Summary
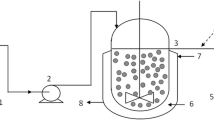
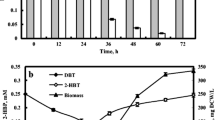
For the investigation of a mixed anaerobic and aerobic degradation of xenobiotics the reductive dechlorination of 1,1,1-trichloro-2,2-bis (4-chlorophenyl)ethane (DDT) to 1,1-dichloro-2,2-bis (4-chlorophenyl)ethane (DDD) and the oxidative degradation of the DDT-conversion product 4,4′-dichlorodiphenylmethane (DDM) were studied. Enrichments from digested sewage sludge led to the isolation of an Enterobacter cloacae-strain which is able to reductive dechlorination of DDT during the fermentation of lactose. From fresh sewage sludge 11 bacterial strains were isolated in batch-culture and in continuous culture utilizing diphenylmethane, a non chlorinated structural analogon of DDM, as sole source of carbon and energy. One of these isolates, Alcaliaenes sp. cometabolizes DDM during the aerobic growth with diphenylmethane. By coimmobilization of Alcaligenes sp. and Enterobacter cloacae in Ca-alginate a system could be established, in which the reductive dechlorination of DDT and the oxidative degradation of DDM and diphenylmethane proceeds simultaneously in one reactor vessel.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bettmann H, Rehm H-J (1985) Continuous degradation of phenol(s) by Pseudomonas putida P8 entrapped in polyacrylamide gel. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 22:389–393
Bettmann H (1985) Abbau von Phenolen durch eingeschlossene Mikroorganismen. Ph. D. Thesis, University of Münster, FB Biologie
Beunink J (1987) Aufbau eines Systems zum aeroben und anaeroben Abbau von Dichlordiphenyltrichlorethan mit immobilisierten Mikroorganismen. Diploma-Thesis, University of Münster, FB Biologie
Dorn E, Hellwig M, Reineke W, Knackmuss H-J (1974) Isolation and characterisation ofa 3-chlorobenzoate degrading Pseudomonad. Arch Microbiol 99:61–70
Eikmeier H, Rehm H-J (1987) Stability of calcium-alginate during citric acid production of immobilized Aspergillus niger. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 26:105–111
Esaac EG, Matsumura F (1980) Metabolism of insecticides by reductive systems. Pharm Ther 9:1–26
Focht DD (1972) Microbial degradation of DDT metabolites to carbon dioxide, water and chloride. Bull Environ Cont Toxicol 7:51–56
Focht DD, Alexander M (1970a) DDT metabolites and analogs: ring fission by Hydrogenomonas. Science 170:91–92
Focht DD, Alexander M (1970b) Bacterial degradation of diphenylmethane, a DDT-model-substrate. Appl Microbiol 20:608–611
Focht DD, Alexander M (1971) Aerobic cometabolism of DDT analogues by Hydrogenomonas sp. J Agric Food Chem 19:20–22
Gosmann B, Rehm H-J (1986) Oxygen uptake of microorganisms entrapped in Ca-alginate. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 23:163–167
Guenzi WD, Beard WE (1968) Anaerobic conversion of DDT to DDD and aerobic stability of DDT in soil. Proc Soil Sci Soc Americ 32:522–524
Iwasaki I, Utsumi S, Ozawa T (1952) New colorimetric determination of chloride using mercuric thiocyanate and ferric ion. Bull Chem Soc Jap 25:226
Iwasaki I, Utsumi S, Hagino K, Ozawa T (1956) A new spectrophotometric method for the determination of small amounts of chloride using the mercuric thiocyanate method. Bull Chem Soc Jap 29:860–864
Kuek C, Armitage TM (1985) Scanning electron microscopic examination of calcium alginate beads immobilizing growing mycelia of Aspergillus phoenicus. Enz Microbiol Technol 7:121–125
Lal R, Saxena DM (1982) Accumulation, metabolism, and effects of organochlorine insecticides on microorganisms. Microbiol Rev 46:95–127
Nickerson WJ, Strauss G (1960) The photochemical cleavage of water by riboflavine.J Amer Chem Soc 82:5007–5008
Pfaender FK, Alexander M (1972) Extensive microbial degradation of DDT in vitro and DDT metabolism by natural communities. J Agric Food Chem 20:842–846
Pfaender FK, Alexander M (1973) Effect of nutrient additions on the apparent cometabolism of DDT. J Agric Food Chem 21:397–399
Pfeiffer P, Radler F (1985) Hochleistungsflüssigkeitschromatographische Bestimmung von organischen Säuren, Zuckern, Glycerin und Alkohol im Wein an einer Kationenaustauschersäule. Z Lebensm Unters Forsch 181:24–27
Pfennig N, Lippert KD (1966) Über das Vitamin B12-Bedürfnis phototropher Schwefelbakterien. Arch Microbiol 55:245–256
Schwien U, Schmidt E (1982) Improved degradation of monochlorophenols by a constructed strain. Appl Environ Microbiol 44:33–39
Tanaka H, Kurosawa H, Murakami H (1986) Ethanol production from starch by a coimmobilized mixed culture system of Aspergillus awamori and Zymomonas mobilis. Biotechnol Bioeng 28:1761–1768
Tilton RC (1981) The genus Alcaligenes. In: Starr MP, Stolp H, Trüper HG, Balows A, Schlegel HG (eds) The procaryotes. Springer Heidelberg New York Berlin, p 856
Wittler R, Baumgärtl H, Lübbers DW, Schügerl K (1986) Investigations of oxygen transfer into Penicillium chrysogenum pellets by microprobe measurements. Biotechnol Bioeng 28:1024–1036
Woodwell GM, Craig PP, Johnson AA (1971) DDT in the biosphere: where does it go? Science 74:1101–1107
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beunink, J., Rehm, HJ. Synchronous anaerobic and aerobic degradation of DDT by an immobilized mixed culture system. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 29, 72–80 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00258354
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00258354