Summary
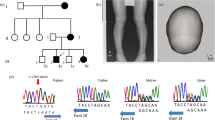
We report a large Italian pedigree in which five out of six males are affected by a syndrome, following an X-linked inheritance pattern, characterized by ichthyosis, hypogonadotropic hypogonadism, and anosmia. The concurrence of features of X-linked ichthyosis (XLI) with those of Kallmann syndrome, another disease often inherited as an X-linked trait, prompted us to perform biochemical, cytogenetic, and molecular studies in relation to the short arm of the X chromosome (Xp). Steroid sulphatase (STS) activity was found to be completely deficient in all affected members of the family. Prometaphase chromosome analyses of two obligate heterozygous women and one affected male showed normal karyotypes. Xg blood group antigen analysis and molecular studies employing cloned DNA sequences from the distal segment of the Xp (probes RC8, 782, dic56, and M1A), did not provide evidence for deletions or rearrangements of the X chromosome. The linkage analysis showed no crossovers between the disease, Xg, and DXS 143, the locus defined by probe dic56, thus suggesting the possibility of a linkage between these two markers of the distal segment of Xp and the X-linked ichthyosis, hypogonadism, and anosmia syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allderdice PW, Aveling JV, Eales BA, Lewis MJ, McAlpine PJ, Ross JB, Simms RJ (1983) Familial t(X:Y)(p223q11) associated with short stature in 4 male and 5 female carriers and with X-linked ichthyosis and anhydrosis in 4 male carriers. Am J Hum Genet 35:124A
Andria G, Ballabio A, Parenti G, Di Maio S, Piccirillo A (1983) Steroid sulphatase deficiency is present in patients with X-linked “ichthyosis and male hypogonadism” and with “Rud syndrome”. Communication at the 21st Annual Symposium of the Society for the Study of Inborn Errors of Metabolism, Lyon, France, September 1983. Edition Fondation Marcel Merieux, Lyon, p 101 (abstr)
Andria G, Ballabio A, Parenti G, Di Maio S, Piccirillo A (1984a) Steroid sulphatase deficiency is present in patients with the syndrome “ichthyosis and male hypogonadism” and with “Rud syndrome”. J Inherited Metab Dis 7 [Suppl 2]:158–160
Andria G, Ballabio A, Parenti G, Di Maio S, Piccirillo A (1984b) Steroid sulphatase deficiency and hypogonadism. Eur J Pediatr 142:304–305
Ballabio A, Parenti G, Napolitano E, Di Natale P, Andria G (1985) Genetic complementation of steroid sulphatase after somatic cell hybridization of X-linked ichthyosis and multiple sulphatase deficiency. Hum Genet 70:315–317
Bergsma D (ed) (1979) Birth defects compendium, 2nd edn, The National Foundation March of Dimes. Liss, New York, p 741
Curry CJR, Magenis RE, Brown M, Lanman JT, Tsai J, O'Lague P, Goodfellow P, Mohandas T, Bergner EA, Shapiro LJ (1984) Inherited chondrodysplasia punctata due to a deletion of the terminal short arm of an X chromosome. N Engl J Med 311:1010–1015
Davies KE, Young BD, Elles RG, Hill ME, Williamson R (1981) Cloning of a representative genomic library of the human X chromosome after sorting by flow cytometry. Nature 293:374–376
Henkin PI, Bartter FC (1966) Studies on olfactory thresholds in normal man and in patients with adrenal cortical insufficiency: the role of adrenal cortical steroids and serum sodium concentration. J Clin Invest 45:1631–1639
Hofker MH, Wapenaar MC, Goor N, Bakker E, van Ommen GJB, Pearson PL (1985) Isolation of probes detecting restriction fragment length polymorphisms from X chromosome specific libraries: potential use for diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Hum Genet 70:148–156
Keats BJB (1981) Linkage and chromosome mapping in man. University Press of Hawaii, Honolulu
Koenig M, Camerino G, Heilig R, Mandel JL (1984) A DNA fragment from the human X chromosome short arm which detects a partially homologous sequence on the Y chromosome long arm. Nucleic Acids Res 12:4097–4109
Lykkesfeldt G, Hoyer H, Lykkesfeldt AE, Skakkebaer NE (1983) Steroid sulphatase deficiency associated with testis cancer. Lancet II:1456
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
McKusick VA (1983) Mendelian inheritance in man, 6th edn. Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
Middlesworth W, Bertelson C, Kunkel LM (1985) An RFLP detecting single-copy X chromosome fragment dic56, from Xp22-Xpter [DXS143]. Nucleic Acids Res 13:5723
Ott J (1974) Estimation of the recombination fraction in human pedigrees: efficient computation of the likelihood for human linkage studies. Am J Hum Genet 26:588–597
Parenti G, Ballabio A, Napolitano E, Di Natale P, Andria G (1985) Hybridization studies of steroid sulphatase on fibroblasts from patients affected by X-linked ichthyosis with and without hypogonadism. Perspect Inherited Metab Dis 6:125–130
Perrin JCS, Idemoto JY, Sotos JF, Maurer WF, Steinberg AG (1976) X-linked syndrome of congenital ichthyosis, hypogonadism, mental retardation and anosmia. Birth Defects 5:267–274
Sanger R, Tippett P, Gavin J (1971) The X-linked blood group system Xg. Tests on unrelated people and families of Northern European ancestry. J Med Genet 8:427–433
Shapiro LJ (1984) Steroid sulfatase deficiency and the genetics of the short arm of the human X chromosome. Adv Hum Genet 14:331–389
Shapiro LJ, Weiss R, Buxman MM, Vidgoff J, Dimond RL, Roller JA, Wells RS (1978) Enzymatic basis of typical X-linked ichthyosis. Lancet II:756–757
Tiepolo L, Zuffardi O, Fraccaro M, Di Natale D, Gargantini L, Muller CR, Ropers HH (1980) Assignment by deletion mapping of the steroid sulfatase X-linked ichthyosis locus to Xp223. Hum Genet 54:205–206
Traupe H, Happle R (1983) Clinical spectrum of steroid sulfatase deficiency: X-linked recessive ichthyosis, birth complication, and cryptorchidism. Eur J Pediatr 140:19–21
Traupe H, Mueller-Migl CR, Kolde G, Happle R, Kovary PM, Hameister H, Ropers HH (1984) Ichthyosis vulgaris with hypogenitalism and hypogonadism: evidence for different genotypes by lipoprotein electrophoresis and steroid sulfatase testing. Clin Genet 25:42–51
Wieringa B, Hustinx Th, Scheres J, Renier W, ter Haar B (1985) Complex glycerol kinase deficiency syndrome explained as X-chromosomal deletion. Clin Genet 27:522–523
Yunis JJ, Chandler ME (1977) High resolution chromosome analysis in clinical medicine. Prog Clin Pathol 7:267–288
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ballabio, A., Parenti, G., Tippett, P. et al. X-linked ichthyosis, due to steroid sulphatase deficiency, associated with Kallmann syndrome (hypogonadotropic hypogonadism and anosmia): linkage relationships with Xg and cloned DNA sequences from the distal short arm of the X chromosome. Hum Genet 72, 237–240 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00291885
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00291885