Abstract
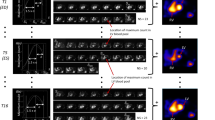
The investigations were carried out in 51 patients with different cardiovascular diseases using a gamma camera coupled to a computer. Pyrophosphate (Sn) injection followed by technetium-99m injection were administered through only one puncture of an antecubital vein. Tc-99m was given as a bolus and its passage through the cardiac cavities was recorded and ejection fraction and wall motion of left ventricle were estimated. It was observed that 10 30 min after Tc-99m injection a steady activity Tc-99m-labeled RBCs was maintained in the vascular bed which made possible evaluation of the motility of cardiac walls by the gating technique. Presence of labeled RBCs also permitted blood pool scans and spleen scans to be obtained. Cases investigated by this method for pericardial effusion and splenomegaly are described for illustration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bałtrukiewicz, Z., Przedlacki, J., Dziuk, E.: In vivo technetium-99m erytrocyte labeling by means of previously injected sodium pyrophosphate and stannous chloride (PYRO-Sn). Eur. J. Nucl. Med (In press)
Chandler, W.M., Shuck, L.D.: Abnormal technetium-99m pertechnetate imaging following stannous pyrophosphate bone imaging (Abstr.). J. Nucl. Med. 16, 518 (1975)
Hamilton, R.G., Alderson, P.O.: A comparative evaluation of techniques for rapid and efficient in vivo labelling of red cells with (99mTc) Pertechnetate. J. Nucl. Med. 18, 1010–1013 (1977)
Khentigan, A., Garrett, M., Lum, D., Winchell, H.S.: Effect of prior administration on Sn (II) complexes used in nuclear medicine on in vivo distribution of subsequently administered Tc-99m pertechnetate and Tc-99m compounds. J. Nucl. Med. 17, 380–384 (1976)
Mc Rae, J., Sugar, R.M., Shipley, B., Hook, G.R.: Alternations in tissue distribution of 99mTc pertechnetate in rats given stannous tin. J. Nucl. Med. 15, 151–155 (1974)
Parker, J.A., Uren, R.F., Jones, A.G., Maddox, D.E., Zimmerman, R.E., Neill, J.M., Holman, B.L.: Radionuclide left ventriculography with the slant hole collimator. J. Nucl. Med. 18, 848–851 (1977)
Pavel, D.G., Zimmer, A.M., Patterson, V.N.: In vivo labeling of red blood cells with 99mTc. A new approach to blood pool visualization. J. Nucl. Med. 18, 305–308 (1977)
Schelbert, H.R., Verba, J.W., Johnson, A.D., Brock, G.W., Alazraki, N.P., Rose, F.J., Ashburn, W.L.: Nontraumatic determination of left ventricular ejection fraction by radionuclide angiocardiography. Circulation 51, 902–909 (1975)
Stokely, E.M., Parkey, R.W., Bonte, F.J., Graham, K.D., Stone, M.J., Willerson, J.T.: Gated blood pool imaging following Tc-99m stannous pyrophosphate imaging. Radiology 120, 433–434 (1976)
Walker, A.G.: Effect of Tc-99m Sn bone scan agents on subsequent pertechnetate brain scans (Abstr.). J. Nucl. Med. 16, 579 (1975)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Czaplicki, S., Dziuk, E., Konieczny, W. et al. Cardiac studies using red blood cells labeled with Tc-99m in vivo with single intravenous injections — First pass technique, gating and blood pool scanning. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 5, 85–88 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00261212
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00261212