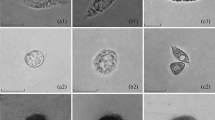
Summary
In the axial complex of Sphaerechinus granularis intense phagocytotic activity is encountered. The phagocytes ingest morula cells and other phagocytes; a lysosomal digestion of the phagocytosed cells is suggested. A subdivision into early and late phagocytes is made according to their granular content. Most of the phagocytes possess intranuclear crystalloids that exhibit a filamentous or particulate substructure. Late stages of phagocytes filled with residual bodies and crystalloids leave the axial complex via the lacunar system to be removed through the rectum. X-ray microanalysis reveals a constant presence of iron and sulphur in the crystalloids. The residual bodies contain iron, sulphur, calcium and zinc in varying amounts. This study confirms that one function of the axial complex is excretion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baccetti B, Rosati F (1968) The fine structure of the Polian vesicles of holothurians. Z Zellforsch 90:148–160
Bachmann S, Goldschmied A (1978a) Fine structure of the axial complex of Sphaerechinus granularis (Lam) (Echinodermata: Echinoidea). Cell Tissue Res 193:107–123
Bachmann S, Goldschmid A (1978b) Ultrastructural, fluorescence microscopic and microfluorimetric study of the innervation of the axial complex in the sea urchin, Sphaerechinus granularis (Lam). Cell Tissue Res 194:315–326
Bachmann S, Goldschmid A (1980) The echinoid axial complex and Tiedemann bodies. The different pathways and accumulation sites of coelomocytes with regard to waste disposal in the organism. In: Jangoux M (ed) Echinoderms: present and past. AA Balkema Rotterdam, pp 254–257
Binyon J (1972) Physiology of echinoderms. Pergamon Press Ltd, Oxford New York Toronto Sydney Braunschweig
Bucher O (1977) Cytologie, Histologie und mikroskopische Anatomie des Menschen. 9th ed. Huber, Bern, pp 100–139
Chandler JA (1976) A method for preparing absolute standards for quantitative calibration and measurement of section thickness with X-ray microanalysis of biological ultrathin specimens in EMMA. J Microsc 106:291–302
Chandler JA (1977) X-ray microanalysis in the electron microscope. Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press, Amsterdam
Chien PK, Johnson PT, Holland ND, Chapman FA (1970) The coelomic elements of sea urchins (Strongylocentrotus) IV. Ultrastructure of the coelomocytes. Protoplasma (Wien) 71:419–442
Cobb JLS, Sneddon E (1977) An ultrastructural study of the gills of Echinus esculentus. Cell Tissue Res 182:265–274
Dingle JT (1972) Lysosomes. North-Holland Publ Comp, Amsterdam London, pp 150–198
Endean R (1966) The coelomocytes and coelomic fluids. In: Boolootian RA (ed) Physiology of echinodermata. Intersci Publ, New York, pp 301–328
Fawcett DW (1973) Atlas zur Elektronenmikroskopie der Zelle. Urban & Schwarzenberg, München Berlin Wien, pp 189–212
Fechter H (1973) Die stickstoffhaltigen Stoffwechselendprodukte und ihre Exkretion bei Paracentrotus lividus. Mar Biol 19:285–289
Fujimoto H, Watanabe H (1976) The characterization of granular amoebocytes and their possible roles in the asexual reproduction of the polystyelid ascidian, Polyzoa vesiculiphora. J Morphol 150:623–638
George SG, Pirie BJS, Cheyne AR, Coombs TL, Grant PT (1978) Detoxication of metals by marine bivalves: an ultrastructural study of the compartmentation of copper and zinc in the oyster, Ostrea edulis. Mar Biol 45:147–156
George SG, Pirie BJS, Coombs TL (1980) Isolation and elemental analysis of metal-rich granules from the kidney of the scallop, Pecten maximus (L). J Exp Mar Biol Ecol 42:143–156
