Abstract
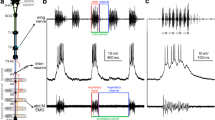
We investigated the modulatory role of a radular mechanoreceptor (RM) in the feeding system of Incilaria. RM spiking induced by current injection evoked several cycles of rhythmic buccal motor activity in quiescent preparations, and this effect was also observed in preparations lacking the cerebral ganglia. The evoked rhythmic activity included sequential activation of the inframedian radular tensor, the supramedian radular tensor, and the buccal sphincter muscles in that order.
In addition to the generation of rhythmic motor activity, RM spiking enhanced tonic activities in buccal nerve 1 as well as in the cerebrobuccal connective, showing a wide excitatory effect on buccal neurons. The excitatory effect was further examined in the supramedian radular tensor motoneuron. RM spiking evoked biphasic depolarization in the tensor motoneuron consisting of fast excitatory postsynaptic potentials and prolonged depolarization lasting after termination of RM spiking. These depolarizations also occurred in high divalent cation saline, suggesting that they were both monosynaptic.
When RM spiking was evoked in the fictive rasp phase during food-induced buccal motor rhythm, the activity of the supramedian radular tensor muscle showed the greatest enhancement of the three muscles tested, while the rate of ongoing rhythmic motor activity showed no increase.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CPG :
-
central pattern generator
- EPSP :
-
excitatory postsynaptic potential
- RBMA :
-
rhythmic buccal motor activity
- RM :
-
radular mechanosensory neuron
- SMT :
-
supramedian radular tensor neuron
References
Benjamin PR, Elliott CJH (1989) Snail feeding oscillator: The central pattern generator and its control by modulatory interneurons. In: Jacklet JW (ed) Neuronal and cellular oscillators. Marcel Dekker, New York Basel, pp 173–214
Cohen JL, Weiss KR, Kupfermann I (1978) Motor control of buccal muscles in Aplysia. J Neurophysiol 41: 157–180
Delaney K, Gelperin A (1990a) Cerebral interneurons controlling fictive feeding in Limax maximus. II. Initiation and modulation of fictive feeding. J Comp Physiol A 166: 311–326
Delaney K, Gelperin A (1990b) Cerebral interneurons controlling fictive feeding in Limax maximus. III. Integration of sensory inputs. J Comp Physiol A 166: 327–343
Demian ES (1962) Comparative morphological studies on the buccal mass of the Lymnaeacea. Goteborgs K Vetensk-Vitterh — Samh Handl 9B: 1–30
Dorsett DA, Sigger JN (1981) Sensory fields and properties of the oesophageal proprioceptors in the mollusc, Philine. J Exp Biol 94: 77–93
Elliott CJH, Benjamin PR (1985) Interaction of the slow oscillator interneuron with feeding pattern-generating interneurons in Lymnaea stagnalis. J Neurophysiol 54: 1412–1421
Elliott CJH, Benjamin PR (1989) Esophageal mechanoreceptors in the feeding system of the pond snail, Lymnaea stagnalis. J Neurophysiol 61: 727–736
Gardner D (1977) Interconnections of identified multiaction interneurons in buccal ganglia of Aplysia. J Neurophysiol 40: 349–361
Gillette R, Gillette MU, Davis WJ (1980) Action-potential broadening and endogenously sustained bursting are substrates of command ability in a feeding neuron of Pleurobranchaea. J Neurophysiol 43: 669–685
Jahan-Parwar B, Wilson AH, Fredman SM (1983) Role of proprioceptive reflexes in control of feeding muscles of Aplysia. J Neurophysiol 49: 1469–1480
Kater SB (1974) Feeding in Helisoma trivolvis: The morphological and physiological bases of fixed action pattern. Am Zool 14: 1017–1036
Kater SB, Rowell CHF (1973) Integration of sensory and centrally programmed components in generation of cyclical feeding activity of Helisoma trivolvis. J Neurophysiol 36: 142–155
Kawahara S, Shimizu H (1991) Radular mechanosensory neuron and feeding motor rhythm of Incilaria fruhstorferi (in Japanese). Biophysics 31: S234
Kawahara S, Yano M, Shimizu H (1993) Modulation of the feeding system by radular mechanosensory neuron in Incilaria. Zool Sci 10 (supplement): 86
Kawahara S, Yano M, Shimizu H (1994) Radular mechanosensory neuron in the buccal ganglia of the terrestrial slug, Incilaria fruhstorferi. J Comp Physiol A 174: 111–120
Kovac MP, Matera EM, Volk PJ, Davis WJ (1986) Food avoidance learning is accompanied by synaptic attenuation in identified interneurons controlling feeding behavior in Pleurobranchaea. J Neurophysiol 56: 891–905
Nagahama T, Takata M (1989) Neural mechanism generating firing patterns in jaw motoneurons during the food-induced response in Aplysia kurodai. I. Identification and characterization of premotor neurons. J Comp Physiol A 166: 143–150
Nagahama T, Takata M (1990) Neural mechanism generating firing patterns in jaw motoneurons during the food-induced response in Aplysia kurodai. II. Functional role of premotor neurons on generation of firing patterns in motoneurons. J Comp Physiol A 166: 277–286
Plummer MR, Kirk MD (1990) Premotor neurons B51 and B52 in the buccal ganglia of Aplysia californica: Synaptic connections, effects on ongoing motor rhythms, and peptide modulation. J Neurophysiol 63: 539–558
Quinlan EM, Murphy AD (1991) Glutamate as a putative neurotransmitter in the buccal central pattern generator of Helisoma trivolvis. J Neurophysiol 66: 1264–1271
Reingold SC, Gelperin A (1980) Feeding motor programme in Limax. II. Modulation by sensory inputs in intact animals and isolated central nervous systems. J Exp Biol 85: 1–19
Rose RM, Benjamin PR (1979) The relationship of the central motor pattern to the feeding cycle of Lymnaea stagnalis. J Exp Biol 80: 137–163
Senseman DM (1978) Short-term control of food intake by the terrestrial slug Ariolimax. J Comp Physiol A 124: 37–48
Siegler MVS (1977) Motor neurone coordination and sensory modulation in the feeding system of the mollusc Pleurobranchaea californica. J Exp Biol 71: 27–48
Smith DA (1988) Radular kinetics during grazing in Helisoma trivolvis (Gastropoda: Pulmonata). J Exp Biol 136: 89–102
Smith DA (1990) Comparative buccal anatomy in Helisoma (Mollusca, Pulmonata, Basommatophora). J Morphol 203: 107–116
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawahara, S., Yano, M. & Shimizu, H. Modulation of the feeding system by a radular mechanosensory neuron in the terrestrial slug, Incilaria fruhstorferi . J Comp Physiol A 176, 193–203 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00239922
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00239922