cones and developing axonal collaterals form synaptic junctions in embryonic mouse spinal cord. J Neurocytol 7:337–363
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This project was supported by N.I.H. grant NS 16905 to S. Brand.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brand, S. A serial section Golgi analysis of the primate claustrum. Anat Embryol 162, 475–488 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00301872
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00301872