Abstract
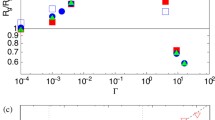
Biochemical and biophysical observations indicate that the erythrocyte membrane skeleton is composed of a swollen network of long, flexible and ionizable macromolecules located at the cytoplasmic surface of the fluid membrane lipid bilayer. We have analyzed the mechanochemical properties of the erythrocyte membrane assuming that the membrane skeleton constitutes an ionic gel (swollen ionic elastomer). Using recently established statistical thermodynamic theory for such gels, our analysis yields mathematical expressions for the mechanochemical properties of erythrocyte membranes that incorporate membrane molecular parameters to an extent not achieved previously. The erythrocyte membrane elastic shear modulus and maximum elastic extension ratio predicted by our membrane model are in quantitative agreement with reported values for these parameters. The gel theory predicts further that the membrane skeleton modulus of area compression, K G, may be small as well as large relative to the membrane elastic shear modulus, G, depending on the environmental conditions. Our analysis shows that the ratio between these two parameters affects both the geometry and the stability of the favoured cell shapes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bennett V (1982) The molecular basis for membrane-cytoskeleton association in human erythrocytes. J Cell Biochem 18:49–65
Bennett V, Davis J, Fowler WE (1982) Brain spectrin, a membrane-associated protein related in structure and function to erythrocyte spectrin. Nature 299:126–131
Ben-Ze'ev A, Duerr A, Solomon F, Penman S (1979) The outer boundary of the cytoskeleton: a lamina derived from plasma membrane proteins. Cell 17:859–865
Brailsford JD, Korpman RA, Bull BS (1976) The red cell shape from discocyte to hypotonic spherocyte — A mathematical delineation based on a uniform shell hypothesis. J Theor Biol 60:131–145
Branton D, Cohen CM, Tyler J (1981) Interaction of cytoskeletal proteins on the human erythrocyte membrane. Cell 24:24–32
Bull B (1972) The red cell biconcavity and deformability. A macromodel based on flow chamber observations. Nouv Rev Fr Hematol 12:835–844
Byers T, Branton D (1985) Visualization of the protein associations in the erythrocyte membrane skeleton. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:6153–6157
Canham PB (1970) The minimum energy of bending as a possible explanation of the biconcave shape of the human red blood cell. J Theor Biol 26:61–81
Cantor CR, Schimmel PR (1980) Biophysical chemistry, vol III. The behavior of biological macromolecules. WH Freeman, San Francisco
Chien S, Sung KLP, Skalak R, Usami S, Tøzeren A (1978) Theoretical and experimental studies on viscoelastic properties of erythrocyte membrane. Biophys J 24:463–487
Clarke M (1971) Isolation and characterization of a watersoluble protein from bovine erythrocyte membranes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 45:1063–1070
Cohen CM (1983) The molecular organization of the red cell membrane skeleton. Sem Hematol 20:141–158
Cohen CM, Tyler JM, Branton D (1980) Spectrin-actin associations studied by electron microscopy of shadowed preparations. Cell 21:875–883
Conrad MJ, Singer SJ (1979) Evidence for a large internal pressure in biological membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:5202–5206
Conrad MJ, Singer SJ (1981) The solubility of amphipathic molecules in biological membranes and lipid bilayers and its implications for membrane structure. Biochemistry 20: 808–818
Deuling HJ, Helfrich W (1976) Red blood cell shapes as explained on the basis of curvature elasticity. Biophys J 16: 861–868
Dunbar JC, Ralston GB (1981) Hydrodynamic characterization of the heterodimer of spectrin. Biochim Biophys Acta 667:177–184
Elgsaeter A (1978) Human spectrin. I. A classical light scattering study. Biochim Biophys Acta 536:235–244
Elgsaeter A, Branton D (1974) Intramembrane particle aggregation in erythrocyte ghosts. I. The effects of protein removal. J Cell Biol 63:1018–1030
