Summary
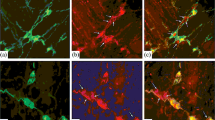
The ultrastructural localization and relations of substance P- and met-enkephalin-labeled neuronal structures were examined in the wall of the human gastric antrum during early fetal life. By 14–16 weeks of gestation, clearly discernable neural plexuses and a well developed external muscle coat were present. In the submucous coat, neural plexuses varied from immature forms consisting of 1–4 neurites partially enveloped by Schwann cell processes to more mature plexuses where neurons were completely enclosed by Schwann cell processes. Neuronal profiles with substance P- and met-enkephalin-like immunoreactivities were observed in the submucous plexus. In the myenteric plexus met-enkephalin-like immunoreactivity was seen within cell bodies and neurites. By contrast, although substance P-like immunoreactivity was observed in neurites in the myenteric plexus, no substance P-labeled somata could be identified. Unlabeled terminals were seen in contact with both unlabeled dendrites and met-enkephalinergic neurons. An increase in electron density was observed at the sites of contact. These structures probably represent early stages in the development of synaptic specializations. In addition, met-enkephalin-labeled varicosities were seen in apposition to smooth muscle cells of the circular muscle coat. This suggests that antral smooth muscle cells are directly innervated by met-enkephalin neurons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alumets J, Hakanson R, Sundler F, Chang J (1978) Leu-enkephalin-like material in nerves and enterochromaffin cells in the gut. Histochemistry 56:187–196
Baumgarten HG, Holstein AF, Owman C (1970) Auerbach's plexus of mammals and man: Electron microscopic identification of three different types of neuronal processes in myenteric ganglia of the large intestine from rhesus monkey, guinea-pigs and man. Z Zellforsch 106:376–397
Cook RD, Burnstock G (1976) The ultrastructure of Auerbach's plexus in the guinea pig. I. Neuronal elements. J Neurocytol 5:171–194
Costa M, Cuello AC, Furness JB, Franco R (1980) Distribution of enteric neurones showing immunoreactivity for substance P in the guinea-pig ileum. Neuroscience 5:323–331
Costa M, Furness JB, Llewellyn-Smith IJ, Cuello AC (1981) Projection of sub P containing neurones with the guinea-pig small intestine. Neuroscience 6:411–424
Dewey MM, Barr L (1964) A study of structure and distribution of the nexus. J Cell Biol 23:553–585
Edin R, Lundberg J, Terenius L, Dahlstrom A, Hokfelt T, Kewenter J, Ahlman H (1980) Evidence for vagal enkephalinergic neural control of the feline pylorus and stomach. Gastroenterology 78:492–497
Epstein ML, Hudis J, Dahl JL (1983) The development of peptidergic neurones in the foregut of the chick. J Neurosci 3:2431–2447
Féhér C, Léranth C (1983) Light and electronmicroscospic immunocytochemical localization of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, VIP-like activity in the rat small intestine. Neuroscience 10:97–106
Franco R (1980) The effect of substance P on the circular muscle of the intestine: Evidence that substance P stimulates cholinergic nerves. Proc Austral Physiol Pharmacol Soc 11:17
Furness JB, Costa M (1980) Types of nerves in the enteric nervous system. Neuroscience 5:1–20
Furness JB, Costa M, Miller RJ (1983) Distribution and projections of nerves with enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in the guinea-pig small intestine. Neuroscience 8:653–664
Gabella G (1972) Fine structure of the myenteric plexus in guinea pig ileum. J Anat 111:69–97
Gabella G (1979) Innervation of the gastrointestinal tract. Int Rev Cytol 59:129–193
Gabella G (1982) On the ultrastructure of the enteric nerve ganglia. In: Polak JM, Bloom SR, Wright NA, Daly MJ (eds) Scand J Gastroenterology, Suppl 71, pp 15–25
Gershon MD, Thompson EB (1973) The maturation of neuromuscular function in a multiply innervated structure: Development of the longitudinal smooth muscle of the foetal mammalian gut and its cholinergic excitatory, adrenergic inhibitory, and non-adrenergic inhibitory innervation. J Physiol (London) 234:257–277
Gershon MD, Sherman D, Gintzler AR (1981) An ultrastructural analysis of the developing enteric nervous system of the guinea pig small intestine. J Neurocytol 10:271–296
Holzer P, Lembeck F (1980) Neurally mediated contraction of ileal longitudinal muscle by substance P. Neurosci Lett 17:101–105
Holzer P, Lembeck F, Donnever J (1980) Caerulein, substance P, serotonin and cholinomimetics induce rhythmic contractions of the intestinal muscle. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 313:131–137
