Summary
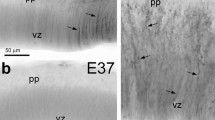
Postnatal development of radial glial cells was examined in albino rats. Until the 10th postnatal day radial glial cells were seen in the lateral ventricles, in the third ventricle (throughout its whole extent), in the aqueduct and in the fourth ventricle. The morphological appearance of radial glial cells was very variable in the different regions.
After the 10th day radial glial cells (tanycytes) were seen only in the wall of the third ventricle. According to their appearance it was possible to undertake a morphological grouping. Considerable changes of the morphology of individual tanycytes could be observed in the median eminence and in the ventral hypothalamus between the 5th and 21st days.
It was found that the peripheral processes of tanycytes ended near the nerve cells or on the cell body, on capillaries of the hypothalamic nuclei or on the pial surface. In a number of cases one tanycyte process contacted both the blood vessels of the hypothalamus and the pial surface.
In view of their morphology the tanycytes can be assumed to transport material between different extracellular spaces, and/or to excrete material.
The radial glial cells of the lateral ventricles can serve as guides for the postnatally formed microneurons and later can either transform to astroglia or degenerate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akmayev IG, Popov AP (1977) Morphological aspects of the hypothalamic-hypophyseal system. VII. The tanycytes: Their relation to the hypophyseal adrenocorticotrophic function. An ultrastructural study. Cell Tissue Res 180:263–282
Altman J, Bayer SA (1978) Development of the diencephalon in the rat. III. Ontogeny of the specialized ventricular linings of the hypothalamic third ventricle. J Comp Neurol 182:995–1016
Bleier RH (1970) Ependymal-neuronal relationships in the hypothalamus. Anat Rec 166:279
Bleier RH (1971) The relations of ependyma to neurons and capillaries in the hypothalamus: A GolgiCox study. J Comp Neurol 142:439–464
Card JP, Rafols JA (1978) Tanycytes of the third ventricle of the neonatal rat: Golgi study. Am J Anat 151:173–190
Colmant HJ (1967) Über die Wandstruktur des dritten Ventrikels des Albinoratte. Histochemie 11:40–61
Fleischhauer K (1957) Untersuchungen am Ependym des Zwischen- und Mittelhirns der Landschildkröte (Tetsudo gracea). Z Zellforsch 46:729–767
Fleischhauer K (1961) Regional differences in the structure of the ependyma and subependymal layers of the cerebral ventricles of the cat. In: SS Kety and J Elkes (eds) Regional Neurochemistry, Pergamon, London
Fleischhauer K (1972) Ependyma and Subependymal layer. In: GH Bourne (Ed) The structure and function of Nervous Tissue. Vol VI: 1–43
Gotow T, Hashimoto P (1979) Fine structure of the ependyma and intercellular junctions in the area postrema of the rat. Cell Tissue Res. 201:207–225
Horstmann E (1954) Die Faserglia des Selachiergehirns. Z Zellforsch 39:588–617
Knowles F (1972) Ependyme of the third ventricle in relation to pituitary function. In: Ariéns F Kappers and JP Schade (Eds) Topics in Neuroendocrinology, Progr Brain Res, Elsevier, Amsterdam Vol 38, pp 255–270
Leveque TF, Hofkin GA (1961) Demonstration of an alcohol-chloroform insoluble periodic acid — Schiff reactive substance in the hypothalamus of the rat. Z Zellforsch 53:185–191
Léranth CS, Schiebler TH (1974) Über die Aufnahme von Peroxidase aus dem 3. Ventrikel der Ratte. Brain Res 67:1–11
Luppa H, Feustel G (1971) Location and characterization of hydrolytic enzymes ofthe IIIrd Ventricle lining in the region of the recessus infundibularis of the rat. A study of the function of the ependyma. Brain Res 29:253–270
Luppa M, Feustel G, Weiss F, Luppa D (1975) Localization of ATPase activity in IIIrd Ventricle ependyma of the rat. A contribution to the function of ependyma. Brain Res 83:15–26
Masai H (1951) Receptor in Hypothalamus. Med J of Osaka University Vol 2: No 2
Millhouse OE (1971) A Golgi study of third ventricle tanycytes in the adult rodent brain. Z Zellforsch 121:1–13
Millhouse OE (1972) Light and electron microscopic studies of the ventricular wall. Z Zellforsch 127:149–174
Monroe BG, Paull WK (1974) Ultrastructural changes in the hypothalamus during development and hypothalamic activity; the median eminence. Prog Brain Res 41:185–208
Oksche A (1958) Histologische Untersuchungen über die Bedeutung des Ependyms, der Glia und der Plexus chorioidei für den Kohlenhydratstoffwechsel des ZNS. Z Zellforsch 48:74–129
Paul E (1967) Über die Typen der Ependymzellen und ihre regionale Verteilung bei Rana temporaria L. Z Zellforsch 80:461–487
Paul E (1968) Histochemische Studien an den Plexus choriodei, an der Paraphyse und am Ependym von Rana temporaria L. Z Zellforsch 91:519–546
Pilgrin Ch (1974) Histochemical differentiation of hypothalamic areas. Prog Brain Res 41:97–110
Ramon y Cajal S (1909) Histologie du Systeme Nerveux de l'Homme et des Vertebres 2:859
Rakic HP (1971) Guidance of neurons migrating to the fetal monkey neocortex. Brain Res 33:471–476
Rakic P (1972) Mode of cell migration to the superficial layers of fetal monkey neocortex. J Comp Neurol 145:61–84
Schachenmayr W (1967) Über die Entwicklung von Ependym und Plexus chorioideus der Ratte. Z Zellforsch 77:25–63
Schmeckel DE, Rakic P (1979) A Golgi study of radial glial cells in developing monkey telencephalon: Morphogenesis and transformation into astrocytes. Anat Embryol 156:115–152
Seress L (1979) Tanycytes and ependymal astrocytes in the wall of the brain ventrical system of developing and adult rats. Acta Anat Nippon 54:166
Sétáló G, Vigh S, Schally V, Arimura A, Flerkó B (1975) LH-RH-containing Neural Elements in the Rat Hypothalamus. Endocrinol 96:135–142
Tennyson VM, Pappas GD (1962) An electron microscope study of ependymal cells of fetal, early postnatal and adult rabbit. Z Zellforsch 56:595–618
Valverde F (1965) Studies on piriform lobe. Harvard Univ Press Cambridge
Walsh RJ, Brawr JR, Peck Sun Lin (1978) Early postnatal development of the ependyma in the third ventricle of male and female rats. Am J Anat 151:377–408
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seress, L. Development and structure of the radial glia in the postnatal rat brain. Anat Embryol 160, 213–226 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00301862
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00301862