Abstract
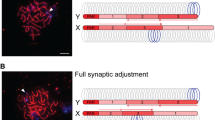
Plethodontid salamanders in the genus Oedipina are characterized by a strongly heteromorphic sex-determining pair of X/Y chromosomes. The telocentric X chromosome and the subtelocentric Y chromosome are clearly distinguished from the autosomes and their behavior during meiosis can be sequentially followed in squash preparations of spermatocytes. In Oedipina the sex chromosomes are not obscured by an opaque “sex vesicle” during early meiotic stages, making it possible to observe details of sex bivalent structure and behavior not directly visible in other vertebrate groups. The sex chromosomes can first be distinguished from autosomal bivalents at the conclusion of zygotene, with X and Y synapsed only along a short segment at their non-centromeric ends, forming a bivalent that contrasts sharply with the completely synapsed autosomes. During pachytene, the XY bivalent becomes progressively shortened and more compact, disappearing as a visible structure when pachytene progresses into the diffuse stage of male meiosis. Diplotene bivalents gradually emerge from the diffuse nuclei, presumably by the return of the loops of chromatin into their respective chromomeres. During early diplotene, the X/Y bivalent is clearly visible with a single chiasma within the synapsed segment. This chiasma is terminalized by first meiotic metaphase with the X and Y appearing either in end-to-end synaptic contact or as univalents separated at opposite poles relative to the equatorially distributed autosomal bivalents. In C-banded preparations, the Y is entirely heterochromatic while the X contains a large centromeric C-band and another block of heterochromatin located at the telomeric end, in the region of synapsis with the Y. We find no cytological evidence of dosage compensation, such as differential staining of the X chromosomes or Barr bodies, in mitotic or interphase cells from female animals.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bull JJ (1983) Evolution of sex determining mechanisms. Benjamin/Cummings, Menlo Park, Calif, USA
Callan HG (1986) Lampbrush chromosomes. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg
Chandley AC, Goetz P, Hargreave TB, Joseph AM, Speed RM (1984) On the nature and extent of XY paring at meiotic prophase in man. Cytogenet Cell Genet 38:241–247
Davidson EH (1976) Gene activity in early development, 2nd edition. Academic Press, New York
Green DM, Bogart JP, Anthony EH (1980) An interactive, microcomputer-based karyotype analysis system for phylogenetic cytotaxonomy. Comput Biol Med 10:219–227
Greenbaum IF, Hale DW, Fuxa KP (1986) The mechanism of autosomal synapsis and the substaging of zygonema and pachynema from deer mouse spermatocytes. Chromosoma 93:203–212
Hale DW, Greenbaum IF (1986) The behavior and morphology of the X and Y chromosomes during prophase I in the Sitka deer mouse. Chromosoma 94:235–242
Kezer J (1970) Observations on salamander spermatocyte chromosomes during the first meiotic division. Dros Inform Serv 45:194–200
Kezer J, Sessions SK (1979) Chromosome variation in the plethodontid salamander, Aneides ferreus. Chromosoma 71:65–80
Kezer J, León P, Sessions SK (1980) Structural differentiation of the meiotic and mitotic chromosomes of the salamander Ambystoma macrodactylum. Chromosoma 81:177–197
Lacroix J-C (1970) Mise en evidence sur les chromosomes in ecouvillion de Pleurodeles poereti Gervais, Amphibien urodele, d'une structure liee au sexe, identifiant le bivalent sexual et marquant le chromosome W. C R Acad Sci 271:102–104
Larson A (1984) Neontological inferences of evolutionary pattern and process in the salamander family Plethodontidae. Evol Biol 17:119–217
León P, Kezer J (1978) Localization of 5S RNA genes on chromosomes of plethodontid salamanders. Chromosoma 65:213–230
Levan A, Fredga K, Sandberg AA (1964) Nomenclature for centromeric position on chromosomes. Hereditas 52:201–220
Meyer BJ, Casson LP (1986) Caenorhabditis elegans compensates for the difference in X chromosome dosage between the sexes by regulating transcript levels. Cell 47:871–881
Muller HJ (1932) Some genetic aspects of sex. Am Nat 66:118–138
Nardi I, Andronica F, DeLucchini S, Batistoni R (1986) Cytogenetics of the European plethodontid salmanders of the genus Hydromantes (Amphibia, Urodela). Chromosoma 96:377–388
Ohno S (1967) Sex chromosomes and sex-linked genes. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, p 192
Ohno S, Kaplan WD, Kinosita R (1958) A photographic representation of mitosis and meiosis in the male of Rattus norvegicus. Cytologia 23:422–428
Pathak S, Lau YF, Drwinga HL (1979) Observations on the synaptonemal complex in Armenian hamster spermatocytes by light microscopy. Chromosoma 73:53–60
Pathak S, Elder FFB, Maxwell BL (1980) Asynaptic behavior of the X and Y chromosomes in the Virginia opossum and the southern pygmy mouse. Cytogenet Cell Genet 26:142–149
Raman R, Nanda I (1986) Mammalian sex chromosomes. 1. Cytogenetic changes in the achiasmatic sex chromosomes of the male musk shrew, Sincus murinus. Chromosoma 93:367–374
Schmid M (1983) Evolution of sex chromosomes and heterogametic systems in Amphibia. Differentiation 23 (Suppl) S13-S22
Schmid M, Olert J, Klett C (1979) Chromosome banding in amphibia. III. Sex chromosomes in Triturus. Chromosoma 71:29–55
Schmid M, Sims SH, Haaf T, Macgregor HC (1986) Chromosome banding in amphibia. VIII. 18S and 28S ribosomal RNA genes, nucleolus organizers and nucleoli in Gastrotheca riobambae. Chromosoma 94:139–145
Schnedl W (1972) End-to-end association of the X and Y chromosomes in mouse meiosis. Nature New Biol 235:29–30
Sessions SK (1982) Cytogenetics of diploid and triploid salamanders of the Ambystoma jeffersonianum complex. Chromosoma 84:599–621
Sessions SK (1984) Cytogenetics and evolution in salamanders. Ph.D. Dissertation, Univ. California, Berkeley
Sessions SK, Kezer (1987) Cytogenetic evolution in the plethodontid salamander genus Aneides. Chromosoma 95:17–30
Sessions SK, Wiley JE (1985) Chromosome evolution in salamanders of the genus Necturus. Brimleyana 10:37–52
Solari AJ, Tres LL (1970) The three-dimensional reconstruction of the XY chromosomal pair in human spermatocytes. J Cell Biol 45:43–53
Urena F, Solari AJ (1970) The three-dimensional reconstruction of the X/Y pair during diplotene in the rat (Rattus norvegicus). Chromosoma 30:258–268
Wake DB, Elias P (1983) New genera and a new species of Central American salamanders, with a review of the tropical genera (Amphibia, Caudata, Plethodontidae). Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County, Contrib Sci 345:1–19
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kezer, J., Sessions, S.K. & León, P. The meiotic structure and behavior of the strongly heteromorphic X/Y sex chromosomes of neotropical plethodontid salamanders of the genus Oedipina . Chromosoma 98, 433–442 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00292789
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00292789