Ghadially FN (1979) Invited review. The technique and scope of electron-probe X-ray analysis in pathology. Pathology 11:95–110
Hall TA (1979) Biological X-ray microanalysis. J Microsc 117:145–163
Höbaus E (1978) Studies on phagocytes of regular sea urchins (Echinoidea, Echinodermata) I. The occurrence of iron containing bodies within the nuclei of phagocytes. Zool Anz Jena 200:31–40
Hruban Z, Rechcigl M (1969) Microbodies and related particles. Morphology, biochemistry and physiology, Int Rev Cytol Suppl 1. Academic Press, New York London
Hübner G (1968) Die pathischen Reaktionen des Lebergewebes. In: Veröffentlichungen aus der morphologischen Pathologie Heft 78. G Fischer, Stuttgart, pp 2–31
Jangoux M, Schaltin P (1977) Le complexe axial de Psammechinus miliaris (Gmelin) (Echinodermata, Echinoidea). Arch Zool Exp Gén 118:285–303
Johnson PT (1969) The coelomic elements of the sea urchins (Strongylocentrotus). II. Cytochemistry of the coelomocytes. Histochemie 17:213–231
Karasaki S (1965) Intranuclear crystals within the phagocytes of the ovary of Arbacia punctulata. J Cell Biol 25:654–660
Lecal J (1971) A propos des “centres organisateurs” nucléaires des coelomocytes d'Echinides. Bull Soc Hist Nat Toulouse 107:7–17
Leclerc M (1974) L'organe axial et ses relations avec la sexualité et l'immunité chez les asterides. Ann Sci Nat Zool 12. sér 16:285–359
Lehninger AL (1975) Biochemistry. 2nd ed. Worth Publ, New York, p 567
Müller HA, Ramin DV (1963) Morphologie und Morphogenese der durch Schwermetalle (Pb, Bi) hervorgerufenen Kerneinschlüsse in den Hauptstückepithelien der Rattenniere. Beitr Pathol Anat 128:445–467
Pirie BJS, George SG (1979) Ultrastructure of the heart and excretory system of Mytilus edulis (L). J Mar Biol Ass U K 59:819–829
Pohla H (1980) Die energie-dispersive Röntgen-Mikroanalyse als Methode zur Lokalisation von Schwermetallen in Haut und Kiemen von Regenbogenforellen (Salmo gairdneri, Rich). Naturwiss Diss Univ Salzburg (in preparation)
Richter GW (1961) Intranuclear aggregates of ferritin in liver cells of mice treated with saccharated iron oxide. Their possible relation to nuclear protein synthesis. J Biophys Biochem Cytol 9:263–270
Simonsberger P, Slattenscheck W, Adam H (1977) Eine digital gesteuerte Stickstoff-Spar-Schaltung für Gefriertrocknungsanlagen. Mikroskopie 33:203–208
Smith AC (1977) A proposed phylogenetic relationship between sea cucumber Polian vesicles and the vertebrate lymphoreticular system. J Invertebrate Pathol 31:353–357
Spurr AR (1969) A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res 26:31–43
Stevenson RA, Ufret SL (1966) Iron, manganese and nickel in skeletons and food of the sea urchins Tripneustes esculentus and Echinometra lucunter. Limnol Oceanogr 11:11–17
Vevers HG (1967) The histochemistry of the echinoid axial organ. Symp Zool Soc London 20:65–74
Vethamany VG, Fung M (1971) The fine structure of coelomocytes of the sea urchin, Strongylocentrotus dröbachiensis (Müller OF). Can J Zool 50:77–81
Vernon-Roberts B (1972) The macrophage. In: Harrison RJ, McNunn RMH (eds) Biological structure and function. University Press, Cambridge
Weinstock A, Albright JT (1967) The fine structure of mast cells in normal human gingiva. J Ultrastruct Res 17:245–256
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bachmann, S., Pohla, H. & Goldschmid, A. Phagocytes in the axial complex of the sea urchin, Sphaerechinus granularis (Lam.). Cell Tissue Res. 213, 109–120 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00236924
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00236924