Summary
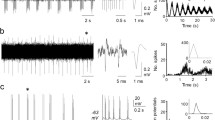
The spontaneous nerve impulse activity of 354 neurons of the mesencephalic reticular formation resp. the superior colliculus of unanesthetized curarized rats resp. cats has been recorded by microelectrodes and processed by means of a LINC computer. A relationship between the shape of interimpulse interval histogram (IH) and the mean interimpulse intervals (MI) of the same spike train has been found. Neurons with long MI's (low frequency of firing) are never characterized by symmetrical IH's, the exponential IH (characterizing random occurrence of impulses) being the most common in these cases. Neurons with symmetrical IH's are usually those with short MI's (fast firing rate). Longlasting recordings with changing MI show that the shape of IH's may not be considered in general a stable feature of certain neurons (in the majority of cases it changes together with the MI). Neurons with symmetrical IH's and short MI's may not be found in the superficial layers but in the depth of the superior colliculus only (having probably like the reticular formation integrative functions). A computer model is presented explaining the observed dependency of the IH shape on the MI duration in terms of the change in the mean frequency of common input process.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell, C. C., Grim, R. D.: Recordings from one and two Purkinje cells. J. Neurophysiol. 32, 1044–1055 (1969).
Bohdanecký, Z., Radil-Weiss, T., Škvařil, J.: The effect of d-phenmetrazine upon reticular unit activity. Int. J. Neuropharmacol. (1970). In press.
Calvin, W. H., Stevens, C. F.: Synaptic noise and other sources of randomness in motoneuron spike intervals. J. Neurophysiol. 31, 574–587 (1968).
Freeman, W. J.: Relations between unit activity and evoked potentials in prepyriform cortex of cats. J. Neurophysiol. 31, 337–348 (1968).
Fukami, Y.: Tonic and phasic muscle spindles in snake. J. Neurophysiol. 33, 28–35 (1970).
Harmon, L. D., Lewis, E. R.: Neural modeling. In: Advances in biomedical engineering and medical physics (S. N. Levine, ed.). New York: Wiley 1968.
Junge, D., Moore, G. P.: Interspike-interval fluctuations in Aplysia pacemaker neurons. Biophys. J. 6, 411–434 (1966).
Khintchine, A. Y.: Mathematical methods in the theory of queueing. London: Griffin 1960.
Koerber, K. C., Pfeiffer, R. R., Warr, W. B., Kiang, N. Y.-S.: Spontaneous spike discharges from single units in the cochlear nucleus after the destruction of the cochlea. Exp. Neurol. 16, 119–130 (1966).
Lummis, R. C.: The secret code of hearing. Bell Labs Rec. 44, 261–266 (1966).
Magni, F., Willis, W. D., Jr.: Identification of reticular formation neurons by intracellular recording. Arch. ital. Biol. 101, 681–702 (1963).
Moore, G. P., Perkel, D. H., Segundo, J. P.: Statistical analysis and functional interpretation of neuronal spike data. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 28, 493–522 (1966).
Murphy, J. T., Sabah, N. H.: Spontaneous firing of cerebellar Purkinje cells in decerebrate and barbiturate anesthetized rats. Brain. Res. 17, 515–519 (1970).
O'Brien, J. H., Fox, S. S.: Single-cell activity in cat motor cortex: II. Functional characteristics of the cell related to conditioning changes. J. Neurophysiol. 32, 285–296 (1969).
Perkel, D. H., Gerstein, G. L., Moore, G. P.: Neuronal spike trains and stochastic point processes. I. The single spike train. Biophys. J. 7, 391–418 (1967).
Pfeiffer, R. R., Kiang, N. Y.-S.: Spike discharge patterns of spontaneous and continuously stimulated activity in the cochlear nucleus of anesthetized cats. Biophys. J. 5, 301–316 (1965).
Radil-Weiss, T., Lakočevič, L., Damjanovič, Z.: Spontaneous activity of neurons in the visceral ganglion of Aplysia depilans. Marine Biol. 6, 241–247 (1970).
— Škvařil, J., Syka, J.: Quantitative analysis of spontaneous impulse activity of neurons in the brain. In: Biokybernetik II. (H. Drischel and N. Tiedt, ed.). Leipzig: VEB Gustav Fisher 1968.
Segundo, J. P., Perkel, D. H., Wyman, H., Hegstad, H., Moore, G. P.: Input-output relations in computer-simulated nerve cells. Kybernetik 4, 157–171 (1968).
Viernstein, L. J., Grosman, R. G.: Neural discharge patterns in the transmission of sensory information. In: Information theory (C. Cherry, ed.). London: Butterworths 1961.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Škvařil, J., Radil-Weiss, T., Bohdanecký, Z. et al. Spontaneous discharge patterns of mesencephalic neurons: interval histogram and mean interval relationship. Kybernetik 9, 11–15 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00272554
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00272554