Abstract
Pharmacokinetic studies were performed in connection with culture experiments. Using the technique of cultivating whole rat embryos of the early postimplantation stage, we measured the concentration of valproic acid (VPA) and 2-en-VPA in the culture medium (free and protein-bound form) and in embryonic tissue. The following results were obtained:
-
1.
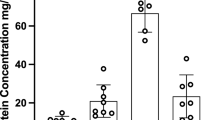
The concentrations of VPA and 2-en-VPA reached in the embryos were lower than corresponding total concentrations added to the culture medium, but exceeded the free concentrations in the medium.
-
2.
The concentrations of 2-en-VPA found in the embryo were lower than the comparable VPA total levels because of the more extensive protein binding of 2-en-VPA in the culture serum.
-
3.
The percentage of binding to serum proteins decreased with increasing total drug concentratrations in the medium; the concentration of the free drug in the medium increased overproportionally with increasing total drug concentrations. Therefore, the free drug concentrations in the medium were not proportional to the dose of the drug dissolved in the medium (for a drug bound to plasma proteins).
-
4.
The concentrations of VPA and 2-en-VPA found in the embryos after incubation in vitro were not proportional to the drug concentrations dissolved in the medium. This result has to be taken into account when dose-response relationships are evaluated.
-
5.
VPA concentrations of 40 μg/g wet weight and above in the embryos clearly induced abnormal development in about 30% of the embryos, while 2-en-VPA concentrations as high as 200 μg/g embryo (wet weight) were inactive. Thus, differences in the embryotoxic potencies — in vivo and in vitro — were not due to pharmacokinetic differences.
-
6.
The results of these investigations show for the first time that pharmacokinetic studies are essential for the interpretation of in vitro experiments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bjerkedal T, Czeizel A, Goujard J, Kallen B, Mastroicacova P, Nevin N, Oakley G, Robert E (1982) Valproic acid and spina bifida. Lancet, ii 1096
Bruckner A, Lee YJ, O'Shea KS, Henneberry RC (1983) Teratogenic effects of valproic acid and diphenylhydantoin on mouse embryos in culture. Teratology 27: 29–42
Cockroft DL (1977) Post implantation embryo culture. In D. Neubert, H.-J. Merker and T. E. Kwasigroch (eds) Methods in prenatal toxicology, Georg Thieme Publ., Stuttgart, pp 231–240
Kao J, Brown NA, Schmid B, Goulding EH, Fabro S (1981) Teratogenicity of valproic acid: in vivo and in vitro investigations. Teratogen Carcinogen Mutagen 1: 367–382
Klug S, Lewandowski C, Neubert D (1985) Modification and standardisation of the culture of early postimplantation embryos for toxicological studies. Arch Toxicol 58: 84–88
Koch A, Jäger-Roman E, Rating D, Helge H (1983) Possible teratogenic effects of valproate during pregnancy. J Pediatr 103: 1007
Lindhout D, Meinardi H (1984) Spina bifida and in utero exposure to valproate. Lancet ii: 396
Löscher W, Nau H, Marescaux C, Vergnes M (1984) Comparative evaluation of anticonvulsant and toxic potencies of valproic acid and 2-en-valproic acid in different animal models of epilepsy. Eur J Pharmacol 99: 211–218
Nau H, Löscher W, Schäfer H (1984) Anticonvulsant activity and embryotoxicity of valproic acid. Neurology 34: 400–401
Nau H, Rating D, Koch S, Häuser I, Helge H (1981a) Valproicacid and its metabolites: placental transfer, neonatal pharmacokinetics, transfer via mother's milk and clinical status in neonates of epileptic mothers. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 219: 768–777
Nau H, Wittfoht W, Schäfer H, Jakobs C, Rating D, Helge H (1981b) Valproic acid and several metabolites: quantitative determination in serum urine, breast milk and tissues by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry using selected ion monitoring. J Chromatogr 226: 69–78
Nau H, Zierer R, Spielmann H, Neubert D, Gansau C (1981c) A new model for embryotoxicity testing: teratogenicity and pharmacokinetics of valproic acid following constant-rate administration in the mouse using human therapeutic drug and metabolite concentrations. Life Sci 29: 2803–2814
New DAT (1978) Whole-embryo-culture and the study of mammalian embryos during organogenesis. Biol Rev 53: 81–122
Robert E, Rosa F (1983) Valproate and birth defects. Lancet ii: 1142
Scott WJ, Nau H (1985) Weak acids as human teratogens: Accumulation in the young mammalian embryo. Teratology 31:25 A
Whittle BA (1976) Pre-clinical, teratological studies on sodium valproate and other anticonvulsants. In: NJ Legg (ed) Clinical and pharmacological aspects of sodium valproate (Epilim) in the treatment of epilepsy, Turnbridge Wells, Kent: MCS Consultants, pp 105–110
Wittfoht W, Duwe K, Kuhnz W, Nau H (1984) Microscale Ultrafiltration technique for determining free drug in 50-μl serum samples. Clin Chem 30: 878
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Data presented in this paper are part of the doctoral theses of Stephan Klug and Constanze Lewandowski to be presented to the Fachbereich Veterinärmedizin, Freie Universität Berlin
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lewandowski, C., Klug, S., Nau, H. et al. Pharmacokinetic aspects of drug effects in vitro: effects of serum protein binding on concentration and teratogenicity of valproic acid and 2-en-valproic acid in whole embryos in culture. Arch Toxicol 58, 239–242 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00297113
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00297113