Summary
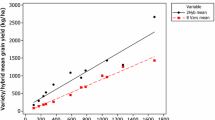
Regression analysis was computed on the grain yield of 15 single cross F1 hybrids of pearl millet (Pennisetum typhoides (Burm.) S. & H.) evaluated in 20 environments at 19 sites in India to assess the nature of genotype X environment interactions. Linear, quadratic, cubic, twoand three-intersecting straight line models were examined for fit. The interactions of six hybrids viz. MH 110, MH 113, MH 114, MH 115, MH 120 and MBH 110 were explained by the linear regression model. The response of the remaining nine hybrids was largely non-linear. The two and three-intersecting straight line models fit better than the quadratic and cubic models and explained non-linearity of response. The two-intersecting straight line models fit for 6 hybrids MH 106, MH 107, MH 112, MH 116, MH 117 and BJ 104. The response of MH 109 was best explained by a three-intersecting straight line model, but there still existed a significant remainder variation. The truncation of environmental range by assuming moving division points was more efficient than the fixed division points for the segmental regression models. The stability of hybrid varieties on the best fitting model has been discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eberhart SA, Russell WA (1966) Stability parameters for comparing varieties. Crop Sci 6:36–40
Finlay KW, Wilkinson GN (1963) The analysis of adaptation in a plant breeding programme. Aust J Agric Res 14:742–754
Jinks JL, Pooni HS (1979) Non-linear genotype X environment interactions arising from response thresholds. I. Parents, F1's and selections. Heredity 43:57–70
Mariani BM, Manmana PN, Stefanini R (1983) Efficiency of linear and multiphase regression methods to evaluate genotype-environment interaction for grain yield and protein content in Italian durum wheat varieties. Z Pflanzen-zücht 90:56–67
Perkins JM, Jinks JL (1968 a) Environmental and genotype environmental components of variability. III. Multiple lines and crosses. Heredity 23:339–356
Perkins JM, Jinks JL (1968 b) Environmental and genotypeenvironmental components of variability. IV. Non-linear interactions for multiple inbred lines. Heredity 23:525–535
Perkins JM, Jinks JL (1973) The assessment and specificity of environmental and genotype-enironmental components of variability. Heredity 30:111–126
Pooni HS, Jinks JL (1980) Non-linear genotype X environment interaction. II. Statistical models and genetical control. Heredity 45:389–400
Verma MM, Chahal GS, Murty BR (1978) Limitations of conventional regression analysis — a proposed modification. Theor Appl Genet 53:89–91
Virk DS, Virk PS (1986) Regression analysis of genotype X environment interactions in pearl millet. Proc 6th Eucarpia Meeting Sect. Biometrics Plant Breed, University of Birmingham (UK), 309–322
Virk DS, Virk PS, Harinarayana G, Arora BS, Kumar R (1986) Analysis of linear and non-linear genotype X environment interactions in pearl millet. SABRAO J 18:45–52
Yates F, Cochran WG (1938) The analysis of groups of experiments. J Agric Sci 28:556–580
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by B.R. Murty
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Virk, D.S., Virk, P.S., Mangat, B.K. et al. Linear and non-linear regression analysis of genotype X environment interactions in pearl millet. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 75, 736–740 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00265597
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00265597