Abstract
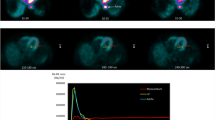
As an alternative procedure to the exercise stress test used in myocardial scanning, vasoactive drugs were employed to elicit deficits in blood flow to myocardial regions supplied by stenotic arteries which maintain normal resting flow or collateral circulation. The data were collected from 35 dogs, some of which had partial stenosis (70–75%) on either major branch of the left coronary artery, and others which had Ameroid constrictor implants. The effects of lidoflazine, dipyridamole, and nitroglycerin on coronary hemodynamics and myocardial dispersion of potassium 43(43K) in animals with partial stenosis were evaluated in ten acute experiments. In the pilot studies, four rapid serial rectilinear control scans from 43K (750 μCi) were reported; dipyridamole (Persantin), lidoflazine, or nitroglycerin were then administered intravenously. When the selected drug reached a peak vasodilatative effect, a second equal bolus of 43K was given and four additional scans recorded. The last scan from the first set was subtracted from the corresponding regional count rates of all serial scans from the second set, and the resulting images were interpreted to be myocardial perfusion patterns induced by the drug intervention. The later studies were performed by giving only a single isotope injection after administering the drug.
The control scans from dogs with partial stenosis or an Ameroid constrictor showed homogeneous distribution of the myocardial 43K. When drugs were used, the region supplied by compromised circulation became apparent because of lower counts when compared to the normally perfused ones. Coronary vasodilators, as opposed to postexercise in myocardial imaging, have a lesser effect on cardiac dynamics, peripheral hemodynamics, and also double the 43K uptake in normally perfused myocardium.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fam, W.M., McGregor, M.: Effects of coronary vasodilator drugs on retrograde flow in areas of chronic myocardial ischemia. Circ. Res. 15, 355–365 (1964)
Flameng, W., Schaper, W., Lewi, P.: Multiple experimental coronary occlusion without infarction. Am. Heart J. 85, 767–776 (1973)
Gould, K.L., Lipscomb, K., Hamilton, G.W.: Physiologic basis for assessing critical coronary stenosis: Instantaneous flow response and regional distribution during coronary hyperemia as measures of coronary flow reserve. Am. J. Cardiol. 33, 87–94 (1974)
Gould, K.L., Hamilton, G.W., Lipscomb, K., Ritchie, J.L., Kennedy, J.W.: Method for assessing stress-induced regional malperfusion during coronary arteriography: Experimental validation and clinical application. Am. J. Cardiol. 34, 557–564 (1974)
Khouri, E., Iza, A.: The effect of glyceryl trinitrate on coronary collateral flow. A preliminary report. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Current Topics in Coronary Research. 39, 191–196. New York: Plenum Press 1973
Linder, E., Seeman, T.: Effects of persantin and nitroglycerin on myocardial blood flow during temporary coronary occlusion in dogs. Angiologica 4, 225–255 (1967)
Linder, E.: Measurements of normal and collateral coronary blood flow by close-arterial and intramyocardial injection of Krypton-85 and Xenon-133. Acta Physiol. Scand. 68 (Suppl 272), 5–31 (1966)
Markov, A.K., Smith, R.O., Lehan, P.H., Flowers, Wm. M., Jr., Hellems, H.K., Keister, T.L.: Vasodilator induced myocardial perfusion patterns. Sou. Med. J. 67, 1379 (1974)
Markov, A.K., Smith, R.O., Keister, T.L., Michenfelder, J., Lehan, P.H., Hellems, H.K.: Pharmacologically induced heterogeneous myocardial blood flow detected with rapid rescanning. Medical Radionuclide Imaging 2, 243–254 IAEA (1977)
Markov, A.K., Smith, R.O., Lehan, P.H., Galyean, J.R., III, Rodriguez, G. and Hellems, H.K.: Detection of coronary artery disease with rapid serial rescanning with potassium-43 at rest. Am. J. Cardiol. 43, 778–786 (1979)
Schaper, W.K.A., Xhonneux, R., Jageneau, A.H.M. and Janssen, P.A.J.: The cardiovascular pharmacology of lidoflazine, a long-acting coronary vasodilator. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 152, 265–274 (1966)
Tauchert, M., Behrenbeck, D.W., Hötzel, J., Hilger, H.H.: Ein neuer pharmakologischer Test zur Diagnose der Koronorinsuffizienz. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 101, 35–37 (1976)
West, J.W., Bellet, S., Manzoli, U.C., Müller O.F.: Effects of persantin (RA8), a new coronary vasodilator, on coronary blood flow and cardiac dynamics in the dog. Circ. Res. 10, 35–44 (1962)
Winbury, M.M., Howe, B.B., Hefner, M.A.: Effect of nitrates and other coronary dilators on large and small coronary vessels: an hypothesis for the mechanism of action of nitrates. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 168, 70–95 (1969)
Zaret, B.L., Martin, N.D., McGowan, R.L., Strauss, H.W., Wells, H.P., Jr., Flamm, M.D., Jr.: Rest and exercise potassium-43 myocardial perfusion imaging for the non-invasive evaluation of aorto-coronary bypass surgery. Circulation 49, 688–695 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Markov, A.K., Smith, R.O., Oglethorpe, N.C. et al. The use of coronary vasodilators in myocardial imaging with 43K. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. 5, 75–84 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00261211
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00261211