Summary
Subject: In urological patients the value of quantitative glucose measurement in urine as a screening test for urinary tract infections is examined.
Method: Glucose content, species and concentration of microorganisms in the urine of 334 urological patients were analysed and the bacteriological findings compared with the result of chemical measurement.
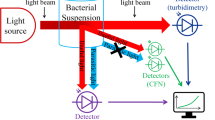
In vitro, the dependence of bacterial growth on different properties of urine was examined.
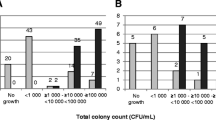
Results: A diagnostic decrease in glucose concentration was found in only about 48% of the infected urines. The result of the glucose test is influenced unfavourably by humerous factors which cannot be standardized.
Conclusions: In its present form, this method is not yet suitable for use as a reliable screening test for urological patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apthorp, G. H.: Investigation of the sugar content of urine from normal subjects and patients with renal and hepatic disease by paper chromatography. J. clin. Path. 10, 84 (1957)
Asscher, A. W., Sussman, M., Waters, W. E., Harvard-Davis, R.: Urine as medium for bacterial growth. Lancet 1966 II, 1037
Barthelmai, W., Czok, R.: Enzymatische Bestimmungen der Glucose in Blut, Liquor and Harn. Klin. Wschr. 40, 585 (1962)
Fine, J.: Glucose content of normal urine. Brit. med. J. 1965 I, 1209
Fritz, H., Köhler, L., Schersten, B.: Assessment of subnormal urinary glucose as an indicator of bacteriuria in population studies. Acta med. scand. (Suppl.) 504 (1969)
Granitzka, S., Hirsch, H. A.: Glucosenachweis im Urin als Screening-Test für Harnwegsinfektionen. Dtsch. med. Wschr. 96, 581 (1971)
Hirsch, H. A.: Screening-Tests zur Erfassung von Bakteriurien. Dtsch. med. Wschr. 95, 1532 (1970)
Matsaniotis, N., Danelatou-Athanassiadou, D., Katerelos, C., Hartokalis, P., Apostolopoulou, E.: Low urinary glucose concentration: A reliable index of urinary tract infection. J. Pediat. 78, 851 (1971)
Petersdorf, R. G., Harter, D. H.: The fall in cerebrospinal fluid sugar in meningitis. Arch. Neurol. 4, 21 (1961)
Renschler, H. E., Weicker, H., von Baeyer, H.: Die obere Normgrenze der Glucosekonzentration im Urin Gesunder. Dtsch. med. Wschr. 90, 2349 (1965)
Scherstén, B.: Subnormal fasting urinary glucose as an indicator of urinary tract infection, Lund: Studentliteratur 1969.
Scherstén, B., Dahlqvist, A., Fritz, H., Köhler, L., Westlund, L.: Screening for bacteriuria with a test paper for glucose. J. Amer. med. Ass. 204, 205 (1968)
Scherstén, B., Fritz, H.: Subnormal levels of glucose in urine: A sign of urinary tract infection. J. Amer. med. Ass. 201, 129 (1967)
Weicker, H., Schönthal, H., Renschler, H. E.: Über physiologische Glucose-Ausscheidung im Urin von Stoffwechsel-Gesunden. Klin. Wschr. 41, 201 (1963)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zimmerman, A., Ansorg, R. & Truss, F. Quantitative glucose measurement in urine as screening test for urinary tract infections. Urol. Res. 1, 131–136 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00257377
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00257377