Abstract
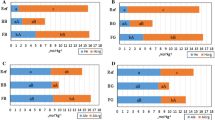
Ion leaching in 3 sandy spruce forest soils of different origin and pH was investigated in the laboratory. Zero-tension lysimeters containing undisturbed soil columns of varying soil depth were subjected to H2SO4 loadings for a period of 9 weeks. The analysis of the resulting leachate supports the hypothesis that Al-sulphate minerals may form in acidic soils when exposed to acid (H2SO4) deposition. In the B horizon of a glaciofluvial sandy soil (pH 4.2), both H+ and sulphate ions were retained to maintain 2pH + PSO4 = 11.9 in the leachate solutions. This relation between H+ and sulphate activity may be due to an adsorption mechanism or a precipitation mechanism. The precipitation mechanism is favored by the good fit of leachate composition to the conditions for jurbanite [AlOHSO4] formation from gibbsite [Al(OH)3]. In the B horizon of a sandy till at pH 3.7, the Al in soil solution (0.5 mmol L−1) was leached with sulphate. As the sulphate load was increased, some sulphate was retained. This may also be due to the dissolution and precipitation of an Al-sulphate mineral. The ion activity products of leachate solutions from the B horizon of this soil were close to the pKs reported for jurbanite. The conditions for the possible existence and/or formation of Al-sulphate minerals in acidic soils are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, F. and Rawajfih, Z.: 1977, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 41, 686.
Arp, P. A. and Quimet, R.: 1986, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 31, 359.
Berdén, M., Nilsson, S. I., Rosen, K., and Tyler, G.: 1987, Soil Acidication—Extent, Causes and Consequences, Report 3292, National Swedish Environmental Protection Board, Solna, Sweden.
Chao, T. T., Harward, M. E., and Fang, S. C.: 1965, Soil Science 99, 104.
Dise, N. and Hauhs, M.: 1987, B. Moldan and T. Paces (eds.), GEOMON, International Workshop on Geochemistry and Monitoring in Representative Basins, Geological Survey, Prague, pp. 58–61.
Erikson, E.: 1981, Nordic Hydrology 12, 43.
Fassbender, H. W. and Matzner, E.: 1977, Mitt. Dtsch. Bodenkdl. Ges. 25, 175.
Falkengren-Grerup, U.: Environ. Pollut. 43, 79.
Freiesleben, N. E. v., Ridder, C., and Rasmussen, L.: 1986, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 30, 135.
Freiesleben, N. E. v.: 1988, J. Environ. Quality 17, 278.
Fuller, R. D., Driscoll, C. T., Lawrence, G. B., and Nodvin, S. C.: 1987, Nature 325, 707.
Griffin, R. A. and Jurinak, J. J.: 1973, Soil Sci. 116, 26.
Hallbäcken, L. and Tamm, C. O.: 1986, J. For. Res. 1, 219.
Johnson, D. W.: 1980, ‘Site Susceptibility to Leaching by H2SO4 in Acid Rainfall’, in T. C. Hutchinson and M. Havas (eds.), Effects of Acid Precipitation on Terrestrial Ecosystems, Plenum Press, New York, pp. 225–235.
Johnson, D. W. and Todd, D. E.: 1983, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 47, 792.
Khanna, P. K., Prenzel, J., Meiwes, K. J., Ulrich, B., and Matzner, E.: 1987, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 51, 446.
Lindsay, W. L.: 1979, Chemical Equilibrium in Soils, Wiley Interscience, New York.
May, H. M., Helmke, P. A., and Jackson, M. L.: 1979, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 43, 861.
Mehra, O. P. and Jackson, M. L.: 1960, ‘Iron Oxide Removal from Soils and Clays by Dithionite-Citrate System Buffered with Sodium Bicarbonate’, Proc. 7th (1958) Natl. Conf. Clays and Clay Minerals, pp. 317–322.
Meiwes, K. J., Ulrich, B., and Khanna, P. K.: 1980, Z. Pflanzenernāhr. Bodenk. 143, 402.
Mulder, J., van Breemen, N., Rasmussen, L., and Driscoll, C. T.: 1988, Advancement in Chemistry (submitted).
Nihlgård, B.: 1986, Handledning for integrated monitoring inom små avrinningsområden/overvakningsområden i Norden, Department of Plant Ecology, University of Lund, Sweden, 25 pp.
Nilsson, S.I. and Bergkvist, B.: 1983, Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 20, 311.
Nodvin, S. C., Driscoll, C. T., and Likens, G. E.: 1986, Soil Science 142, 69.
Nordstrom, D. K.: 1982, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 46, 681.
Prenzel, J.: 1982, Göttinger Bodenkundliche Berichte 72, 1.
Prenzel, J.: 1983, ‘A Mechanism of Storage and Retrieval of Acid in Acid Soils’, in B. Ulrich and Pankrath (eds.), Effects of Air Pollutants on Forest Ecosystems, D. Reidel Publ. Co., Dordrecht, pp. 157–170.
Rajan, S. S. S.: 1978, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 42, 39.
Rasmussen, L., Freiesleben, N. E. V., and Jørgensen, P.: 1988, Geoderma (submitted).
Rost-Siebert, K.: 1983, Allgem. Forstzeitschr. 26/27, 686.
Scheffer, F. and Schachtschabel, P.: 1979, Lehrbuch der Bodenkunde, Ferdinand Enke Verlag, Stuttgart.
Singh, B. R., Abrahamsen, G., and Stuanes, A.: 1980, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 44, 75.
Singh, B. R.: 1984a, Soil Science 138, 294.
Singh, B. R.: 1984b, Soil Science 138, 346.
Singh, S. S. and Brydon, J. E.: 1970, Can. J. Soil Sci. 50, 219.
Sposito, G.: 1984, The Surface Chemistry of Soils, Oxford University Press, New York.
Stumm, W. and Morgan, J. J.: 1981, Aquatic Chemistry, Wiley-Interscience, New York.
Ulrich, B., Mayer, R., and Khanna, P. K.: 1979, ‘Deposition von Luftverunreinigungen und ihre Auswirkung in Waldökosystemen im Sollingen’, Schriften aus der Forstlichen Fakultät der Universität Göttingen und der Niedersächsischen Forstlichen Versuchanstalt, Vol. 58, pp. 1–291.
Ulrich, B. and Matzner, E.: 1983, Abiotische Folgewirkungen der weiträumigen Ausbreitung von Luftverunreinigungen, Forschungsbericht, Vol. 104, 02615 UBA. Berlin.
Ulrich, B., Murach, D., and Pirouzpanah, D.: 1984, Forstarchiv 55, 127.
Ulrich, B.: 1980, ‘Production and Consumption of Hydrogen Ions in the Ecosphere’, in T. C. Hutchinson and M. Havas (eds.), Effects of Acid Precipitation on Terrestrial Ecosystems, Plenum Press, New York, pp. 255–282.
Ulrich, B.: 1984, Atmos. Environ. 18, 621.
Van Breemen, N.: 1973, Soil Sci. Soc. Amer. Proc. 37, 694.
Von Grenzius, R.: 1984, Forew. Cbl. 103, 131
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gundersen, P., Beier, C. Aluminium sulphate solubility in acid forest soils in Denmark. Water Air Soil Pollut 39, 247–261 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00279472
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00279472