Hoyes AD, Barber P (1980) Axonal terminal ultrastructure in the myenteric ganglia of the guinea pig stomach. Cell Tissue Res 209:329–343
Jaffe JH, Martin WR (1975) Narcotic analgesics and antagonists. In: Goodman LS, Gilman A (eds) The pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 5th ed Macmillan, New York, pp 245–254
Katayama Y, North RA, Williams JT (1979) The action of substance P on neurons of the myenteric plexus of the guinea pig small intestine. Proc R Soc London 206:191–208
Larsson LI, Stengaard-Pedersen K (1982) Immunocytochemical and ultrastructural differentiation between met-enkephalin, leuenkephalin, met/leu-enkephalin-immunoreactive neurones of feline gut. J Neurosci 2:861–878
Linnoila RI, Di Augustine RP, Miller RJ, Chang KJ, Cautrecasas P (1978) An immunochistochemical and radioimmunological study of the distribution of (met5)- and (Leu5)-enkephalin in the gastrointestinal tract. Neuroscience 3:1187–1196
Llewellyn-Smith IJ, Wilson AJ, Furness JB, Costa M, Rush RA (1981) Ultrastructural identification of noradrenergic axons and their distribution within the enteric plexuses of the guineapig small intestine. J Neurocytol 10:331–352
Llewellyn-Smith IJ, Furness JB, Murphy R, O'Brien PE, Costa M (1984a) Substance P — containing nerves in the human small intestine. Gastroenterology 86:421–425
Llewellyn-Smith IL, Furness JB, O'Brien PE, Costa M (1984b) Noradrenergic nerves in human small intestine. Gastroenterology 87:513–529
Nilsson G, Larsson LI, Hakanson R, Brodin E, Pernow B, Sundler F (1975) Localization of substance P-like immunoreactivity in mouse gut. Histochemistry 43:97–99
Okamato E, Ueda T (1967) Embryogenesis of intramural ganglia of the gut and its relation to Hirschsprung's disease. J Pediat Surg 3:437–443
Padykula HA (1979) The digestive tract: In: Weiss L, Greep RO (eds) Histology. McGraw Hill Book Company, USA, pp 643–763
Pearse AGE, Polak JM (1975) Immunohistochemical localization of substance P in mammalian intestine. Histochemistry 41:373–375
Pick J, De Lemos C, Cianella A (1967) Fine structure of nerve terminals in the human gut. Anat Rec 159:131–146
Probert L, De Mey J, Polak JM (1983) Ultrastructural localization of four different neuropeptides within separate populations of P-type nerves in the guinea pig colon. Gastroenterology 85:1094–1104
Read JB, Burnstock G (1970) Development of the adrenergic innervation and chromaffin cells in the human fetal gut. Dev Biol 22:513–534
Richardson KC (1958) Electron microscopic observations on Auerbach's plexus in the rabbit, with special reference to the problem of smooth muscle innervation. Am J Anat 103:99–135
Saffrey MJ, Polak JM, Burnstock G (1982) Distribution of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide-substance P-enkephalin and neurotensin-like immunoreactive nerves in the chicken gut during development. Neuroscience 7:279–293
Schultzberg M, Hökfelt T, Nilsson G, Terenius L, Rehfeld JF, Brown N, Elde R, Goldstein M, Said S (1980) Distribution of peptide and catecholamine containing neurones in the gastrointestinal tract of rat and guinea pig: immunohistochemical studies with antisera to substance P, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, enkephalins, somatostatin, gastrin/cholecystokinin, neurotensin and dopamine beta-hydroxylase. Neuroscience 5:689–744
Stefanini M, DeMartino C, Zamboni L (1967) Fixation of ejaculated spermatozoa for electron microscopy. Nature (Lond) 216:173–174
Sternberger LA (1979) Immunocytochemistry, 2nd Edition. John Wiley, New York
Sundler F, Hàkanson R, Larsson LI, Brodin E, Nilsson G (1977) Substance P in the gut. An immunochemical and immunohistochemical study of its distribution and development. In: Von Euler US, Pernow B (eds) Substance P. Raven Press, New York, pp 59–65
Uddman R, Alumets J, Håkanson R, Sundler F, Walles B (1980) Peptidergic (enkephalin) innervation of the mammalian oesophagus. Gastroenterology 78:732–737
Wilson AJ, Furness JB, Costa M (1981a) The fine structure of the submucous plexus of the guinea pig ileum. I. The ganglia, neurons, Schwann cells and neuropil. J Neurocytol 10:759–784
Wilson AJ, Furness JB, Costa M (1981b) The fine structure of the submucous plexus of the guinea pig ileum. II. Description and analysis of vesiculated nerve profiles. J Neurocytol 10:785–804
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kapadia, S.E., Kapadia, C.R. Ultrastructure and localization of substance P and met-enkephalin immunoreactivity in the human fetal gastric antrum. Cell Tissue Res. 243, 289–297 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00251042
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00251042