Elgsaeter A, Shotton DM, Branton D (1976) Intramembrane particle aggregation in erythrocyte ghosts. II. The influence of spectrin aggregation. Biochim Biophys Acta 426:101–122
Evans EA (1973) New membrane concept applied to the analysis of fluid shear- and micropipette-deformed red blood cells. Biophys J 13:941–954
Evans EA (1983) Bending elastic modulus of red blood cell membrane derived from buckling instability in micropipet aspiration tests. Biophys J 43:27–30
Evans E, Buxbaum K (1981) Affinity of red blood cell membrane for particle surfaces measured by extent of particle encapsulation. Biophys J 34:1–12
Evans EA, La Celle PL (1975) Intrinsic material properties of the erythrocyte membrane indicated by mechanical analysis of deformation. Blood 45:29–43
Evans EA, Skalak R (1979) Mechanics and thermodynamics of biomembranes, Parts 1 and 2. Crit Rev Bioeng 3: 181–418
Flory PJ (1953) Principles of polymer chemistry. Cornell University Press, Ithaca, New York
Flory PJ (1976) Statistical thermodynamics of random networks. Proc R Soc London A 351:351–380
Flory PJ (1977) Theory of elasticity of polymer networks. The effect of local constraints on junctions. J Chem Phys 66: 5720–5729
Glenney JR Jr, Glenney P (1983) Fodrin is the general spectrin-like protein found in most cells whereas spectrin and the TW protein have a restricted distribution. Cell 34: 503–512
Goodman SR, Shiffer K (1983) The spectrin membrane skeleton of normal and abnormal erythrocytes: a review. Am J Physiol 244 (Cell Physiol 13): C121-C141
Gratzer WB (1983) The cytoskeleton of the red blood cell. In: Stracher A (ed) Muscle and nonmuscle motility. Academic Press, New York, pp 37–124
Gratzer WB (1984) More red than dead. Nature 310:368–369
Hartwig JH, Stossel TP (1981) Structure of macrophage acti-binding protein molecules in solution and interacting with actin filaments. J Mol Biol 145:563–581
Johnson RM, Robinson J (1976) Morphological changes in asymmetric erythrocyte membranes induced by electrolytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 70:925–931
Johnson RM, Taylor G, Meyer DB (1980) Shape and volume changes in erythrocyte ghosts and spectrin-actin networks. J Cell Biol 86:371–376
Kam Z, Josephs R, Eisenberg H, Gratzer WB (1977) Structural study of spectrin from human erythrocyte membranes. Biochemistry 16:5568–5572
Lange Y, Hadesman RA, Steck TL (1982) Role of the reticulum in the stability and shape of the isolated human erythrocyte membrane. J Cell Biol 92:714–721
Lemaigre-Dubreuil Y, Henry Y, Cassoly R (1980) Rotational dynamics of spectrin in solution and ankyrin bound in human erythrocyte membrane. FEBS Lett 113:231–234
Lemaigre-Dubreuil Y, Cassoly R (1983) A dynamical study on the interactions between the cytoskeleton components in the human erythrocyte as detected by saturation transfer electron paramagnetic resonance of spin-labeled spectrin, ankyrin, and protein 4.1. Arch Biochem Biophys 223: 495–502
Lis LJ, McAlister M, Fuller N, Rand RP, Parsegian VA (1982) Measurement of the lateral compressibility of several phospholipid bilayers. Biophys J 37:667–672
Liu SC, Palek J (1980) Spectrin tetramer-dimer equilibrium and the stability of erythrocyte membrane skeletons. Nature 285:586–588
Liu SC, Windisch P, Kim S, Palek J (1984) Oligomeric states of spectrin in normal erythrocyte membranes: Biochemical and electron microscopic studies. Cell 37:587–594
Luna EJ, Fowler VM, Swanson J, Branton D, Taylor DL (1981) A membrane cytoskeleton from Dictyostelium discoideum. I. Identification and partial characterization of an actin-binding activity. J Cell Biol 88:396–409
Mescher MF, Jose MJL, Balk SP (1981) Actin-containing matrix associated with the plasma membrane of murine tumour and lymphoid cells. Nature 289:139–144
Morrow JS, Marchesi VT (1981) Self-assembly of spectrin oligomers in vitro: A basis for a dynamic cystoskeleton. J Cell Biol 88:463–468
Mikkelsen A, Elgsaeter A (1978) Human spectrin. II. An electro-optic study. Biochim Biophys Acta 536:245–251
