Abstract
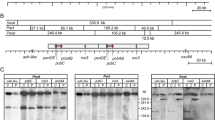
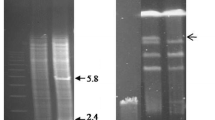
We have placed two different penicillin structural genes from Aspergillus nidulans, ipnA (encoding isopenicillin N synthetase, IPNS) and acyA (encoding acyl-CoA:6-aminopenicillanic acid acyltransferase, AAT), under the control of the strong alcA promoter [alcA(p)]. Single copies of these transcriptional fusions were targeted to the same chromosomal location and conditions have been worked out which simultaneously allow induction of the alcA(p) and support penicillin biosynthesis. Transcriptional induction of the chimeric genes alcA(p)::ipnA or alcA(p)::acyA(cdna) in the relevant recombinant strains results in 10-fold higher levels of the ipnA or acyA transcripts than those resulting from transcription of the corresponding endogenous genes. This increase causes a 40-fold rise in IPNS activity or a 8-fold rise in AAT activity. Despite this rise in enzyme levels, forced expression of the ipnA gene results in only a modest increase in levels of exported penicillin, whereas forced expression of the acyA gene reduces penicillin production, showing that neither of these enzymes is rate-limiting for penicillin biosynthesis in A. nidulans. A genomic version of the alcA(p)::acyA fusion, in which the acyA gene is interrupted by three small introns, is inducible by threonine to a lesser extent (as determined by both acyA mRNA levels and AAT enzyme levels) than the corresponding cDNA version, suggesting that processing of the introns present in the primary transcript may limit acyA expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams TH, Boylan MT, Timberlake WE (1988) brlA is necessary and sufficient to direct conidiophore development in Aspergtillus nidulans. Cell 54:353–362
Alvarez E, Messchaert B, Montenegro E, Gutiérrez S, Diez B, Barredo JL, Martin JF (1993) The isopenicillin-N acyltransferase of Penicillium chrysogenum has isopenicillin-N amidohydrolase, 6-aminopenicillanic acid acyltransferase and penicillin amidase activities, all of which are encoded by the single penDE gene. Eur J Biochem 215:323–332
Arst HN Jr, Bailey CR (1977) The regulation of carbon metabolism in Aspergillus nidulans. In: Smith J, Pateman J (eds) Genetics and physiology of Aspergillus. Academic Press, London, pp 131–146
Bailey CR, Arst HN Jr (1975) Carbon catabolite repression in Aspergillus nidulans. Eur J Biochem 51:573–577
Brakhage AA, Browne P, Turner G (1992) Regulation of Aspergtillus nidulans penicillin biosynthesis and penicillin biosynthesis genes acvA and ipnA by glucose. J Bacteriol 174:3789–3799
Clutterbuck AJ (1974) Aspergillus nidulans. In: King RC (ed) Handbook of genetics, vol 1. Plenum Press, New York, pp 447–510
Dowzer CEA, Kelly JM (1991) Analysis of the creA gene, a regulator of carbon catabolite repression in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Cell Biol 11:5701–5709
Espeso E, Peñalva MA (1992) Carbon catabolite repression can account for the temporal pattern of expression of a penicillin structural gene in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Microbiol 6:1457–1465
Fernández-Cañón JM, Reglero A, Martínez-Blanco H, Luengo JM (1989) Uptake of phenylacetic acid by Penicillium chrysogenum Wis 54–1255: a critical regulatory point in penicillin biosynthesis. J Antibiotics 9:1398–1409
Fraenkel DG (1992) Genetics and intermediary metabolism. Annu Rev Genet 26:159–177
Gómez-Pardo E, Peñalva MA (1990) The upstream region of the ipnA gene determines expression during secondary metabolism in Aspergillus nidulans. Gene 89:109–115
Gurr SJ, Unkles, SE, Kinghorn JR (1987) The structure and organization of nuclear genes of filamentous fungi. In: Kinghorn JR (ed) Gene structure in eukaryotic microbes. IRL Press, Oxford, pp 93–139
Gwynne DI, Buxton FP, Williams SA, Garven S, Davies RW (1987) Genetically engineered secretion of active human interferon and a bacterial endoglucanase from Aspergillus nidulans. Biotechnology 5:713–719
Holt G, Macdonald KD (1968) Penicillin production and its mode of inheritance in Aspergillus nidulans. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 34:409–416
Kell DB, Westerhoff HV (1986) Metabolic control theory: its role in microbiology and biotechnology. FEMS Microbiol Rev 39:305–320
Kulmburg P, Prangé T, Mathieu M, Sequeval D, Scazzocchio C, Felenbok, B (1991) Correct intron splicing generates a new type of putative zinc-binding domain in a transcriptional activator of Aspergillus nidulans. FEBS Lett 280:11–16
Kulmburg P, Judewicz N, Mathieu M, Lenouvel F, Sequeval D, Scazzocchio C, Felenbok B (1992) Specific binding sites for the activator protein, ALCR, in the alcA promoter of the ethanol regulon of Aspergillus nidulans. J Biol Chem 267:21146–21153
Kulmburg P, Mathieu M, Dowzer C, Kelly J, Felenbok B (1993) Specific binding sites in the alcR-alcA promoters of the ethanol regulon for the CREA repressor governing carbon catabolite repression in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Microbiol 7:847–857
Ligget RW, Koffier H (1948) Corn steep liquor in microbiology. Bacteriol Rev 12:297–311
Lockington RA, Sealy-Lewis HM, Scazzocchio C, Davies RW (1985) Cloning and characterisation of the ethanol utilisation regulon in Aspergillus nidulans. Gene 33:137–149
