Summary
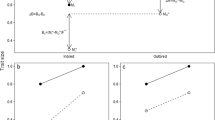
Two types of disruptive selection (HL and LH) were performed on three lines (M, F and K) which had reached different plateaus, following a previous directional selection applied independently on the two sexes. Increase in phenotypic variability and the appearance of a bimodal frequency distribution of wing length measurements were considered as responses to disruptive selection.
These responses are shown not to be linearly related; moreover both responses seem not to be related to the genetic and phenotypic variability present in the population when disruptive selection was started.
These results and the persistent differences between LH and HL selections are interpreted as to suggest that the effects of disruptive selection are mainly dependent on changes in the developmental patterns of the genes involved and of their connections.
The suggestion is advanced that the results presented are inconsistent with the assumption that the effects of disruptive selection be explained by genetic or developmental switch mechanisms or by chromosomal polymorphism.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Alicchio, R., Palenzona, D. L.: Genetic heterogeneity and disruptive selection. Boll. Zool. 40, 223–229 (1973).
Falconer, D. S., Robertson, A.: Selection for environmental variability of body size in mice. Z. indukt. Abstamm.- u.-Vererb.lehre 87, 385–391 (1956).
Mather, K.: Polymorphism as an outcome of disruptive selection. Evolution 9, 52–61 (1955).
Palenzona, D. L., Alicchio, R.: Differential response to selection on the two sexes in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 74, 533–542 (1973a).
Palenzona, D. L., Alicchio, R.: Genetic variability and selection progress. Polymorphism as an outcome of directional selection. I. Sexual dimorphism for wing length. Atti Accad. Sci. Bo. Memorie Ser. III 2, 27–38 (1973b).
Palenzona, D. L., Graziani, M.: Control of phenotypic variability in selected populations of Drosophila melanogaster. Theor. Appl. Genet. 42, 316–318 (1972).
Robertson, A.: A note on disruptive selection experiments in Drosophila. Am. Natur. 106, 561–569 (1970).
Scharloo, W.: Stabilizing and disruptive selection on a mutant character in Drosophila. II. Polymorphism caused by a genetical switch mechanism. Genetics 65, 681–691 (1970a).
Scharloo, W.: Stabilizing and disruptive selection on a mutant character in Drosophila. III. Polymorphism caused by a developmental switch mechanism. Genetics 65, 693–705 (1970b).
Scharloo, W.: Reproductive isolation by disruptive selection: did it occur? Am. Natur. 105, 83–86 (1971).
Thoday, J. M.: Effects of disruptive selection: the experimental production of a polymorphic population. Nature, Lond., 181, 1124–1125 (1958).
Thoday, J. M.: Effects of disruptive selection. I. Genetic flexibility. Heredity 13, 187–203 (1959).
Thoday, J. M.: Effects of disruptive selection. III. Coupling and repulsion. Heredity 14, 35–49 (1960).
Thoday, J. M.: The general importance of disruptive selection. Genet. Res. 9, 119–120 (1967).
Thoday, J. M., Boam, T. B.: Effects of disruptive selection. II. Polymorphism and divergence without isolation. Heredity 13, 205–218 (1959).
Thoday, J. M., Gibson, J. B.: Isolation by disruptive selection. Nature, Lond., 193, 1164–1166 (1962).
Thoday, J. M., Gibson, J. B.: The probability of isolation by disruptive selection. Am. Natur. 104, 219–230 (1970).
Thoday, J. M., Gibson, J. B.: Reply to Scharloo. Am. Natur. 105, 86–88 (1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by W. Seyffert/H. Stubbe
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alicchio, R., Palenzona, L.D. Phenotypic variability and divergence in disruptive selection. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 45, 122–125 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00291141
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00291141