Abstract
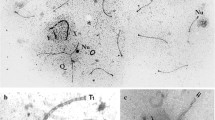
The fate of the synaptonemal complex and its elements after pachytene has been studied by serial sectioning of diplotene nuclei in mouse spermatocytes. The lateral elements of the synaptonemal complex separate from each other during diplotene, and they form single axes, 300 Å wide, surrounded by chromatin fibrils. The single axes are continuous and end on the nuclear membrane by two different ends: the basal knob and the simple end. The single axes do not cross-over each other, but they remain approached at the convergence regions. In these regions a modified piece of synaptonemal complex is found. This piece changes into a chromatin bridge during diplotene. It has been inferred that the convergence regions represent chiasmata and that the single axes do not represent axial structures of chromatids.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, T. G., Franchi, L. L.: The structure of the chromosomes in human primordial oocytes. Chromosoma (Berl.) 22, 358–377 (1967).
Callan, H. G.: The nature of lampbrush chromosomes. Int. Rev. Cytol. 15, 1–34 (1963).
Coleman, J. R., Moses, M. J.: DNA and the fine structure of synaptic chromosomes in the domestic rooster (Gallus domesticus). J. Cell Biol. 23, 63–78 (1964).
Franchi, L. L., Mandl, A. M.: The ultrastructure of oogonia and oocytes in the foetal and neonatal rat. Proc. roy. Soc. Lond. B 157, 99–114 (1962).
Gassner, G.: Synaptinemal complexes in the achiasmatic spermatogenesis of Bolbe nigra Giglio-Tos (Mantoidea). Chromosoma (Berl.) 26, 22–34 (1969).
Meyer, G. F.: Possible correlation between submicroscopic structure of meiotic chromosomes and crossing-over. Third Europ. Conf. on Electron Microscopy B, 461–462 (1964).
Moens, P. B.: The structure and function of the synaptinemal complex in Lilium longiflorum sporocytes. Chromosoma (Berl.) 23, 418–451 (1968).
Moses, M. J.: The relation between the axial complex of meiotic prophase chromosomes and chromosome pairing in a salamander (Plethodon cinereus). J. biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 4, 633–638 (1958).
—, Synaptinemal complex. Ann. Rev. Genet. 2, 363–412 (1968).
- Structure and function of the synaptonemal complex. In: Nuclear physiology and differentiation. Genetics, Suppl. 61, 41–51 (1969).
Roth, T. F.: Changes in the synaptinemal complex during meiotic prophase in mos quito oocytes. Protoplasma (Wien) 61, 346–386 (1966).
—, Parchman, L. G.: Diplotene achiasmatic chromosomes following normal synapsis at pachynema. Proc. 25th Meeting Electron Micr. Soc. (C. J. Arceneaux, ed.), p. 86–87. Baton Rouge, La.: Claitor's 1967.
Sjöstrand, F. J.: Electron microscopy of cells and tissues. I. Instrumentation and and techniques. New York: Academic Press 1967.
Solari, A. J.: The evolution of the ultrastructure of the sex chromosomes (sex vesicle) during meiotic prophase in mouse spermatocytes. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 27, 289–305 (1969a).
Solari, A. J.: Changes in the sex chromosomes during meiotic prophase in mouse spermatocytes. In: Nuclear physiology and differentiation. Genetics, Suppl. 61, 113–120 (1969b).
—, The spatial relationship of the X and Y chromosomes during meiotic prophase in mouse spermatocytes. Chromosoma (Berl.) 29, 217–236 (1970).
Sotelo, R. J., Trujillo-Cenoz, O.: Electron microscopic study on spermatogenesis. Chromosome morphogenesis at the onset of meiosis (cyte I) and nuclear structure of early and late spermatids. Z. Zellforsch. 51, 243–277 (1960).
Tsuda, H.: An electron microscope study on the oogenesis in the mouse, with special reference to the behaviours of oogonia and oocytes at meiotic prophase. Arch. histol. jap. 25, 533–555 (1965).
Wettstein, R., Sotelo, R. J.: Electron microscope serial reconstruction of the spermatocyte I nuclei at pachytene. J. de Microsc. 6, 557–576 (1967).
Woollam, D. H., Ford, D. H.: The fine structure of the mammalian chromosome in meiotic prophase with special reference to the synaptinemal complex. J. Anat. (Lond.) 98, 163–173 (1964).
—, Millen, J.: The attachment of pachytene chromosomes to the nuclear membrane in mammalian spermatocytes. Exp. Cell Res. 42, 657–661 (1966).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Solari, A.J. The behaviour of chromosomal axes during diplotene in mouse spermatocytes. Chromosoma 31, 217–230 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00285149
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00285149