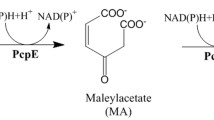
Abstract
The maleylacetate reductase of 3-chlorobenzoate-grown cells of Pseudomonas sp. strain B13 has been purified 50-fold. The enzyme converted 2-chloromaleylacetate to 3-oxoadipate with temporary occurrence of maleylacetate; 1 mol of chloride was eliminated during the conversion of 1 mol of 2-chloro- and 2,3-dichloromaleylacetate; 2 mol of NADH were consumed per mol of 2-chloro- and 2,3-dichloromaleylacetate while only 1 mol was necessary to catalyze the conversion of maleylacetate or 2-methylmaleylacetate. The maleylacetate reductase failed to use fumarylacetate as a substrate. The role of the enzyme in the chloroaromatics degradation is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bollag J-M, Helling CS, Alexander M (1968a) 2,4-d Metabolism. Enzymatic hydroxylation of chlorinated phenols. J Agric Food Chem 16: 826–828
Bollag J-M, Briggs GG, Dawson JE, Alexander M (1968b) 2,4-d Metabolism: enzymatic degradation of chlorocatechols. J Agric Food Chem 16: 829–833
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72: 248–254
Brinkmann U, Reineke W (1992) Degradation of chlorotoluenes by in vivo constructed hybrid strains: problems of enzyme specificity, induction and prevention of meta-pathway. FEMS Microbiol Lett 96: 81–88
Buswell JA, Eriksson KE (1979) Aromatic ring cleavage by the white-rot fungus Sporotrichum pulverulentum. FEBS Lett 104: 258–260
Chapman PJ (1979) Degradation mechanisms. In: Bourquin AW, Pritchard PH (eds) Microbial degradation of pollutants in marine environments. EPA-600/9–79–012 Environ Prot Agency, Gulf Breeze, Fla., USA, pp 28–66
Chapman PJ, Ribbons DW (1976) Metabolism of resorcinylic compounds by bacteria: alternative pathways for resorcinol catabolism in Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol 125: 985–998
Chatterjee DK, Kellog ST, Hamada S, Chakrabarty AM (1981) Plasmid specifying total degradation of 3-chlorobenzoate by a modified ortho-pathway. J Bacteriol 146: 639–646
DeBont JAM, Vorage MJAW, Hartmans S, Tweel WJJvan den (1986) Microbial degradation of 1,3-dichlorobenzene. Appl Environ Microbiol 52: 677–680
Ditzelmüller G, Loidl M, Streichsbier F (1989) Isolation and characterization of a 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid-degrading soil bacterium. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 31: 93–96
Dorn E, Hellwig M, Reineke W, Knackmuss H-J (1974) Isolation and characterization of 3-chlorobenzoate degrading pseudomonad. Arch Microbiol 99: 61–70
Dorn E, Knackmuss H-J (1978a) Chemical structure and biodegradability of halogenated aromatic compounds. Two catechol 1,2-dioxygenases from a 3-chlorobenzoate-grown pseudomonad. Biochem J 174: 73–84
Dorn E, Knackmuss H-J (1978b) Chemical structure and biodegradability of halogenated aromatic compounds. Substituent effects on 1,2-dioxygenation of catechol. Biochem J 174: 85–94
Duxbury JM, Tiedje JM, Alexander M, Dawson JE (1970) 2,4-d Metabolism: enzymatic conversion of chloromaleylacetic acid to succinic acid. J Agric Food Chem 18: 199–201
Eisner U, Elvidge JA, Linstead RP (1951) Unsaturated lactones and related substances. (V) Dihydro-β-ketomuconic acid and carboxy-lactones of the protoanemonin type. Chem Soc 1501–1512
Evans WC, Smith BSW, Fernley HN, Davies JI (1971a) Bacterial metabolism of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate. Biochem J 122: 543–551
Evans WC, Smith BSW, Moss P, Fernley HN (1971b) Bacterial metabolism of 4-chlorophenoxyacetate. Biochem J 122: 509–517
Freier RK (1974) Wasseranalyse. Chemische, physiko-chemische und radio-chemische Untersuchungsverfahren, 2. Aufl. W. de Gruyter, Berlin, pp 45–46
Gaal AB, Neujahr HY (1979) Metabolism of phenol and resorcinol in Trichosporon cutaneum. J Bacteriol 137: 13–21
Haigler BE, Nishino SF, Spain JC (1988) Degradation of 1,2-dichlorobenzene by a Pseudomonas sp. Appl. Environ Microbiol 54: 294–301
Haigler BE, Spain J (1989) Degradation of p-chlorotoluene by a mutant of Pseudomonas sp. strain JS6. Appl Environ Microbiol 55: 372–379
Hartmann J, Reineke W, Knackmuss H-J (1979) Metabolism of 3-chloro-, 4-chloro-, and 3,5-dichlorobenzoate by a pseudomonad. Appl Environ Microbiol 37: 421–428
Hartmann J, Engelberts K, Nordhaus B, Schmidt E, Reineke W (1989) Degradation of 2-chlorobenzoate by in vivo constructed hybrid pseudomonads. FEMS Microbiol Lett 61: 17–22
Havel J, Reineke W (1991) Total degradation of various chlorobiphenyls by cocultures and in vivo constructed pseudomonads. FEMS Microbiol Lett 78: 163–170
Holding AJ, Collee JG (1971) The decomposition of simple carbohydrates, organic acids and some other compounds. In: Norris JR, Ribbons DW (eds) Methods in microbiology. Academic Press, London, 6a, pp 3–12
