Summary
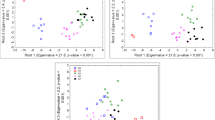
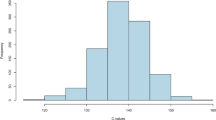
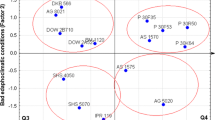
Simple correlations were calculated between nine different cms sources (cms-S, -R, -ML, -L, -CA, -EK, -C, -Rb, -T) on the basis of the weighted restoring reactions of 41 inbred lines. The Principal Component Analysis was applied to a 9 × 9 matrix which clearly grouped cytoplasms according to their similarities. The Principal Component I included S, R, ML, L, CA and EK cytoplasms; the Principal Component II contained C and Rb cytoplasms while T-cytoplasms was placed in Principal Component III. This corresponds to the main groupings indicated in the literature (Beckett 1971). However, after varimax rotation of the Principal Components, the S main group, including the 6 tested cytoplasms, fell into 3 subgroups: I.: S, R, ML; II.: L, CA; III.: EK.
These data indicate that the Principal Component Analysis can be used to select a limited number of cms sources from the S group, representing the variability of the cytoplasmic gene pool of that group.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Beckett, J.B. (1971): Classification of male-sterile cytoplasms in maize (Zea mays L.). Crop. Sci. 11, 724–727
Duvick, D.N. (1965): Cytoplasmic pollen sterility in corn. Adv. Genet. 13, 1–56
Gracen, V.E.; Grogan, C.O. (1974): Diversity and suitability for hybrid production of different sources of cytoplasmic male-sterility in maize. Agron. J. 65, 654–657
Gracen, V.E.; Kheyr-Pour, A.; Earle, E.D.; Gregory, P. (1979): Cytoplasmic male sterility and pest resistance. In: Proc. 34th Annual Corn Sorghum Conf. vol. 34, pp. 76–92. Washington, DC: Am. Seed Trade Assoc.
Koncz, Cs.; Kálmán, L.; Vargha, J. (1980): Key for classification of cytoplasmic male sterile types in maize. Plant Sci. Lett. 17, 317–326
Laughnan, J.R.; Gabay, S.J. (1973): Mutations leading to nuclear restoration of fertility in S male sterile cytoplasm in maize. Theor. Appl. Genet. 43, 109–116
Laughnan, J.R.: Gabay, S.J. (1978): Nuclear and cytoplasmic mutations to fertility in male-sterile maize. In: Maize Breeding and Genetics (ed. Walden, D.B.) pp. 427–447. New York: Wiley
Levings, C.S., III; Pring, D.R. (1976): Biochemical basis of normal and male sterile cytoplasms of corn. In: Proc. 31st Corn Res. Conf., vol. 31, pp. 110–117. Washington, DC: Am. Trade Seed Assoc.
Levings, C.S., III; Pring, D.R. (1977): Diversity of mitochondrial genomes among normal cytoplasms of maize. J. Hered. 68, 350–354
Pring, D.R.; Levings, C.S., III (1978): Heterogenity of maize cytoplasmic genomes among male-sterile cytoplasms. Genetics 89, 121–136
Pring, D.R.; Conde, M.F.; Levings, C.S., III (1980): DNA heterogenity within the C group of male-sterile cytoplasms. Crop. Sci. 20, 159–162
Smith, D.R.; Hooker, A.L.; Lim, S.M.; Beckett, J.B. (1971): Disease reaction of thirty sources of cytoplasmic male sterile corn to Helminthosporium maydis race T. Crop. Sci. 11, 712–713
Sváb, J. (1979): Többvàltozós Módszerek a Biometriában. (Multi-Variate Methods in Biometrics). Budapest: Mezögazdasági Kiadó
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by R. Hagemann
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kálmán, L., Dévényi, M. A method for subgrouping the S-type of CMS forms in maize. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 62, 209–212 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00276240
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00276240