Lockington RA, Scazzocchio C, Sequeval D, Mathieu M, Felenbok B (1987) Regulation of alcR, the positive regulatory gene of the ethanol utilization regulon of Aspergtillus nidulans. Mol Microbiol 1:275–281
Luengo JM, Peñalva, MA (1994) Penicillin biosynthesis. In: Martinelli S, Kinghorn JR (eds) A spergillus: 50 years on. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 603–638
Luengo JM, Iriso JL, López-Nieto MJ (1986) Direct evaluation of phenylacetyl-CoA: 6-aminopenicillanic acid acyltransferase of Penicillium chrysogenum by bioassay. J Antibiotics 39:1565–1573
MacCabe A, Riach M, Unkles S, Kinghorn J (1990) The Aspergtillus nidulans npeA locus consists of three contiguous genes required for penicillin biosynthesis. EMBO J 9:279–287
MacCabe A, van Liempt H, Palissa H, Unkless S, Riach M., Pfeifer E., von Döhren H, Kinghorn J (1991) δ-(L-α-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine synthetase from Aspergillus nidulans. J Biol Chem 256:12646–12654
Marshall MA, Timberlake WE (1991) Aspergillus nidulans wetA activates spore-specific gene expression. Mol Cell Biol 11:55–62
Martín-Villacorta J, Reglero A, Luengo JM (1991) Acyl-CoA: 6-APA acyltransferase from Penicillium chrysogenum. Studies on its hydrolytic activity. J Antibiotics 44:108–110
Mart'inez-Blanco H, Reglero A, Fernández-Valverde M, Ferrero MA, Moreno MA, Peñalva MA, Luengo JM (1992) Isolation and characterization of the acetyl-CoA synthetase from Penicillium chrysogenum. Involvement of this enzyme in the biosynthesis of penicillins. J Biol Chem 267:5474–5481
Merrick MJ, Caten CE (1975) The inheritance of penicillin titre in wild-type isolates of Aspergillus nidulans. J Gen Microbiol 86:283–293
Mirabito PM, Adams TH, Timberlake WE (1989) Interactions of three sequentially expressed genes control temporal and spatial specificity in Aspergillus development. Cell 57:859–868
Montenegro E, Barredo JL, Gutiérrez S, Díez B, Alvarez E, Martín JF (1990) Cloning, characterization of the acyl-CoA:6-amino penicillanic acid acyltransferase gene of Aspergillus nidulans and linkage to the isopenicillin N synthetase gene. Mol Gen Genet 221:322–330
Mullaney EJ, Hamer JE, Roberti KA, Yelton M, Timberlake W (1985) Primary structure of the trpC gene from Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Gen Genet 199:37–45
Müller WH, van der Krift TP, Krouwer AJJ, Wönsten HAB, van der Voort LHM, Smaal EB, Verkleij, AJ (1991) Localization of the pathway of penicillin biosynthesis in Penicillium chrysogenum. EMBO J 10:489–495
Parker R, Siciliano PG, Guthrie C (1987) Recognition of the TACTAAC box during mRNA splicing in yeast involves base pairing to the U2-like snRNA. Cell 49:229–239
Peñalva MA, Vian A, Patiño C, Pérez-Aranda A, Ramón D (1989) Molecular biology of penicillin production in Aspergillus nidulans. In Hershberger CL, Queener SW (eds) Genetics and molecular biology of industrial microorganisms. American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC, pp 256–261
Pérez-Esteban B, Orejas M, Gómez-Pardo E, Peñalva MA (1993) Molecular characterisation of a fungal secondary metabolism promoter: transcription of the Aspergillus nidulans ipnA gene is modulated by upstream negative elements. Mol Microbiol 9:881–895
Peñalva MA, Moya A, Dopazo J, Rambn D (1990) Sequences of isopenicillin N synthetase genes suggest horizontal gene transfer from prokaryotes to eukaryotes. Proc R Soc Lond B 241:164–169
Peñalva MA, Pérez-Esteban B, Gómez-Pardo E., Orejas M, Espeso E (1992) Penicillin production by Aspergillus nidulans: studies on the regulation of expression of the ipnA gene. In: Stahl U, Tudzynski P (eds) Molecular biology of filamentous fungi. VCH, Weinheim, FRG, pp 217–227
Ramón D, Carramolino L, Patiño C, Sánchez F, Peñalva MA (1987) Cloning and characterization of the isopenicillin N synthetase gene mediating the formation of the β-lactam ring in Aspergillus nidulans. Gene 57:171–181
Ramos FR, López-Nieto MJ, Martin JF (1985) Isopenicillin N synthetase of Penicillium chrysogenum, an enzyme which converts δ-(L-α-aminoadipyl)-L-cysteinyl-D-valine to isopenicillin N. Antimicrobial Agents Chemother 27:380–387
Smith DJ, Bull JH, Edwards J, Turner G (1989) Amplification of the isopenicillin N synthetase gene in a strain of Penicillium chrysogenum producing high levels of penicillin. Mol Gen Genet 216:492–497
Timberlake W, Marshall M (1989) Genetic engineering of filamentous fungi. Science 244:1313–1317
Veenstra AE, van Solingen P, Bovenberg RAL, van der Voort LHM (1991) J Biotechnol 17:81–90
Walsh K, Koshland DE Jr (1985) Characterization of rate-controlling steps in vivo by use of an adjustable expression vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:3577–3581
Waring RB, May GS, Morris RN (1989) Characterization of an inducible expression system in Aspergillus nidulans using alcA and tubulin-coding genes. Gene 79:119–130
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by C. A. M. J. J. van den Hondel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernández-Cañón, J.M., Peñalva, M.A. Overexpression of two penicillin structural genes in Aspergillus nidulans . Molec. Gen. Genet. 246, 110–118 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00290139
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00290139