Summary
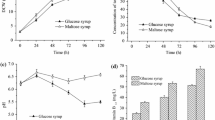
The production of a pectolytic enzyme complex in a 10-l strirred tank bioreactor was studied using the Aspergillus niger mutant A 138. A time course of the fermentation showed that the enzyme synthesis is not associated with growth. Maximal activity was reached after 95 h and from that time on it remained constant. Redox potential and pH values proved to be valuable indicators of the initiation and end of enzyme synthesis. The specific morphology of the fungus, growing in distinct pellets with long peripheral hyphae, resulted in a very dense and viscous broth. It represented a special problem for heat and mass transfer. An attempt was made to overcome this problem by different agitation and aeration regimes. These parameters did not change the morphology but had a marked influence on enzyme synthesis. When, at the time of maximal growth rate, aeration was increased from 0.5 vvm to 1.2 vvm, and agitation from 300 rpm to 500 rpm, the depectinizing activity was doubled in comparison with the results obtained when 0.5 vvm and 300 rpm were used throughout fermentation. When more intensive agitation was employed from the beginning of the process, the depectinizing activity was lowered from 60 to 45 units/ml, together with the viscosity and polygalacturonase activity. However, at the same time, the pectin esterase and pectinlyase yields increased. The required fermentation time was reduced from 95 to 65 h.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayers WA, Papavizas GC, Diem AF (1966) Polygalacturonate trans-eliminase and polygalacturonase production by Rhizoctonia solani. Phytopathology 56:1006–1011
Berry DR (1975) The environmental control of the physiology of filamentous fungi. In: Smith JE, Berry DR (eds) The filamentous fungi. I. Industrial mycology. Arnold, London, pp 16–32
Friedrich J, Cimerman A, Humski-Pavlovič L (1986) Comparison of screening test and fermentation test for the selection of pectolytic Aspergillus niger strains. Prehrambeno-Tehnol Biotehnol Rev 24:159–162
Gould BJ (1975) Enzyme data. In: Wiseman A (ed) Handbook of enzyme biotechnology. Ellis Horwood, New York, pp 128–162
Hermesdörfer H, Jelke E, Leuchtenberger A, Wardsack Ch, Ruttloff H (1984) Gewinnung von pektinolytischen Enzymen aus Aspergillus niger in Submerskultur. Z Allg Mikrobiol 24:413–424
Keller H, Müller-Beissenhirtz W, Neumann E (1967) Klin Wschr 45:314, cited in Klinisches Labor (1974) 12 Auflage, Merck, Darmstadt, p 104
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Rombouts FM, Pilnik W (1980) Pectic enzymes. In: Rose AH (ed) Microbial enzymes and bioconversions. Academic Press, London, pp 227–282
Schormüller J (1967) Handbuch der Lebensmittelchemie, vol 2. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, p 2155
Tuttobello R, Mill PJ (1961) The pectic enzymes of Aspergillus niger. 1. The production of active mixtures of pectic enzymes. Biochem J 79:51–57
Wang MC, Keen NT (1970) Purification and characterization of endopolygalacturonase from Verticillium albo-atrum. Arch Biochem Biophys 141:749–757
Zetelaki-Horváth K, Békássy-Molnár E (1975) Factors affecting polygalacturonase yield and kinetic types of enzyme production by Aspergillus awamori. Acta Aliment 4:167–179
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This paper is dedicated to Prof. Robert M. Lafferty on the occasion of his 60th birthday
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Friedrich, J., Cimerman, A. & Steiner, W. Submerged production of pectolytic enzymes by Aspergillus niger: effect of different aeration/agitation regimes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 31, 490–494 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00270782
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00270782