Kaschabek SR (1990) Untersuchungen zur Dechlorierung von Chlormaleylacetaten in Pseudomonas sp. Stamm B13. Diploma Thesis, University of Wuppertal, FRG
Latorre J, Reineke W, Knackmuss H-J (1984) Microbial metabolism of chloroanilines: enhanced evolution by natural genetic exchange. Arch Microbiol 140: 159–165
Loidl M, Hinteregger C, Ditzelmüller G, Ferschl A, Streichsbier F (1990) Degradation of aniline and monochlorinated anilines by soil-born Pseudomonas acidovorans strains. Arch Microbiol 155: 56–61
Mokross H, Schmidt E, Reineke W (1990) Degradation of 3-chlorobiphenyl by in vivo constructed hybrid pseudomonads. FEMS Microbiol Lett 71: 179–186
Oltmanns RH, Rast HG, Reineke W (1988) Degradation of 1,4-dichlorobenzene by enriched and constructed bacteria. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 28: 609–616
Reineke W, Knackmuss H-J (1979) Construction of haloaromatics utilising bacteria. Nature 277: 385–386
Reineke W, Knackmuss H-J (1980) Hybrid pathway for chlorobenzoate metabolism in Pseudomonas sp. B13 derivatives. J Bacteriol 142: 467–473
Reineke W, Knackmuss H-J (1984) Microbial metabolism of haloaromatics: isolation and properties of a chlorobenzene-degrading bacterium. Appl Environ Microbiol 47: 395–402
Sander P, Wittich R-M, Fortnagel P, Wilkes H, Francke W (1991) Degradation of 1,2,4-trichloro- and 1,2,4,5-tetrachlorobenzene by Pseudomonas strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 57: 1430–1440
Schlömann M, Schmidt E, Knackmuss H-J (1990) Different types of dienelactone hydrolase in 4-fluorobenzoate-utilizing bacteria. J Bacteriol 172: 5112–5118
Schmidt E, Knackmuss H-J (1980) Chemical structure and biodegradability of halogenated aromatic compounds. Conversion of chlorinated muconic acids into maleoylacetic acid. Biochem J 192: 339–347
Schmidt E, Remberg G, Knackmuss H-J (1980) Chemical structure and biodegradability of halogenated aromatic compounds. Halogenated muconic acids as intermediates. Biochem J 192: 331–337
Schraa G, Boone ML, Jetten MSM, Neerven ARWvan, Colberg PJ, Zehnder AJB (1986) Degradaton of 1,4-dichlorobenzene by Alcaligenes sp. strain A175. Appl Environ Microbiol 52: 1374–1381
Schwien U, Schmidt E (1982) Improved degradation of monochlorophenols by constructed strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 44: 33–39
Schwien U, Schmidt E, Knackmuss H-J, Reineke W (1988) Degradation of chlorosubstituted aromatic compounds by Pseudomonas sp. strain B13: fate of 3,5-dichlorocatechol. Arch Microbiol 150: 78–84
Sharpee KW, Duxbury JM, Alexander M (1973) 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetate metabolism by Arthrobacter sp.: accumulation of a chlorobutenolide. Appl Microbiol 26: 445–447
Spain JC, Nishino SF (1987) Degradation of 1,4-dichlorobenzene by a Pseudomonas sp. Appl Environ Microbiol 53: 1010–1019
Sparnins VL, Burbee DG, Dagley S (1979) Catabolism of l-tyrosine in Trichosporon cutaneum. J Bacteriol 138: 425–430
Tiedje JM, Alexander M (1969) Enzymatic cleavage of the ether bond of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetate. J Agric Food Chem 17: 1080–1084
Tiedje JM, Duxbury JM, Alexander M, Dawson JE (1969) 2,4-d Metabolism: pathway of degradation of chlorocatechols by Arthrobacter sp. J Agric Food Chem 17: 1021–1026
Van derMeer JR, Roelofsen W, Schraa G, Zehnder AJB (1988) Degradation of low concentrations of dichlorobenzenes and 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene by Pseudomonas sp. strain P51 in nonsterile soil columns. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 45: 333–341
Van derMeer JR, Neerven ARWvan, Vries EJde, Vos WMde, Zehnder AJB (1991) Cloning and characterization of plasmidencoded genes for the degradation of 1,2-dichloro-, 1,4-dichloro-, and 1,2,4-trichlorobenzene of Pseudomonas sp. strain P51. J Bacteriol 173: 6–15
You IS, Bartha R (1982) Metabolism of 3,4-dichloroaniline by Pseudomonas putida. J Agric Food Chem 30: 274–277
Zeyer J, Kearney PC (1982) Microbial degradation of para-chloroaniline as sole carbon and nitrogen source. Pest Biochem Physiol 17: 215–223
Zeyer J, Wasserfallen A, Timmis KN (1985) Microbial mineralization of ring-substituted anilines through an ortho-cleavage pathway. Appl Environ Microbiol 50: 447–453
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaschabek, S.R., Reineke, W. Maleylacetate reductase of Pseudomonas sp. strain B13: dechlorination of chloromaleylacetates, metabolites in the degradation of chloroaromatic compounds. Arch. Microbiol. 158, 412–417 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00276301
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00276301