Abstract
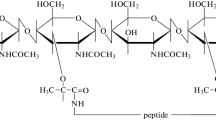
The effect of treatment of Lactobacillus fermentum with several protein- and carbohydrate-modifying reagents on the bacterium's ability to flocculate Saccharomyces cerevisiae was investigated. The proteinaceous nature of the cell-surface components of L. fermentum which are responsible for floc formation was confirmed by inactivation of floc formation following photo-irradiation, with Methylene Blue or Rose Bengal as sensitizer, or acylation with acetic anhydride, maleic anhydride or acetylimidazole, and by the reaction of the components with nitrous acid, I2 and performic acid.
The phenolic hydroxyl group of tyrosine and the indole group of tryptophan appear essential for flocculation. Proteinaceous components of the yeast cell surface and carbohydrate components on the bacterial cell surface were not required for flocculation but carbohydrate residues on the yeast surface were essential.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amorim, H.V. & Oliveira, A.J. 1982 Infecção na fermentação: cono evitá-la. Álcool e Açúcar 5, 12–18.
Firon, N., Ofek, I. & Sharon, N. 1983 Carbohydrate specificity of the surface lectins of Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Salmonella typhimurium. Carbohydrate Research 120, 235–249.
Henriksson, A., Szewzyk, R. & Conway, P.L. 1991 Characteristics of the adhesive determinants of Lactobacillus fermentum 104. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 57, 499–502.
Miki, B.L.A., Poon, N.H., James, A.P. & Seligy, V.L. 1982 Possible mechanism for flocculation interactions governed by gene FLO1 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Journal of Bacteriology 150, 878–889.
Nishihara, H. & Toraya, T. 1987 Essential roles of cell surface protein and carbohydrate components in flocculation of a brewer's yeast. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry 51, 2721–2726.
Nishihara, H., Toraya, T. & Fukui, S. 1977 Effect of chemical modification of cell components of a brewer's yeast on the flocforming ability. Archives of Microbiology 115, 19–23.
Ofek, I. & Beachey, E.H. 1978 Mannose binding and epithelial cell adherence of Escherichia coli. Infection and Immunity 22, 247–254.
Santos, M.T. & Yokoya, F. 1993 Characteristics of yeast cell flocculation by Lactobacillus, fermentum. Journal of Fermentation and Bioengineering 75, 151–154.
Stratford, M. 1992 Yeast flocculation: reconciliation of physiological and genetic viewpoints. Yeast 8, 25–38.
Yokoya, F. & Oliva-Neto, P. 1991 Características da floculação de leveduras por Lactobacillus fermentum. Revista de Microbiologia 22, 12–16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bromberg, R., Yokoya, F. Chemical modifications of the cell-surface components of Lactobacillus fermentum FTPT 1405 and their effect on the flocculation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae . World J Microbiol Biotechnol 11, 508–511 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00286363
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00286363