Abstract
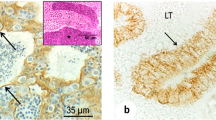
The present study deals with the immunohistochemical localization of S-100 protein in the testes of seven mammalian species including rat, cat, dog, pig, sheep, cattle and horse. Significant differences are demonstrated in the cellular distribution and intensity of immunoreaction for the protein. In bull, ram, boar and cat tests S-100 protein was localized in the cytoplasm and nuclei of Sertoli cells. A particularly intense staining was seen in the modified Sertoli cells of the terminal tubular segment. With the exception of the cat and horse S-100 protein immunoreactivity was additionally found in epithelial cells of the straight testicular tubules and in the epithelial cells of the rete testis. Endothelial cells of capillaries, veins and lymphatic vessels are regularly S-100 immunoreactive in ruminants. Leydig cells were found to be strongly positive for S-100 protein in the cat and rat testes and to a lower degree in pig and horse testes. Finally a distinct immunostaining of peritubular cells was restricted to the testis of dogs and rats. The remarkable species-specific variations of immunoreactivity for S-100 protein in different cell types of the testis support the hypothesis that S-100 protein is a multifunctional protein and may have a different function in testicular physiology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amselgruber W, Sinowatz F, Schams D, Lehmann M (1992) S-100 protein immunoreactivity in bovine testis. Andrologia 24:231–235
Baudier J, Briving C, Deinum J, Haglid K, Sörskog L, Wallin M (1982) Effect of S-100 proteins and calmodulin on Ca2+-induced disassembly of brain microtubule proteins in vitro. FEBS Lett 147:165–167
Baudier J, Mochly-Rosen D, Newton A, Lee SK, Cole R (1987) Comparison of S 100-b protein with calmodulin: interactions with melittin and microtubule-associated proteins and inhibition of phosphorylation of proteins by protein kinase C. Biochemistry 26:2886–2893
Berridge MJ, Irvine RF (1984) Inositol triphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature 312:315
Bock E (1978) Nervous system specific proteins. J Neurochem 30:7–14
Donato R (1983) Effect of S-100 protein on assembly of brain microtubule proteins in vitro. FEBS Lett 162:310–313
Donato R (1984) Mechanism of action of S-100 protein(s) on brain microtubule protein assembly. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 124:850–856
Donato R (1986) S-100 Proteins. Cell Calcium 7:123–145
Endo T, Hidaka H (1983) Effect of S-100 protein on microtubule assembly-disassembly. FEBS Lett 161:235–238
Ferrer L, Rabanal RM, Fondevila D, Prats N (1990) Immunocytochemical demonstration of intermediate filament proteins, S-100 protein and CEA in apocrine sweat glands and apocrine gland derived lesions of the dog. J Vet Med A 37:569–576
Fujii T, Gochou N, Akabane Y, Fujii M, Kondo Y, Suzuki T, Ohki K (1986) Effect of zinc ions on the interaction of S-100 protein with brain microtubule proteins. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 34:5040–5045
Haimoto H, Hosoda S, Kato K (1987) Differential distribution of immunoreactive S 100-a and S 100-b proteins in normal non-nervous human tissues. Lab Invest 57:489–498
Isobe T, Ishioka N, Kocha T, Okuyama T (1982) In: Peeters H (ed) Protides of the biological fluids, vol 30. Pergamon Press, pp 21–24
Iwanaga T, Fujita T, Takahashi Y, Isobe T (1987) Immunohistochemical demonstration of S-100 protein in the endothelial cells of blood vessels in the pig and cattle. Biomed Res 8:329–334
Michetti F, Lauriola L, Rende M, Stolfi V, Battaglia F, Coccia D (1985) S-100 protein in the testis. An immunochemical and immunohistochemical study. Cell Tissue Res 240:137–142
Moore B (1965) A soluble protein characteristic of the nervous system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 19:739–744
Petersen OH, Maruyama Y (1984) Calcium-activated potassium channels and their role in secretion. Nature 307:693
Promt CA, Quinton PM (1978) Functions of calcium in sweat secretion. Nature 272:171
Sugimura M, Shirogane D, Atoji Y, Suzuki Y, Ohshima K, Kon Y, Hashimoto Y (1990) A comparative study on S-100 protein-immunoreactive cells in lymph nodes. Jpn J Vet Sci 52:1015–1021
Van Eldik L, Hertzber E, Berdan R, Gilula N (1985) Interaction of calmodulin and other calcium-modulated proteins with mammalian and arthropod junctional membrane proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 126:825–832
Vanstapel M, Gatter K, Wolf-Peeters C, Mason D, Desmet VD (1985) New site of human S-100 immunoreactivity detected with monoclonal antibodies. Am J Clin Pathol 85:160–168
Waites GMH (1977) Fluid secretion. In: Johnson AD, Gomes WR (eds) The testis, vol 4. Academic Press, New York, pp 91–123
Wrobel K, Sinowatz F, Mademann R (1982) The fine structure of the terminal segment of the bovine seminiferous tubule. Cell Tissue Res 225:29–44
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amselgruber, W.M., Sinowatz, F. & Erhard, M. Differential distribution of immunoreactive S-100 protein in mammalian testis. Histochemistry 102, 241–245 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00268901
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00268901



