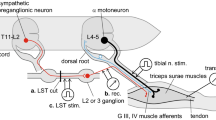
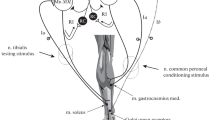
Summary
Effects of repetitive stimulation of the contralateral caudate nucleus on the static discharge and dynamic sensitivity of soleus muscle spindle primary and secondary endings were studied in cats anaesthetized with Halothane (Fluothane). By progressive increasing the depth of anaesthesia two different fusimotor effects could be observed.
-
1.
A static facilitatory effect; under light anaesthesia the static discharge of primary and secondary endings were strongly increased. The response of the primary endings to phasic stretch of the muscle was generaly decreased.
-
2.
A depressant effect; under deep anaesthesia the static discharge of primary and secondary endings were decreased. The dynamic sensitivity of the primary endings was lightly increased or remained unaltered.
The ventro-lateral part of the caudate nucleus is mainly responsible for these effects.
Caudate nucleus fusimotor effects were compared with those induced by gamma dynamic and gamma static fibers stimulations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Références
Appelberg, B.: Muscle spindles in a flexion reflexe elicited by natural stimulation. Acta physiol. scand. 89, 145–153 (1973)
Appelberg, B., Bessou, P., Laporte, Y.: Action of static and dynamic fusimotor fibres on secondary endings of cat's spindles. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 185, 160–171 (1966)
Appelberg, B., Emonet-Denand, E.: Central control of static and dynamic sensitivities of muscle spindle primary endings. Acta physiol. scand. 63, 487–494 (1965)
Appelberg, B., Molander, C.: A rubro-olivary pathway. I. Identification of a descending system for control of the dynamic sensitivity of muscle spindles. Exp. Brain Res. 3, 372–381 (1967)
Bessou, P., Laporte, Y., Pages, B.: Frequencygrams of spindle primary endings elicited by stimulation of static and dynamic fusimotor fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 196, 47–64 (1968)
Bessou, P., Pages, B.: Spindle secondary ending responses elicited by stimulation of static fusimotor axons. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 202, 569–585 (1969)
Crowe, A., Matthews, P.B.C.: The effects of stimulation of static and dynamic fusimotor fibres on the response to stretching of the primary endings of muscle spindles. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 174, 109–131 (1964a)
Crowe, A., Matthews, P.B.C.: Further studies of static and dynamic fusimotor fibres. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 174, 132–151 (1964b)
Durkovic, R. G., Piwonka, R.W., Preston, J.P.: Cortical modulation of spindle afferent discharge patterns in the pyramidal cat. Brain Res. 40, 171–179 (1972)
Granit, R., Kaada, B.R.: Influence of stimulation of central nervous structures on muscle spindles in cat. Acta physiol. scand. 27, 130–160 (1952)
Harvey, R. J., Matthews, P.B. C.: The response of de-efferented muscle spindle endings in the cat's soleus to slow extension of the muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 157, 370–393 (1961)
Jansen, J.K.S., Matthews, P.B.C.: The central control of the dynamic response of muscle spindle receptors. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 161, 357–378 (1962)
Laporte, Y.: Un fréquencemétre instantané simplifié. J. Physiol. (Paris) 56, 592 (1964)
Matthews, B.H.C.: Nerve endings in mammalian muscle. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 78, 1–53 (1933)
Matthews, P.B.C.: The differenciation of two types of fusimotor fibres by their effects on the dynamic response of muscle spindle primary endings. Quart. J. exp. Physiol. 47, 324–333 (1962)
Matthews, P.B.C.: Apparatus for studying the response of muscle spindles to stretching. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 169, 58P (1963)
McPhedran, A.M., Wuerker, R.B., Henneman, E.: Properties of motor units in a homogenous red muscle (Soleus) of the cat. J. Neurophysiol. 28, 71–84 (1965)
Shimazu, H., Hongo, T., Kubota, K.: Two types of central influences on gamma motor system. J. Neurophysiol. 25, 309–323 (1962)
Vedel, J.P., Mouillac-Baudevin, J.: Contrôle de l'activité des fibres fusimotrices dynamiques et statiques par la formation réticulée mésencéphalique chez le Chat. Exp. Brain Res. 9, 307–324 (1969a)
Vedel, J.P., Mouillac-Baudevin, J.: Etude fonctionnelle du contrôle de l'activité des fibres fusimotrices dynamiques et statiques par les formations réticulées mésencéphalique, pontique et bulbaire, chez le Chat. Exp. Brain Res. 9, 325–345 (1969b)
Vedel, J.P., Mouillac-Baudevin, J.: Contrôle pyramidal de l'activité des fibres fusimotrices dynamiques et statiques chez le Chat. Exp. Brain Res. 10, 39–63 (1970)
Wuerker, R.B., McPhedran, A.M., Henneman, E.: Properties of motor units in a heterogeneous pale muscle (M. Gastrocnemius) of the cat. J. Neurophysiol. 28, 85–99 (1965)
Yokota, T., Voorhoeve, P.E.: Pyramidal control of fusimotor neurons supplying extensor muscles in the Cat's forelimb. Exp. Brain Res. 9, 96–116 (1969)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vedel, J.P. Effets des stimulations du noyau caudé sur l'activité des terminaisons fusoriales primaires et secondaires du muscle soléaire. Exp Brain Res 22, 113–128 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237683
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237683