Summary
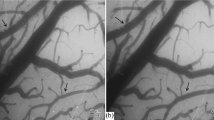
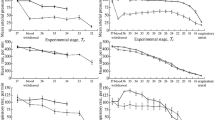
A new photochemical method was employed to cause disorders in the inner ear's microcirculation, using the rat as an animal model. Hearing loss was used as a measure for establishing the altered microcirculation. Under pentobarbital anesthesia, the middle ear was opened by a ventral approach. The lateral wall of the cochlea was then illuminated with a filtered xenon lamp (wavelength 540 nm) while rose bengal was infused intravenously. Photoactivated rose bengal produces oxygen radicals and oxygen singlets, which subsequently damage the vascular epithelium to cause the adhesion and aggregation of platelets in the small vessels. Disintegration of the inner ear hair cells at the irradiated site became evident 24 h after the illumination. These findings further suggest that the photochemical occlusion in the inner ear's microcirculation led to ischemic damage of the stria vascularis and the hair cells in the inner ear. When the action potential (AP) of the cochlea was measured with an electrocochleogram a gradual decrease occurred after the illumination. When acetylsalicylic acid was injected intravenously before treatment, the time required to completely suppress the AP was prolonged in a dose-dependent manner. Findings indicate that our method causes a photochemically induced occlusion in the inner ear's microcirculation and is therefore potentially useful for evaluating the various effects of drugs on the ear.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barna BP, Hughes GB (1988) Autoimmunity and otologic disease: clinical and experimental aspects. Clin Lab Med 8:385–398
Dietrich WD, Watson BR, Busto R, Grinsberg MD, Bethea JR (1987) Photochemically induced cerebral infarction. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 72:315–325
Igarashi M, Alford BR, Konishi S, Shaver EF, Guilford FR (1969) Functional and histopathological correlations after microembolism of the peripheral labyrinthine artery in the dog. Laryngoscope 79:603–623
Jaffe BF (1975) Hypercoagulation and other causes of sudden hearing loss. Otolaryngol Clin North Am 8:395–403
Johnson A, Hawke M, Berger G (1984) Sudden deafness and vertigo due to inner ear hemorrhage — a temporal bone case report. J Otolaryngol 13:201–207
Johnsson LG, Hawkins JE Jr (1972) Vascular changes in the human inner ear associated with aging. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 81: 364–376
Kimura RS, Perlman HB (1958) Arterial obstruction of the labrinth.l. Cochlear changes. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 67: 5–25
Nanda SK, Hatchell DL, Tiedeman JS, Dutton JJ, Hatchell MC, McAdoo T (1987) A new method for vascular occlusion. Arch Ophthalmol 105:1121–1124
Pooler JP, Valenzeno DP (1981) Dye-sensitized photodynamic inactivation of cells. Med Phys 8:614–628
Schuknecht HF, Kimura RS, Naufal PM (1973) The pathology of sudden deafness. Acta Otolaryngol (Stockh) 76:75–97
Watson BD, Dietrich WD, Busto R, Wachetel MS, Ginsberg MD (1985) Induction of reproducible brain infarction by photochemically initiated thrombosis. Ann Neurol 17:497–504
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: K. Umemura, Department of Pharmacology, Hamamatsu University School of Medicine, 3600 Handa-cho, Hamamatsu 431-31, Japan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Umemura, K., Kohno, Y., Matsuno, H. et al. A new model for photochemically induced thrombosis in the inner ear microcirculation and the use of hearing loss as a measure for microcirculatory disorders. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 248, 105–108 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00240231
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00240231