Summary
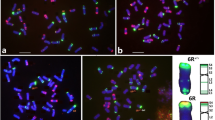
C-banding patterns of T. ovatum (Ae. ovata) and four T. aestivum cv ‘Poros’-T. ovatum chromosome addition lines are presented, and the added chromosomes of T. ovatum have been identified. Furthermore, nucleolar activity and powdery mildew resistance were analyzed in the ‘Poros’-ovatum addition lines and compared to that of T. ovatum and T. aestivum cv ‘Poros’. The addition lines II, III and IV and ‘Poros’ were highly susceptible to powdery mildew isolates nos. 8 and 9, whereas the addition lines VI1 and VI2 showed high resistance. Even for an Ml-k virulent isolate, these two lines were highly resistant. By combining the cytological results and those of the powdery mildew analysis, the added chromosomes of T. ovatum can be excluded from responsibility for the high powdery mildew resistance of the addition lines VI1 and VI2. The same is true for a modified chromosome 6B, which is present in the ‘Poros’-ovataum addition lines II, III and VI. The high variation in C-banding pattern observed in the A-, B- and D-genome complement of the addition lines is believed to be the result of crossing different lines of T. aestivum instead of ‘Poros’ alone. Thus, we cannot trace the powdery mildew resistance back to a specific chromosome.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bowden WM (1959) The taxonomy and nomenclature of the wheats, barleys and ryes and their wild relatives. Can J Bot 37:130–136
Cermeño MC, Orellana J, Santos JL, Lacadena JR (1984 a) Nucleolar activity and competition (amphiplasty) in the genus Aegilops. Heredity 53:603–611
Cermeño MC, Orellana J, Santos JL, Lacadena JR (1984 b) Nucleolar organizer activity in wheat, rye and derivatives analyzed by a silver-staining procedure. Chromosoma 89:370–376
Chennaveeraiah MS (1960) Karyomorphologic and cytotaxonomic studies in Aegilops. Acta Horti Gotob 23:85–178
Endo TR (1986) Complete identification of common wheat chromosomes by means of the C-banding technique. Jpn J Genet 61:89–93
Endo TR, Gill BS (1983) Identification of wheat chromosomes by N-banding. In: Sakamoto S (ed) Proc 6th Intern Wheat Genet Symp Kyoto. Japan, pp 355–359
Endo TR, Gill BS (1984) Somatic karyotype, heterochromatin distribution, and nature of chromosome differentiation in common wheat, Triticum aestivum L. em Thell. Chromosoma 89:361–369
Friebe B, Larter EN (1988) Identification of a complete set of isogenic wheat/rye D-genome substitution lines by means of Giemsa C-banding. Theor Appl Genet 76:473–479
Gill BS (1981) Evolutionary relationships based on heterochromatin bands in six species of the Triticinae. J Hered 72:391–394
Gil BS (1987) Chromosome banding methods, standard chromosome band nomenclature and applications in cytogenetic analysis. In: Heyne EG (ed) Wheat and wheat improvement. American Society of Agronomy Monograph 13, Madison, pp 243–254
Gill BS, Sharma HC, Raupp WJ, Browder LE, Hatchett JH, Harvey TL, Moseman JG, Waines JG (1985) Evaluation of Aegilops species for resistance to wheat powdery mildew, wheat leaf rust, hessian fly and greenbug. Plant Dis 69:314–316
Giraldez R, Cermeno MC, Orellana J (1979) Comparison of C-banding pattern in the chromosomes of inbred lines and open pollinated varieties of rye, Secale cereale L. Z Pflanzenzuecht 83:40–48
Heun M, Fischbeck G (1987 a) Identification of wheat powdery mildew resistance genes by analyzing host-pathogen interactions. Plant Breed 98:124–129
Heun M, Fischbeck G (1987 b) Genes for powdery mildew resistance in cultivars of spring wheat. Plant Breed 99:282–288
Kihara K (1937) Genomanalyse bei Triticum und Aegilops. VII. Kurze Übersicht über die Ergebnisse der Jahre 1934–1936. Mem Coll Agric Kyoto Univ 41:1–61
Kihara K (1946) Genomanalyse bei Triticum and Aegilops. IX. Systematischer Aufbau der Gattung Aegilops auf genomanalytischer Grundlage. Cytologia 14:135–144
Kimber G, Sears ER (1983) Assignment of genome symbols in the Triticinae. In: Sakamoto S (ed) Proc 6th Intern Wheat Genet Symp Kyoto, Japan, pp 1195–1196
Kimber G, Sears ER (1987) Evoluation in the genus Triticum and the origin of cultivated wheat. In: Heyne EG (ed) Wheat and wheat improvement. American Society of Agronomy Monograph 13, Madison, pp 154–164
Kimer G, Pignone D, Sallee PJ (1983) The relationships of the M and Mu genomes of Triticum. Can J Genet Cytol 25:509–512
Kimber G, Sallee PF, Feiner MM (1987) The interspecific and evolutionary relationships of Triticum ovatum. Genome 30:218–221
Lacadena JR, Cermeño MC (1985) Nucleolus organizer competition in Triticum aestivum-Aegilops umbellulata chromosome addition lines. Theor Appl Genet 71:278–283
Lacadena JR, Cermeño MC, Orellana J, Santos JL (1984) Evidence for wheat-rye nucleolar competition (amphiplasty) in triticale by silver staining procedure. Theor Appl Genet 67:207–213
Lukaszewski AJ, Gustafson JP (1983) Translocations and modifications of chromosomes in triticale x wheat hybrids. Theor Appl Genet 64:239–248
Martini G, O'Dell M, Flavell RB (1982) Partial inactivation of wheat nucleolus organizers by the nucleolus organizer chromosomes from Aegilops umbellulata. Chromosoma 84:687–700
Mettin D, Blüthner WD, Schäfer HJ, Buchholz U, Rudolph A (1977) Untersuchungen an Samenproteinen in der Gattung Aegilops. Tagungsber Akad Landwirtschaftswiss DDR 158:95–106
Pathak GN (1940) Studies in the cytology of cereals. J Genet 39:437–467
Teoh SB, Hutchinson J (1983) Interspecific variation in C-banded chromosomes of diploid Aegilops species. Theor Appl Genet 65:31–40
Teoh SB, Hutchinson J, Miller TE (1983 a) A comparison of the chromosomal distribution of cloned repetitive DNA sequences in different Aegilops species. Heredity 51:635–641
Teoh SB, Miller TE, Reader SM (1983 b) Intraspecific variation in C-banded chromosomes of Aegilops comosa and Aegilops speltoides. Theor Appl Genet 65:343–348
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by K. Tsunewaki
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Friebe, B., Heun, M. C-banding pattern and powdery mildew resistance of Triticum ovatum and four T. aestivum-T. ovatum chromosome addition lines. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 78, 417–424 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00265306
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00265306