Mikkelsen A, Elgsaeter A (1981) Human spectrin. V. A comparative electro-optic study of heterotetramers and heterodimers. Biochim Biophys Acta 668:74–80
Mikkelsen A, Stokke BT, Elgsaeter A (1984) An electro-optic study of human erythrocyte spectrin dimers. The presence of calcium ions does not alter spectrin flexibility. Biochim Biophys Acta 786:95–102
Nelson WJ, Lazarides E (1983) Expression of the β subunit of spectrin in nonerythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:363–367
Nicolson GL, Marchesi VT, Singer SJ (1971) The localization of spectrin on the inner surface of human red blood cell membranes by ferritin-conjugated antibodies. J Cell Biol 51:265–272
Papahadjopoulos D (1968) Surface properties of acidic phospholipids: Interaction of monolayers and hydrated liquid crystals with uni- and bivalent metal ions. Biochim Biophys Acta 163:240–254
Pinto da Silva P (1972) Translational mobility of the membrane intercalated particles of human erythrocyte ghosts. pH-dependent, reversible aggregation. J Cell Biol 53: 777–787
Ralston GB (1976) Physico-chemical characterization of the spectrin tetramer from bovine erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 455:163–172
Reich MH, Kam Z, Eisenberg H, Worcester D, Ungewickell E, Gratzer WB (1982) Solution scattering studies of dimeric and tetrameric spectrin. Biophys Chem 16:307–316
Scanus E, Booth S, Hallaway B, Rosenberg A (1985) The elasticity of spectrin-actin gels at high protein concentration. J Biol Chem 260:3724–3730
Schliwa M (1982) Action of cytochalasin D on cytoskeletal networks. J Cell Biol 92:79–91
Sheetz MP, Singer SJ (1974) Biological membranes as bilayer couples. A molecular mechanism of drug-erythrocyte interactions. Proc natl Acad Sci USA 71:4457–4461
Shotton DM, Burke BE, Branton D (1979) The molecular structure of human erythrocyte spectrin. Biophysical and electron microscopic studies. J Mol Biol 131:303–329
Siegel DL, Branton D (1985) Partial purification and characterization of an actin-bundling protein, band 4.9, from human erythrocytes. J Cell Biol 100:775–785
Skalak R, Tozeren A, Zarda RP, Chien S (1973) Strain energy function of red blood cell membranes. Biophys J 13: 245–264
Speicher DW, Marchesi VT (1984) Erythrocyte spectrin is comprised of many homologues triple helical segments. Nature 311:177–180
Steck TL (1974) The organization of proteins in the human red blood cell membrane. J Cell Biol 62:1–19
Stokke BT, Elgsaeter A (1981) Human spectrin. VI. A viscometric study. Biochim Biophys Acta 640:640–645
Stokke BT, Mikkelsen A, Elgsaeter A (1985a) Human erythrocyte spectrin dimer intrinsic viscosity: Temperature dependence and implications for the molecular basis of the erythrocyte membrane free energy. Biochim Biophys Acta 816:102–110
Stokke BT, Mikkelsen A, Elgsaeter A (1985b) Some viscoelastic properties of human erythrocyte spectrin end-linked in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta 816:111–120
Stokke BT, Mikkelsen A, Elgsaeter A (1986) The human erythrocyte membrane skeleton may be an ionic gel. II. Numerical analyses of cell shapes and shape transformations. Eur Biophys J 13:219–233
Tanaka T, Fillmore D, Sun ST, Nishio I, Swislow G, Shah A (1980) Phase transitions in ionic gels. Phys Rev Lett 45: 1636–1639
ter Haar D, Wergeland H (1966) Elements of thermodynamics. Addison_Wesley, London
Treloar LRG (1975) The physics of rubber elasticity. 3rd edit. Clarendon Press, Oxford
Tyler JM, Anderson JM, Branton D (1980) Structural comparison of several actin-binding macromolecules. J Cell Biol 85:489–495
Ungewickell E, Gratzer W (1978) Self-association of human spectrin. A thermodynamic and kinetic study. Eur J Biochem 88:379–385
Waugh R, Evans EA (1979) Thermoelasticity of red blood cell membrane. Biophys J 26:115–132
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stokke, B.T., Mikkelsen, A. & Elgsaeter, A. The human erythrocyte membrane skeleton may be an ionic gel. Eur Biophys J 13, 203–218 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00260368
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00260368